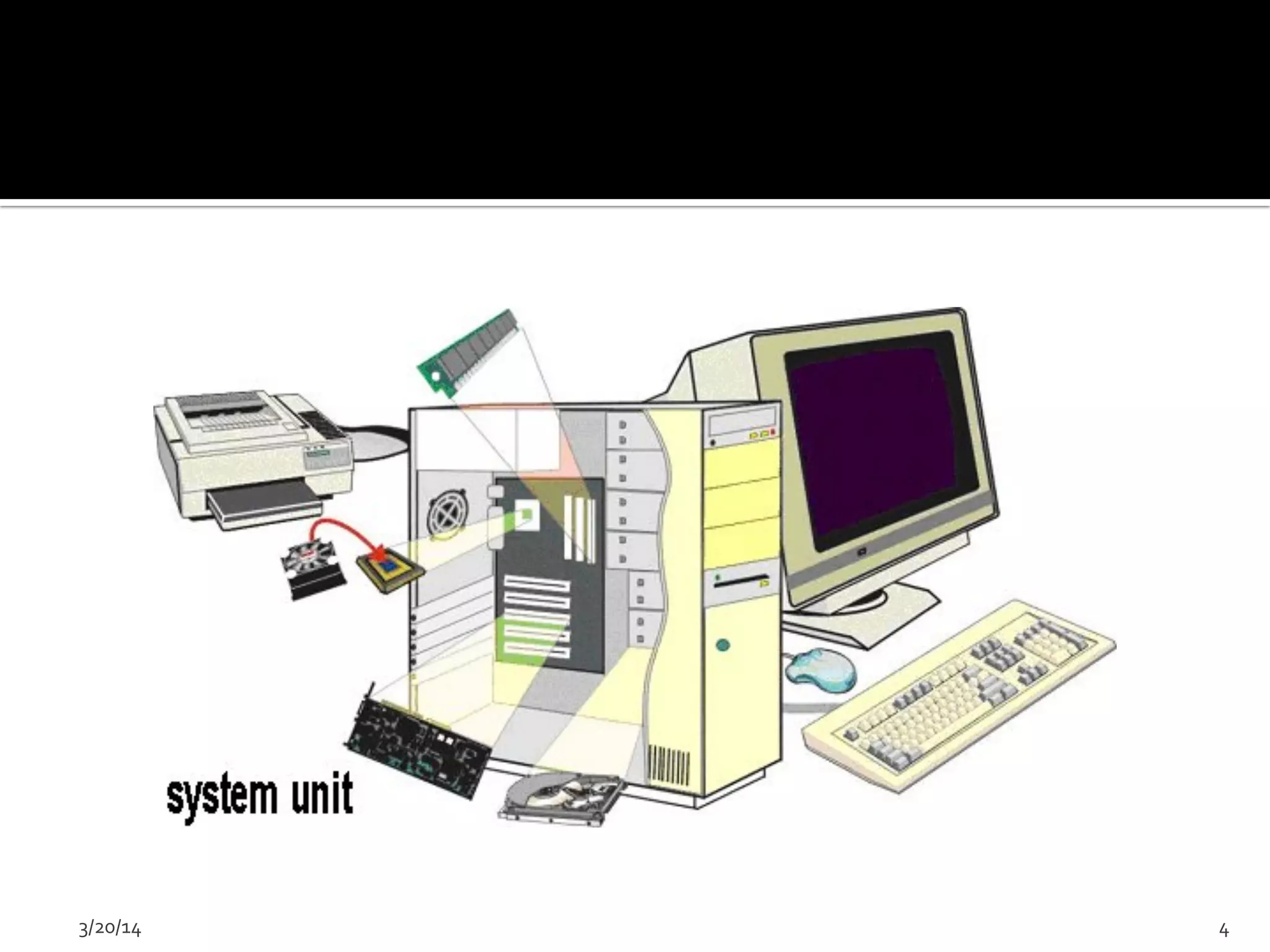
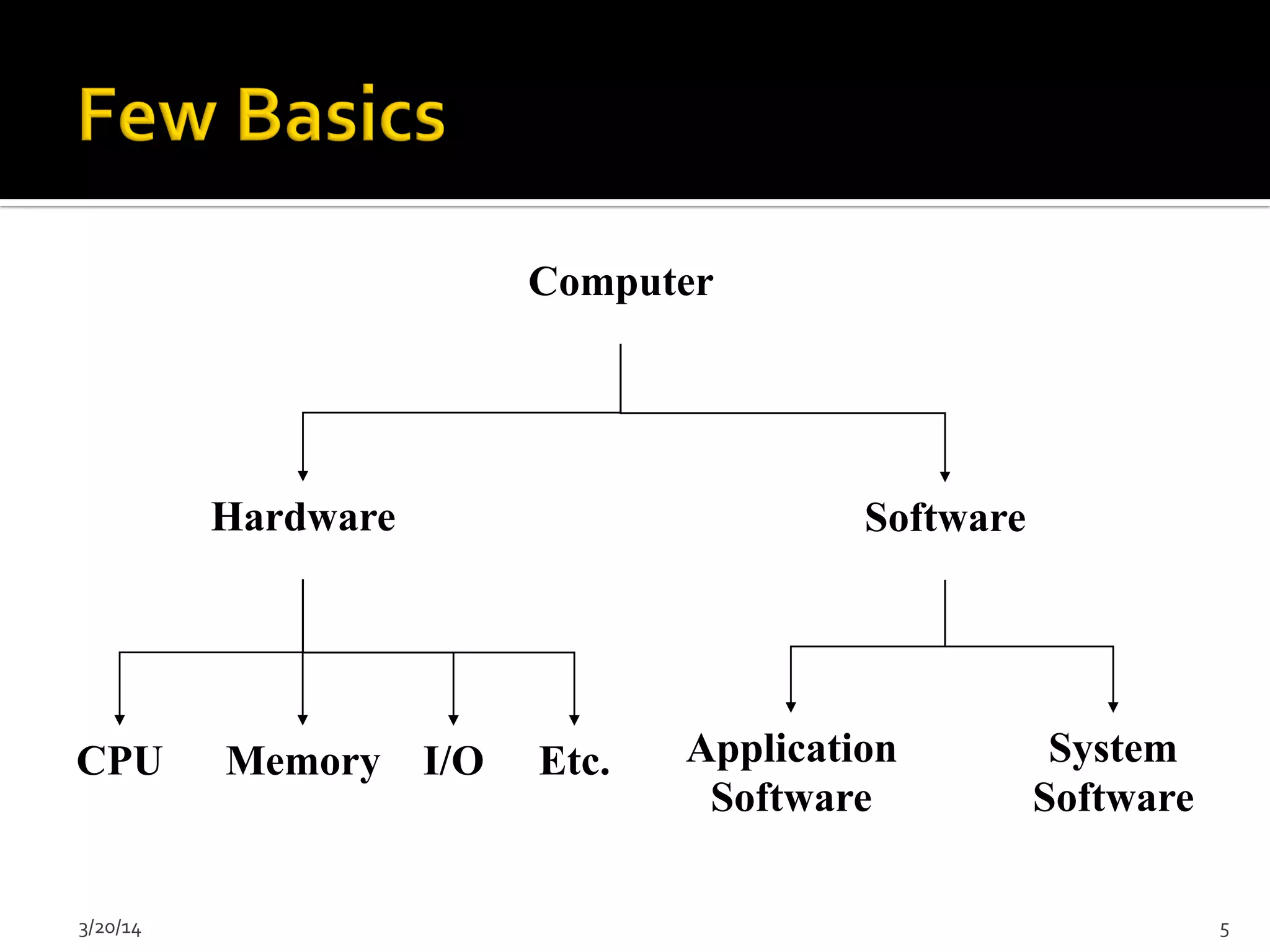
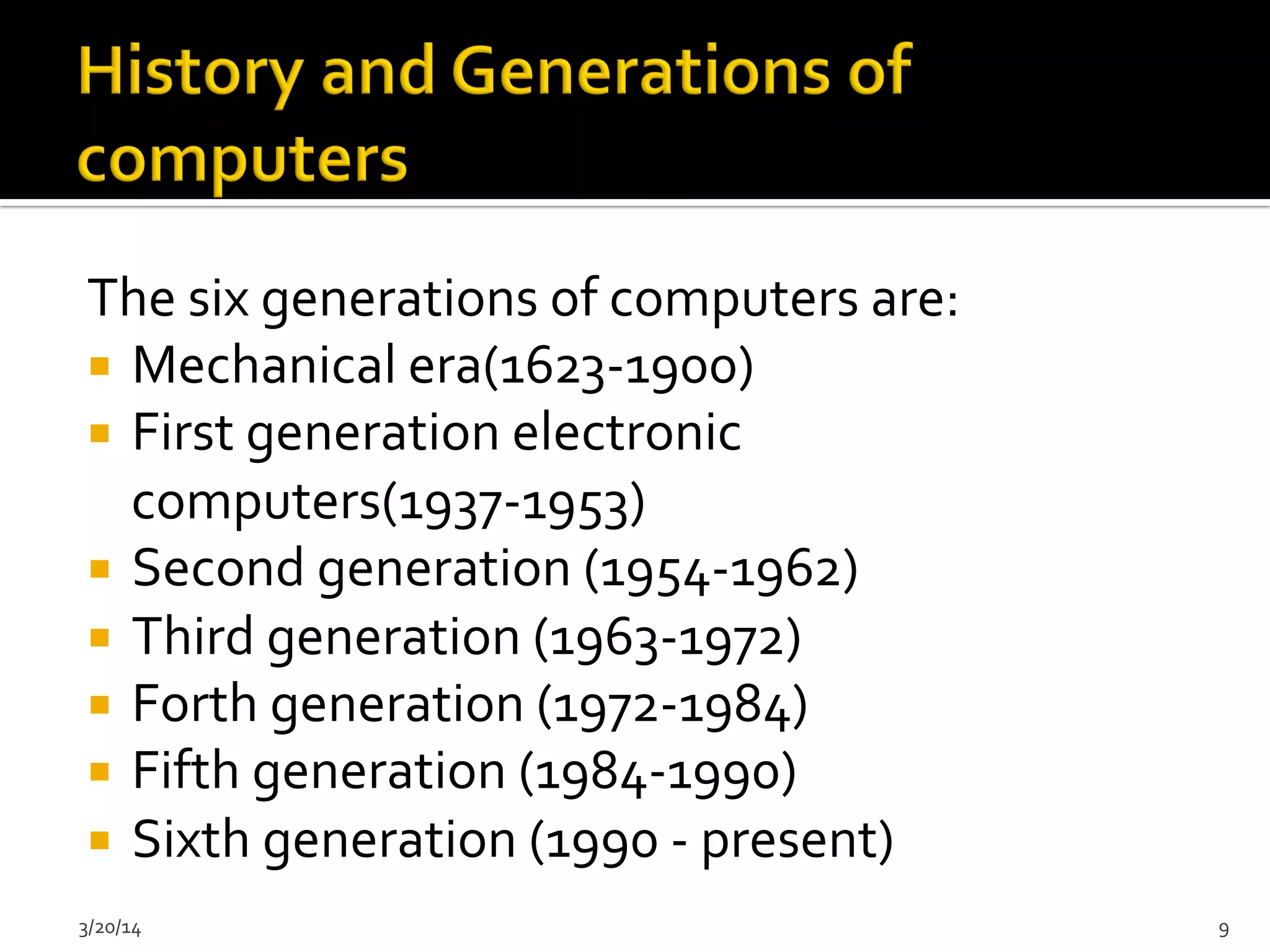
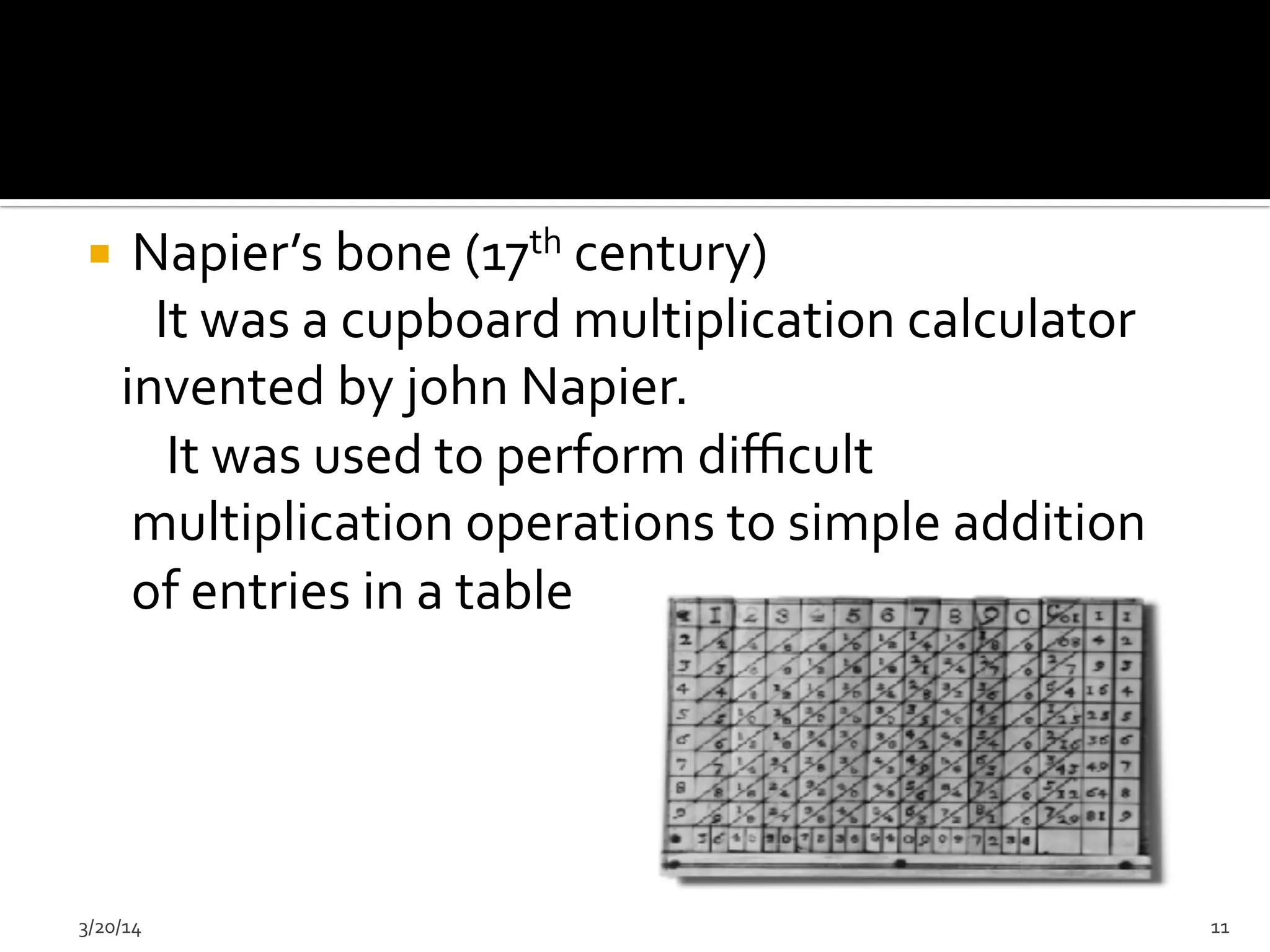
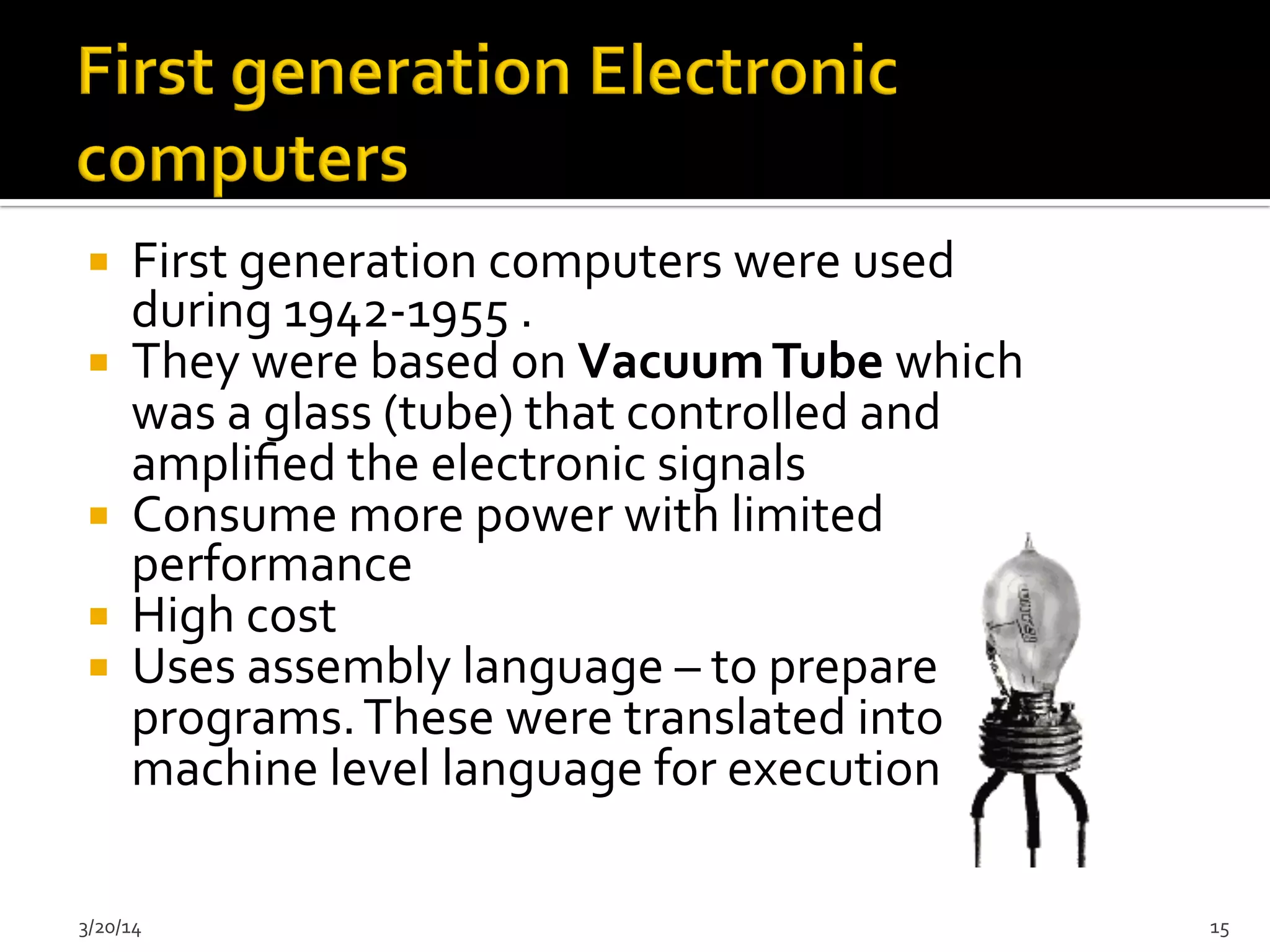
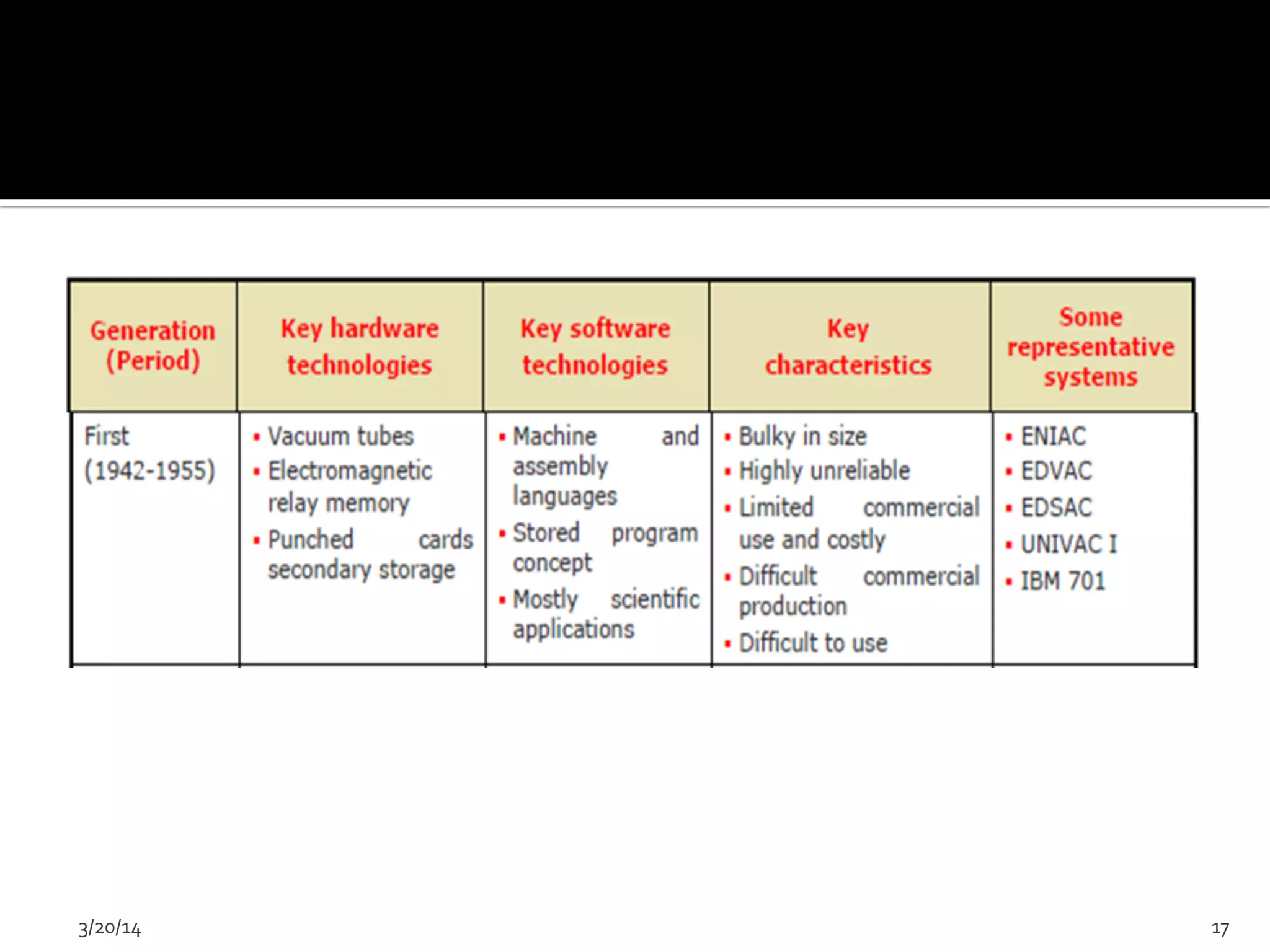
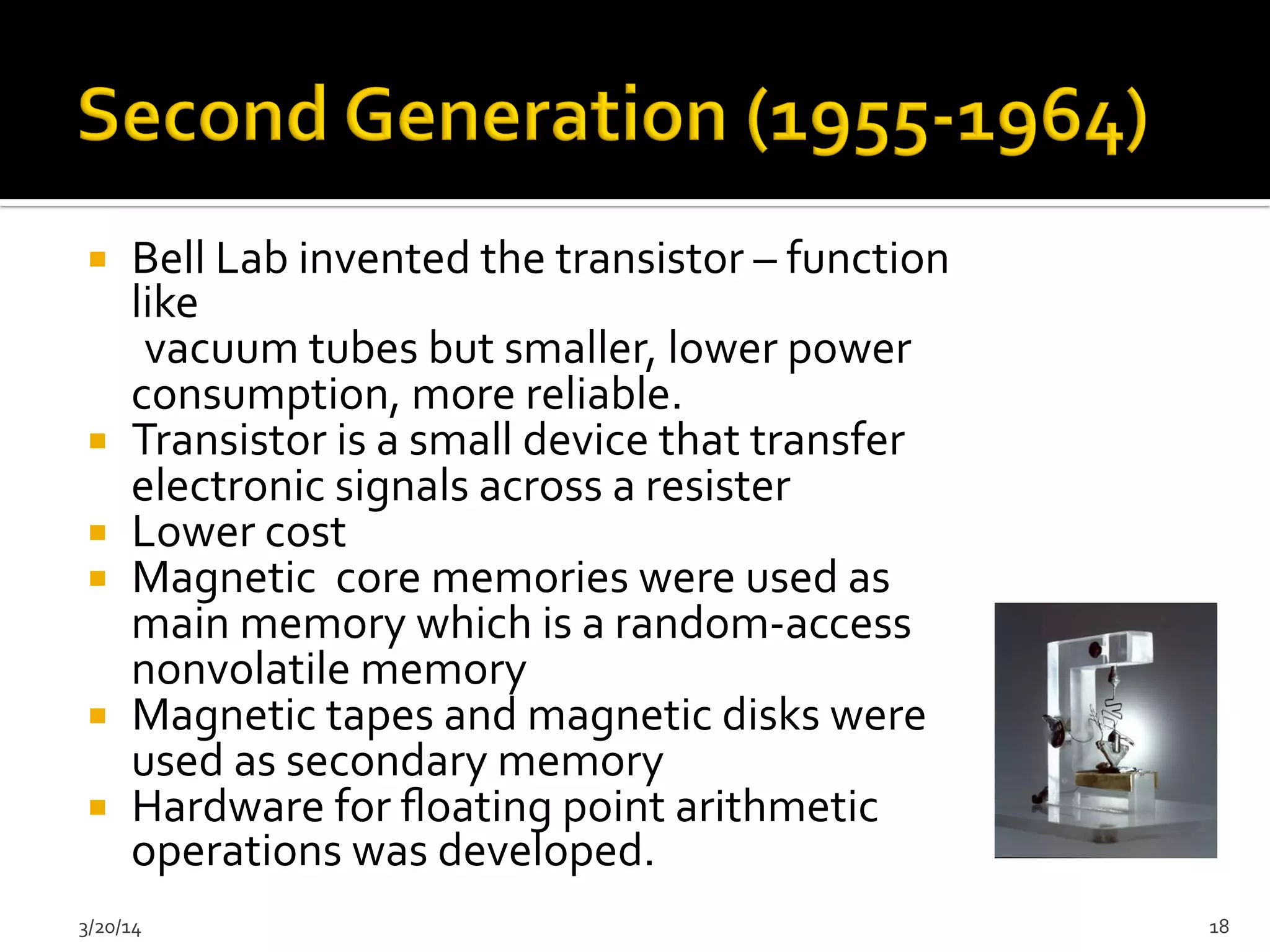
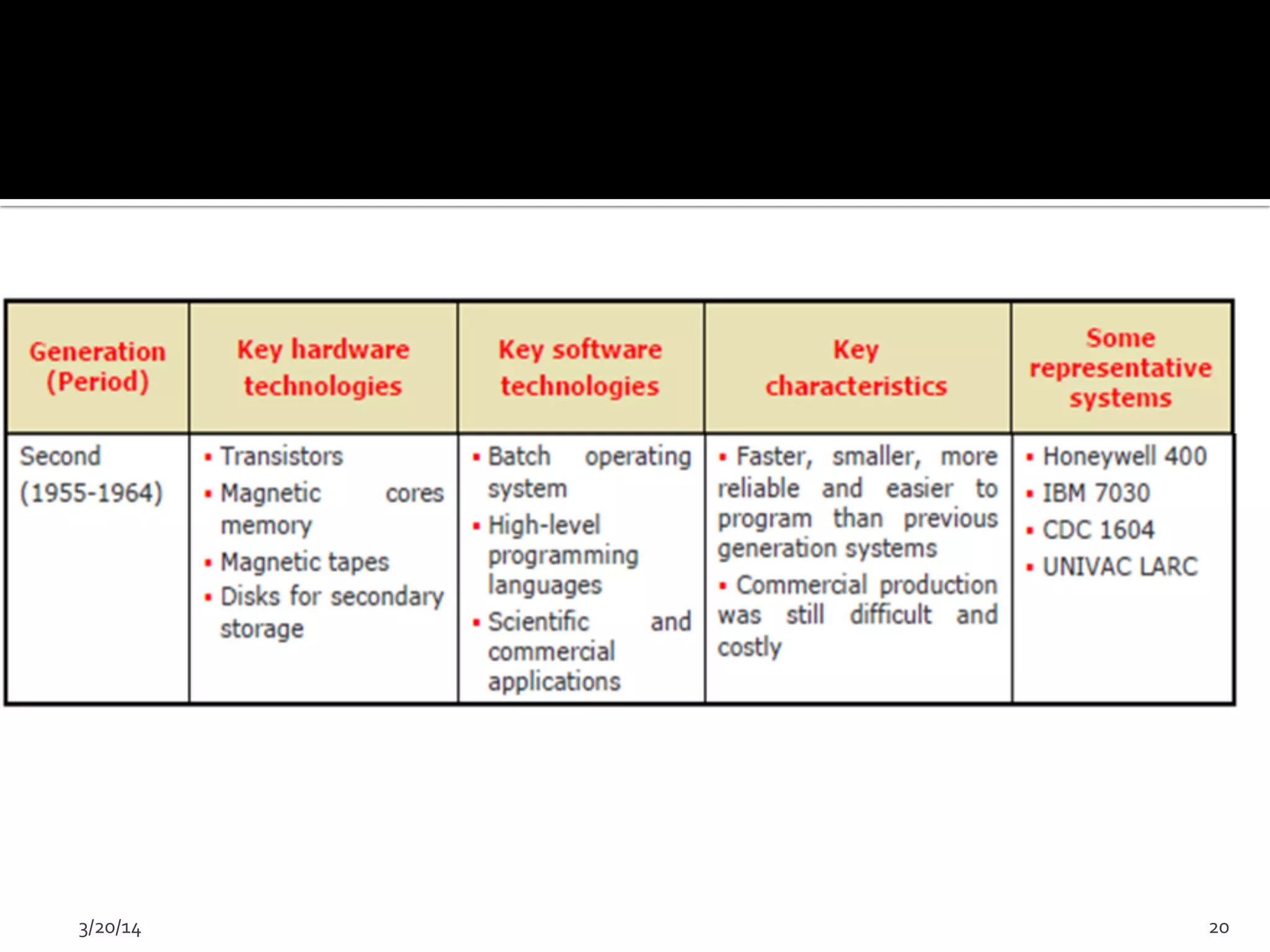
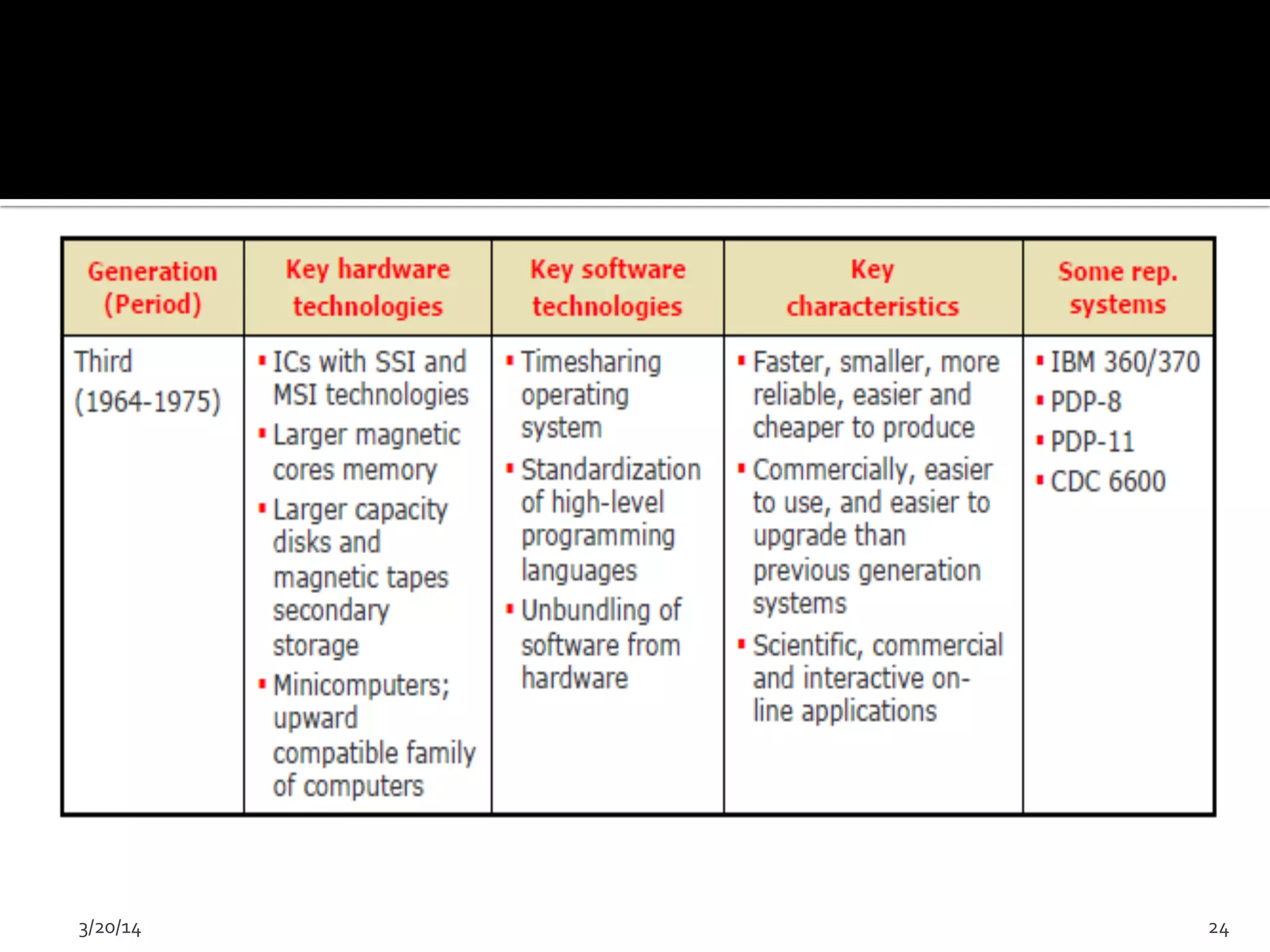
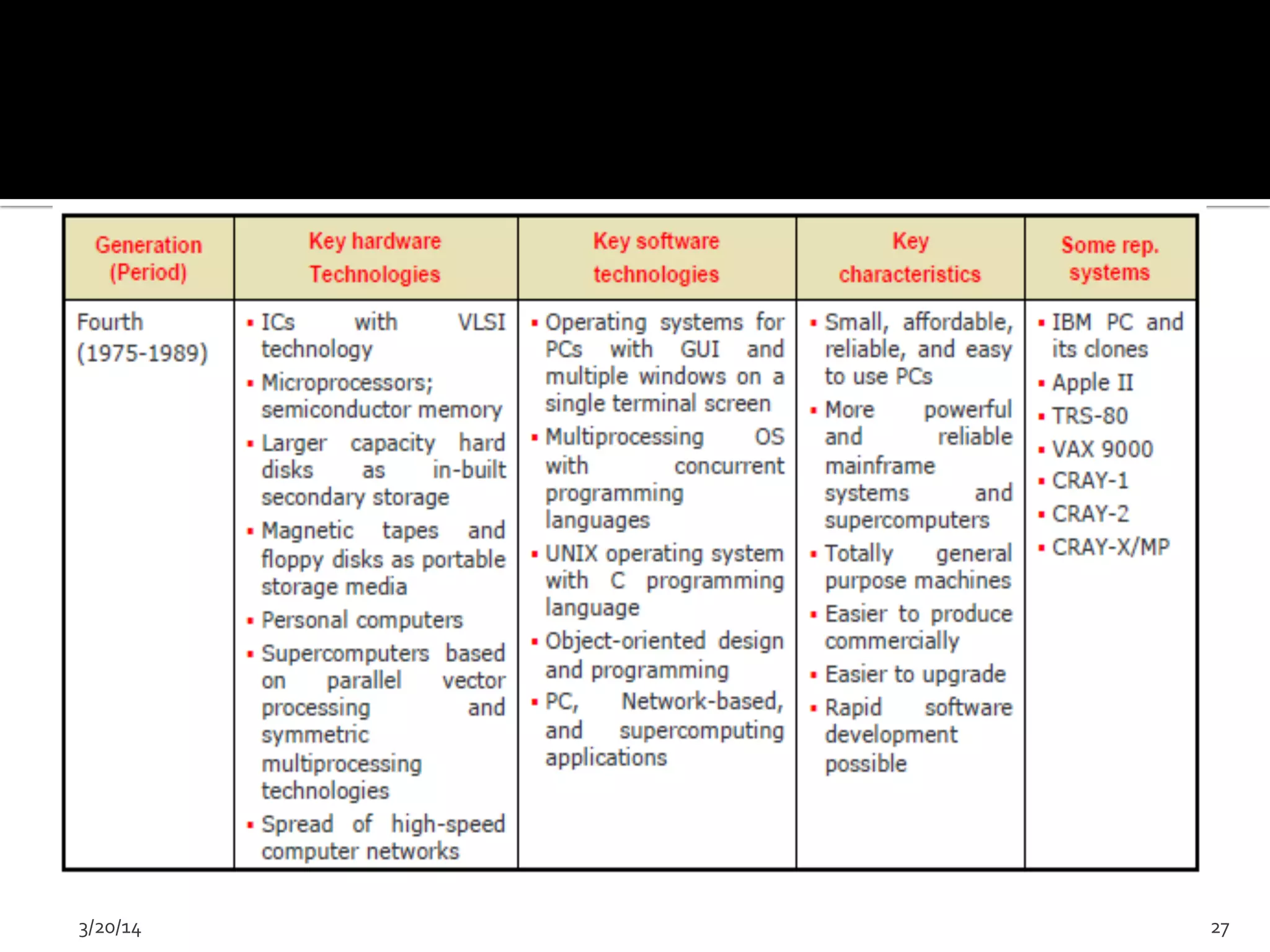
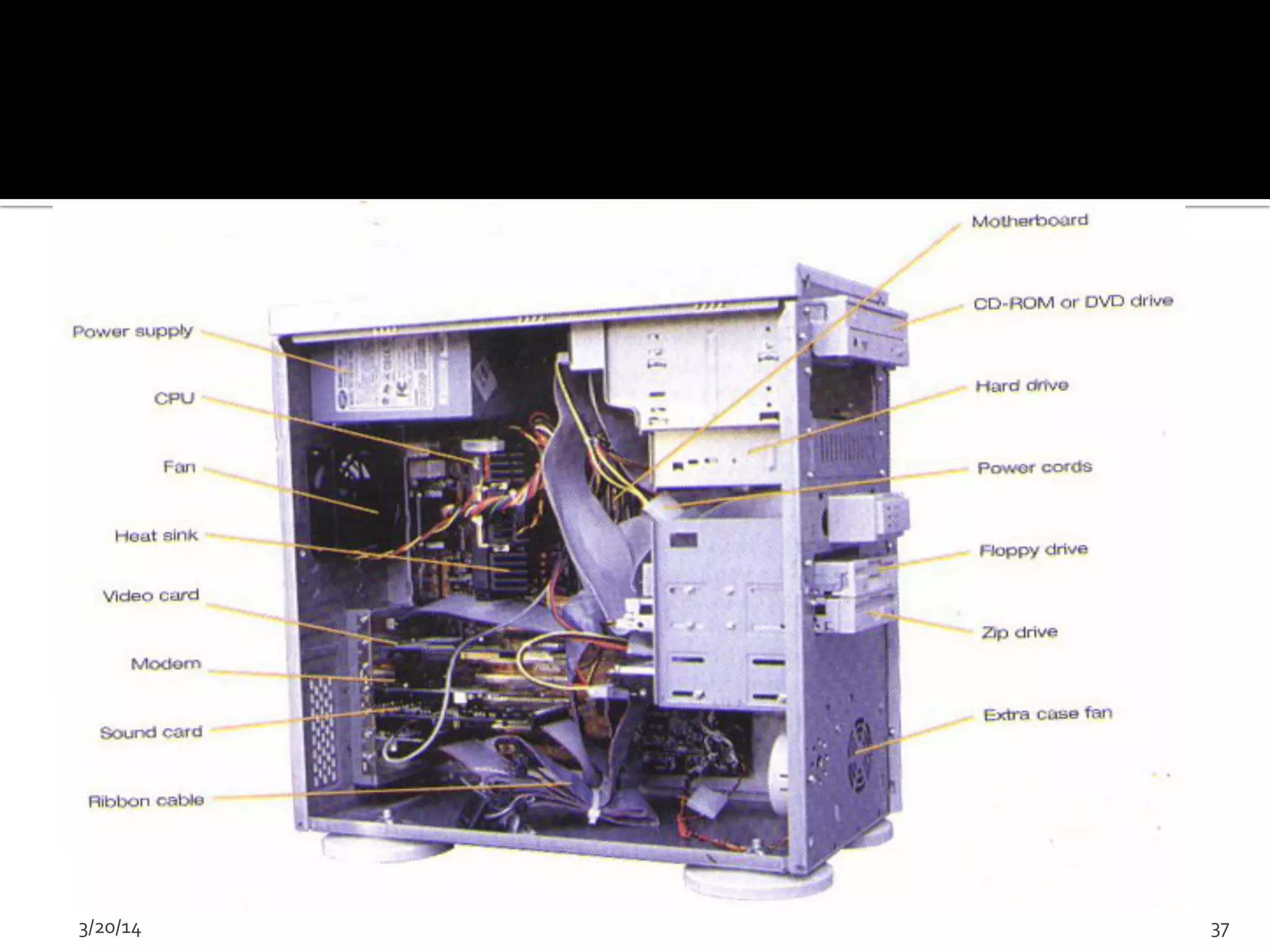
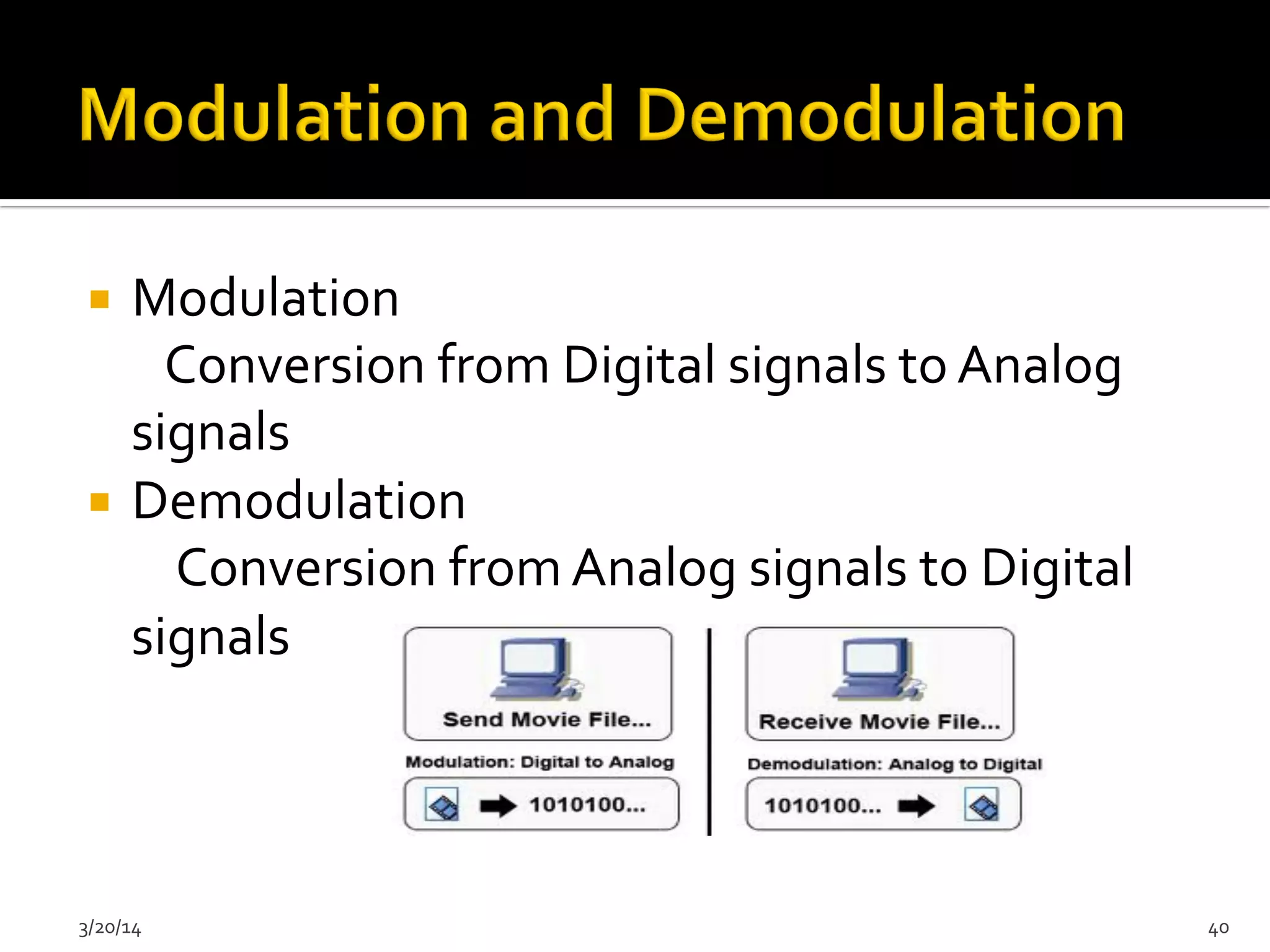
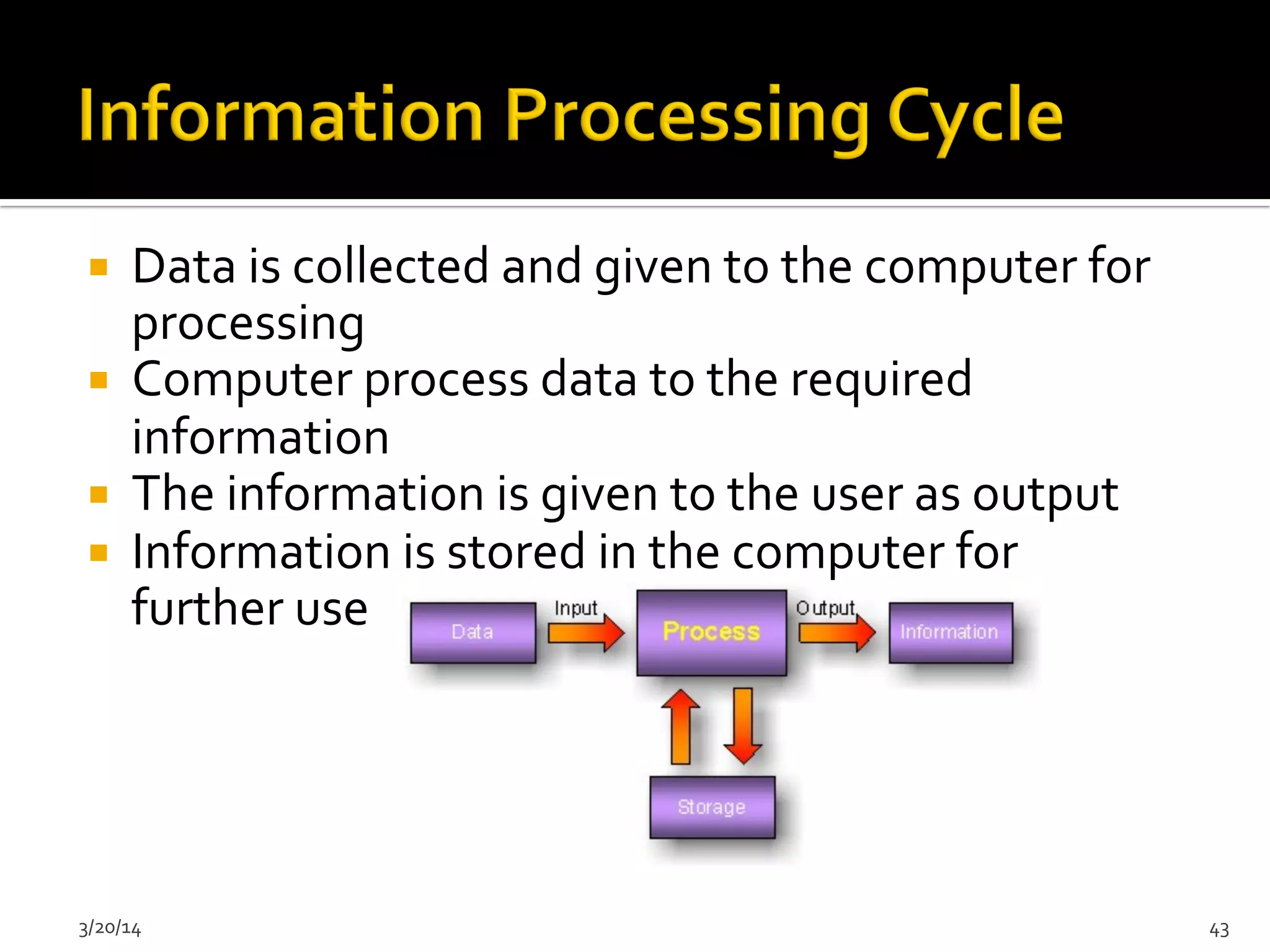
The document discusses the history and evolution of computers from ancient times to modern digital computers. It begins with early mechanical calculating devices like the abacus and Napier's bones. Important early electronic computers that used vacuum tubes are discussed from the first generation in the 1940s-1950s like ENIAC. The development of the transistor is described as key to the second generation of computers in the 1950s-1960s, replacing vacuum tubes and enabling smaller, cheaper computers. The text provides a technical overview of the components, workings and applications of early computer generations.