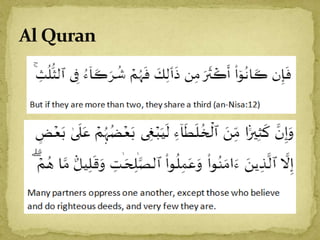
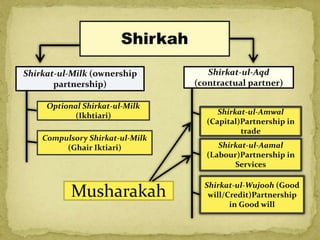
The document discusses Musharakah, which is an Islamic financing structure based on profit-and-loss sharing partnership. It defines Musharakah and various types of Shirkah (partnership). It also describes how Musharakah works as a financing model, including diminishing Musharakah. The key differences between interest-based financing and Musharakah are that Musharakah shares profits and losses between partners according to contribution ratios, while interest guarantees a fixed return. The document proposes using market prices and rental data rather than interest rates to determine profit rates for Musharakah financing.