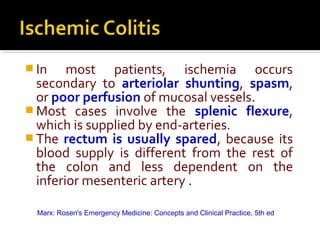
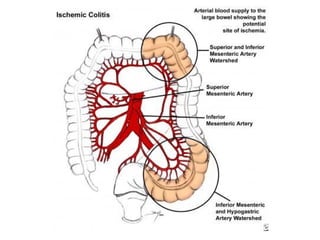
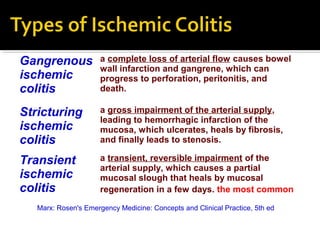
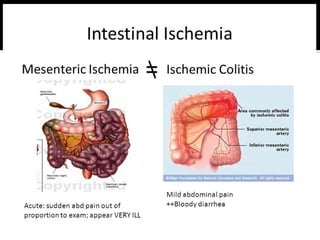
1. Ischemic colitis most often affects the elderly and is usually nonocclusive, with the most common cause being emboli cutting off blood flow.
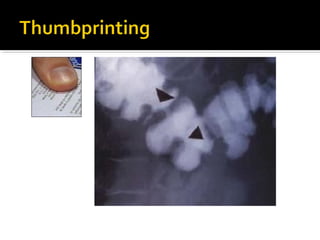
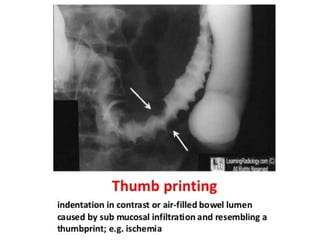
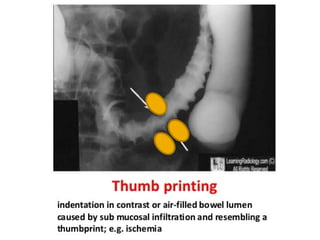
2. Symptoms include sudden onset of abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea, with physical exam possibly showing signs of peritonitis in severe cases. Plain abdominal films may show thumbprinting from hemorrhage.
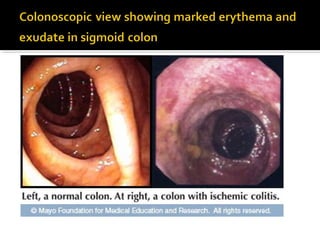
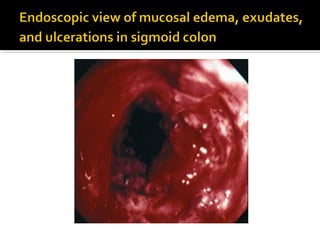
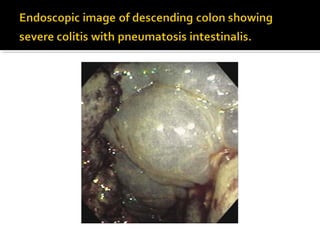
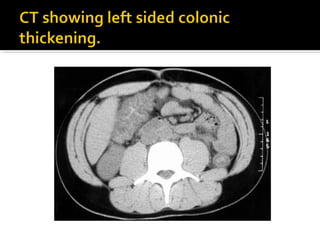
3. Colonoscopy can detect ulcerations and bulging folds but is not diagnostic; surgery is warranted for gangrenous ischemic colitis or perforation. The diagnosis of ischemic colitis should always be considered in elderly patients with suspected inflammatory bowel disease.