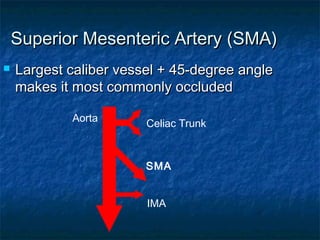
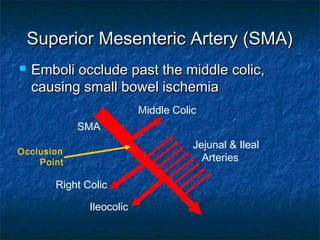
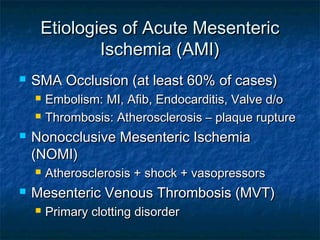
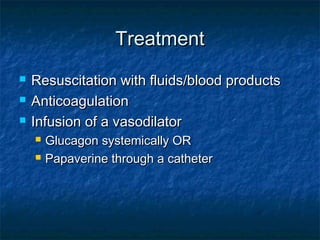
Acute mesenteric ischemia and infarction can result from ischemia or reduced blood flow to the small bowel or colon. The most common cause is occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery, often due to embolism from heart conditions. Clinical presentation involves severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis relies on blood tests, imaging like CT scan, and mesenteric angiography. Treatment requires resuscitation followed by efforts to restore blood flow surgically or with medications, and resection of any infarcted tissue.