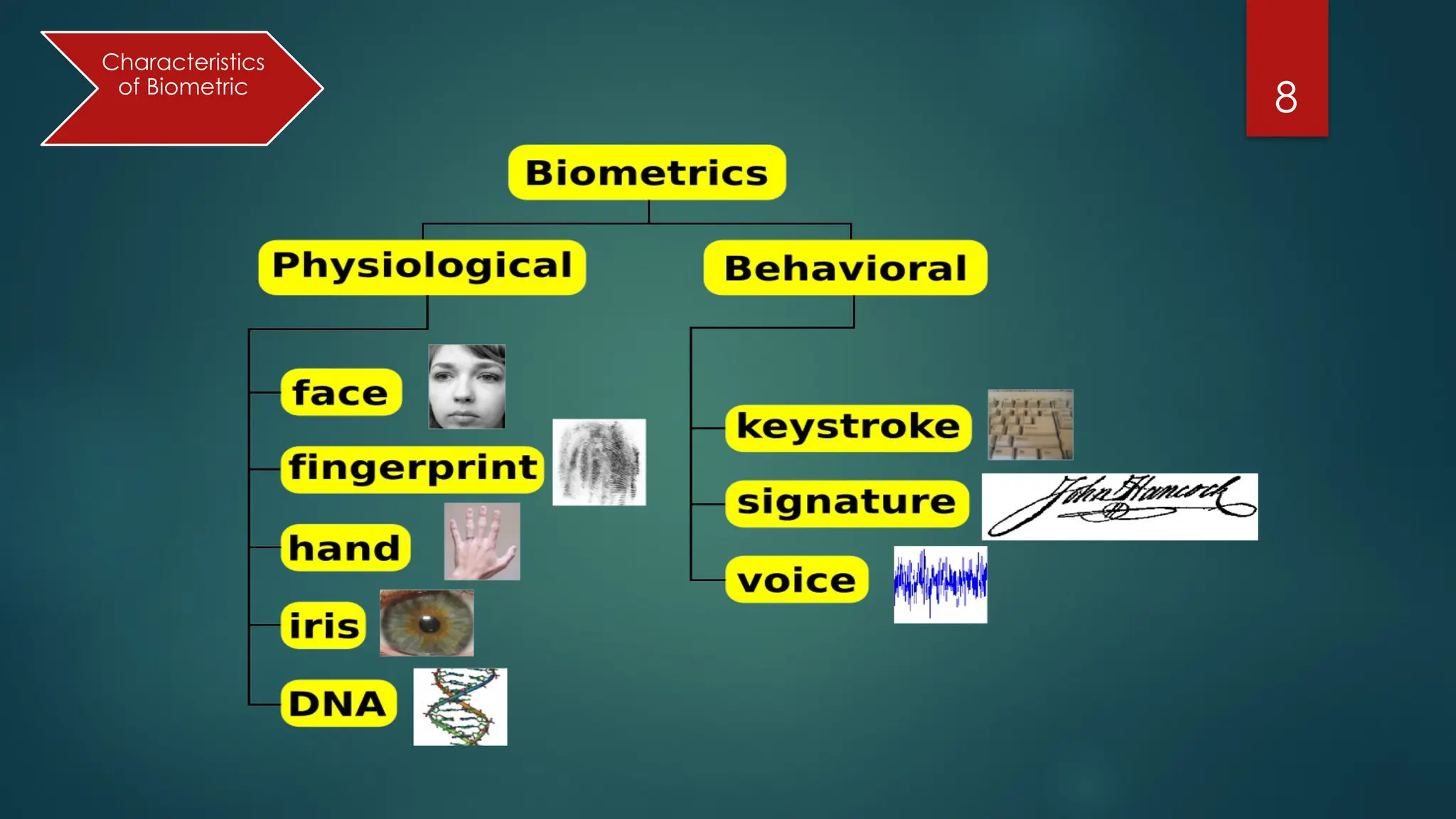
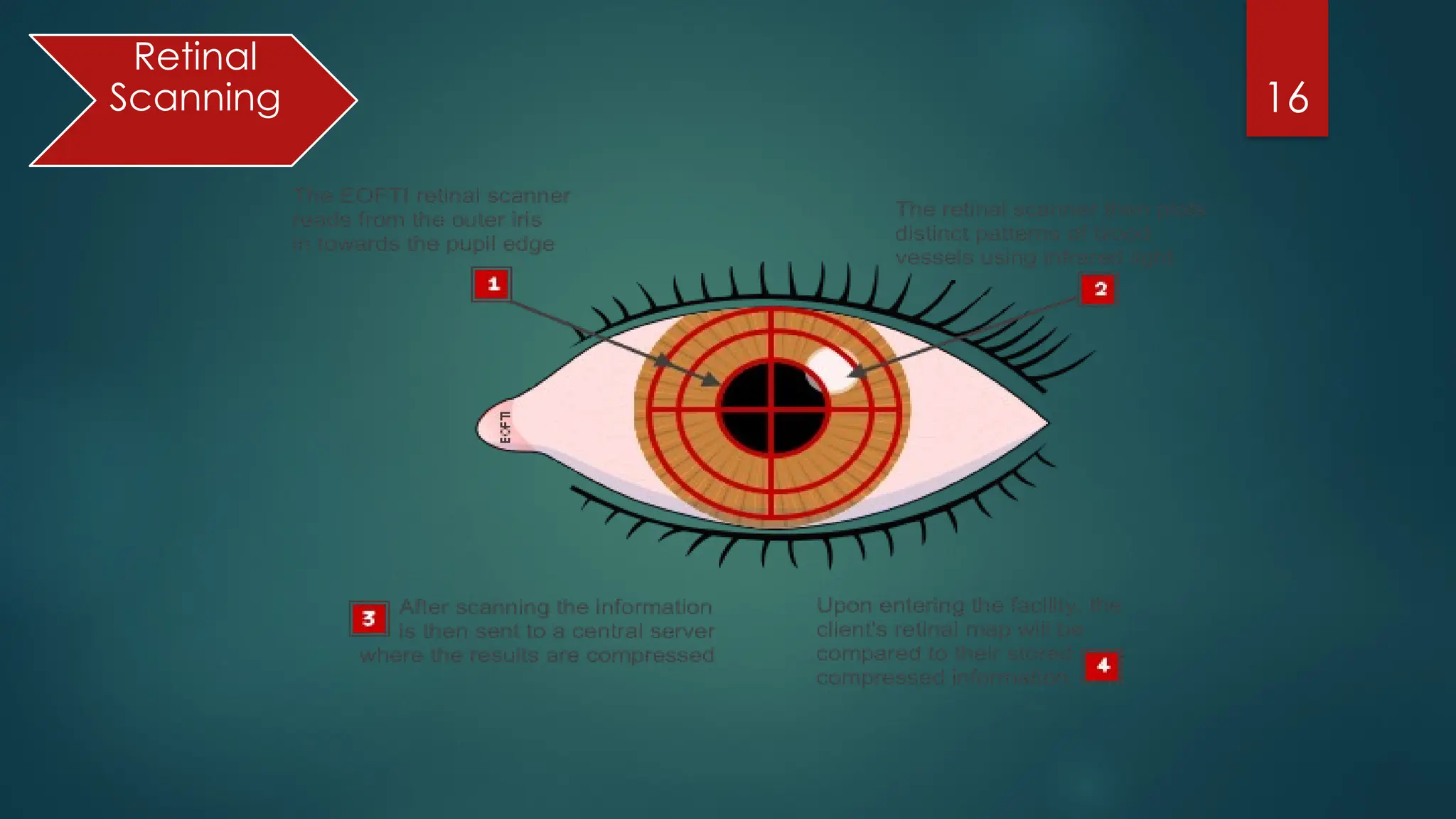
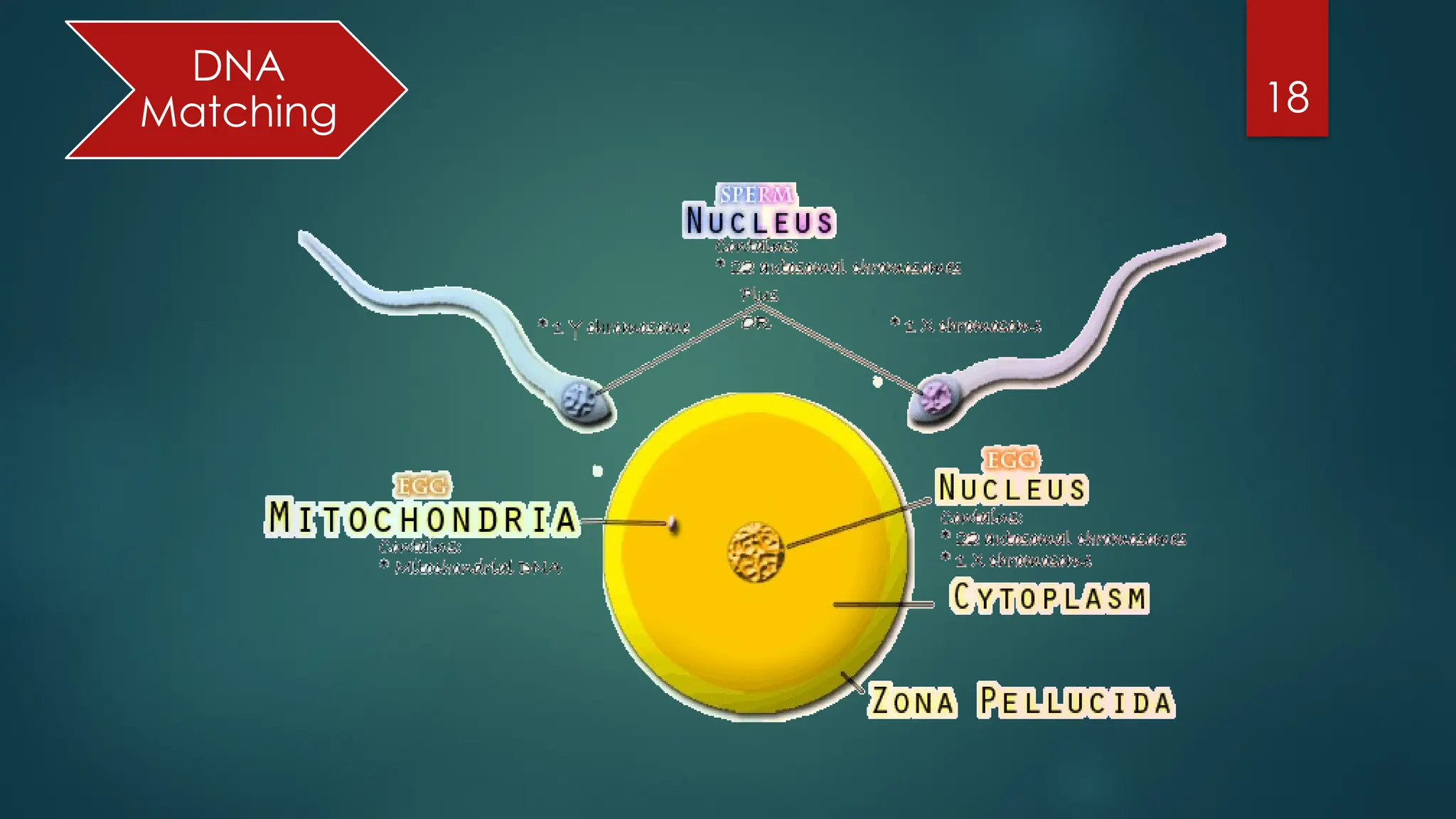
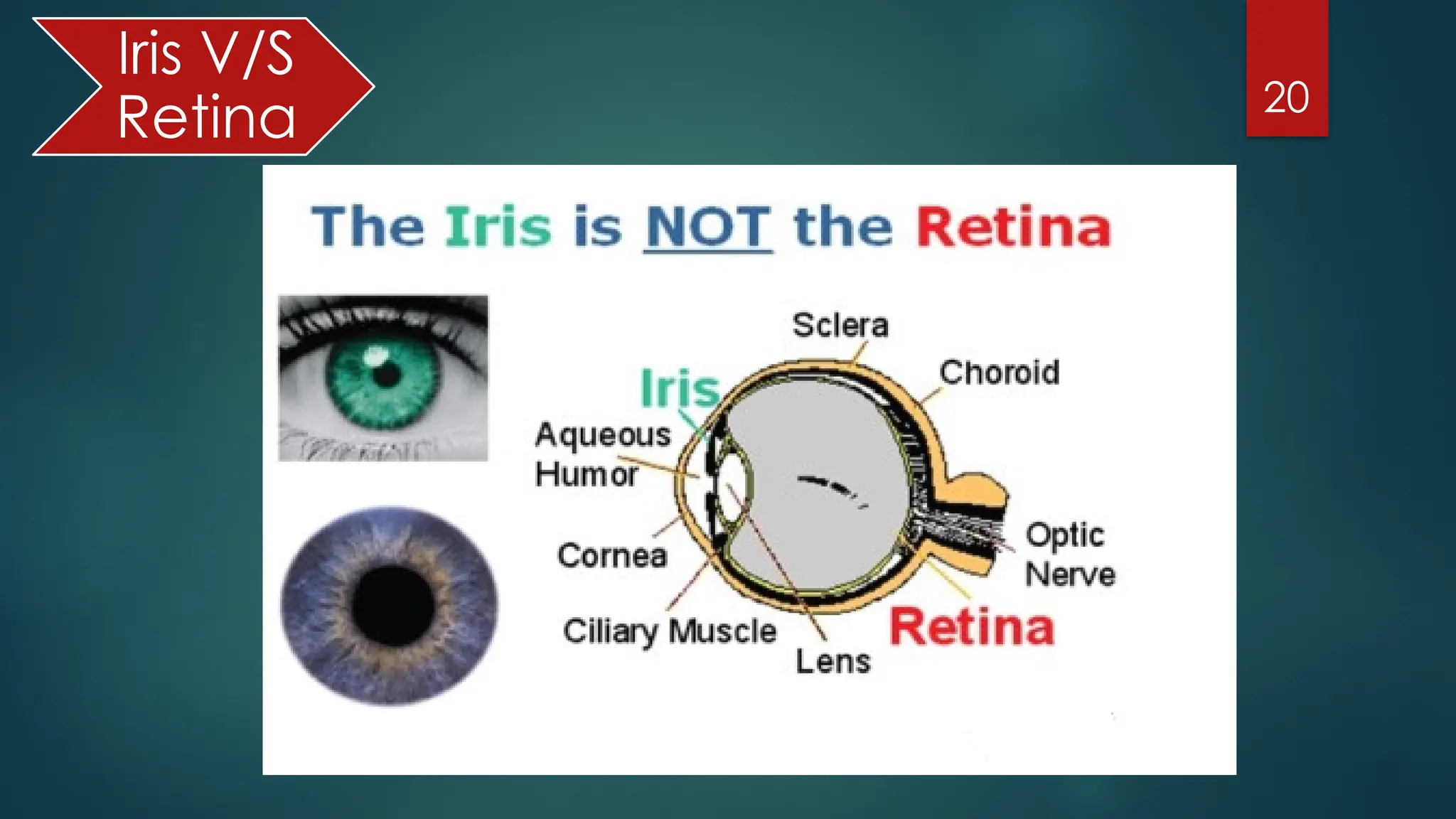
The document presents an overview of biometric authentication, including its history, types, characteristics, and applications. Biometric technologies recognize individuals based on unique physiological or behavioral traits, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans. The advantages of biometric systems include enhanced security, convenience, and reduction of password-related issues.