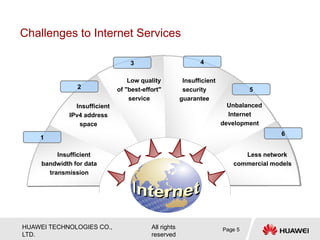
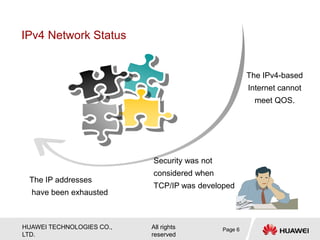
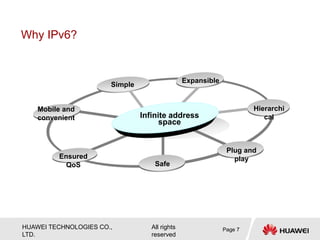
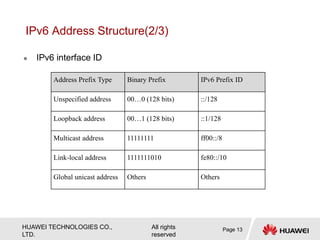
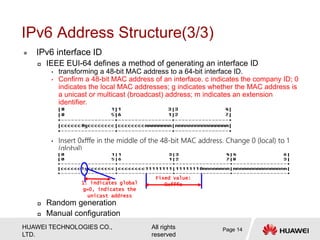
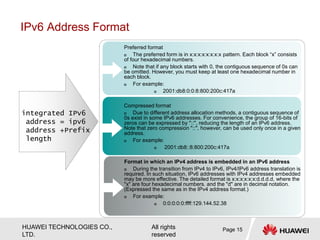
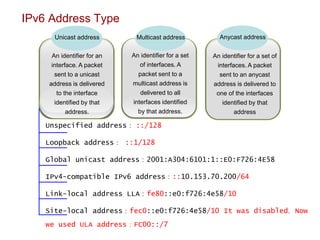
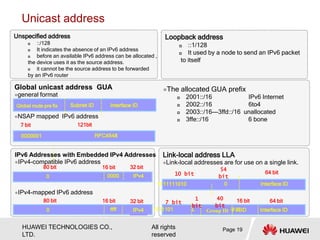
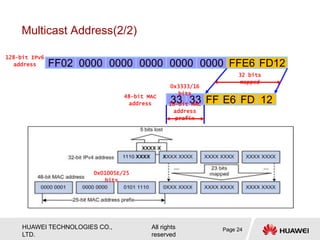
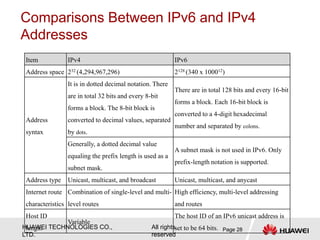
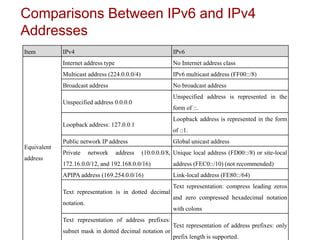
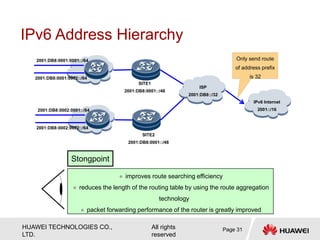
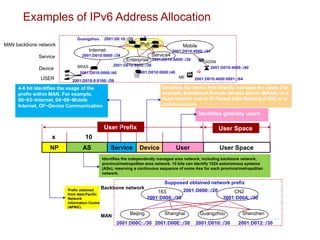
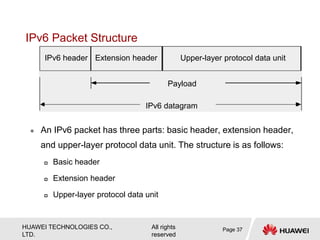
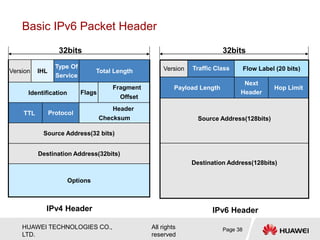
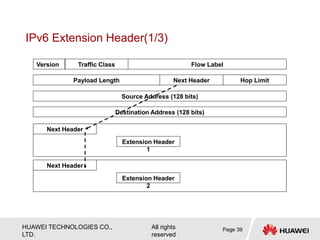
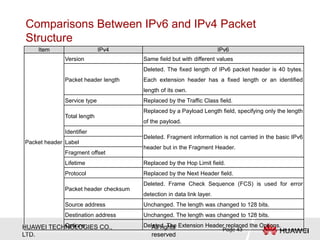
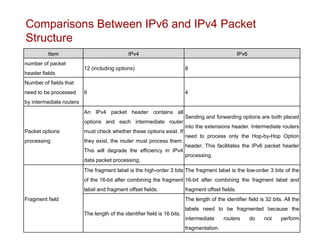
The document provides an overview of Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6), discussing its importance, structure, and comparison to IPv4. Key topics include IPv6 address characteristics, address types (unicast, multicast, anycast), and packet structure, emphasizing the benefits of IPv6 such as infinite address space and improved quality of service. It also outlines the differences between IPv4 and IPv6, including address allocation and the absence of a need for subnet masks in IPv6.