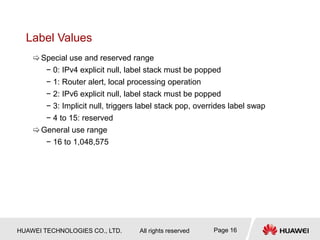
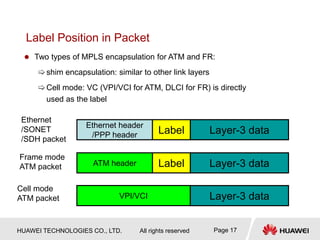
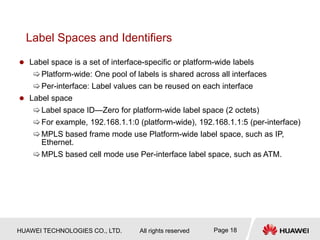
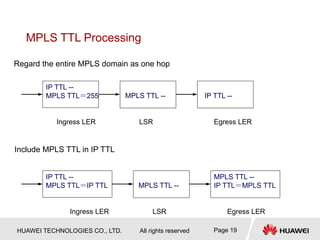
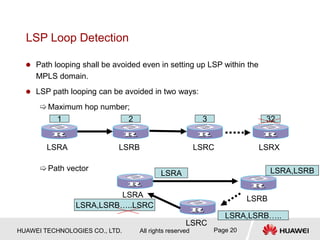
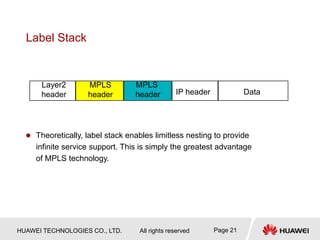
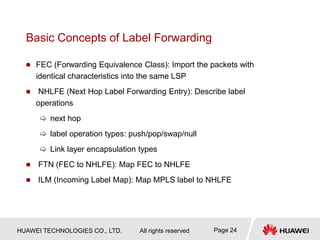
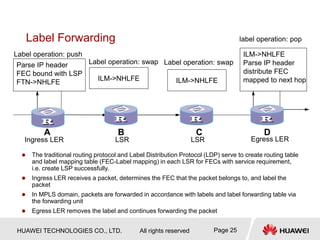
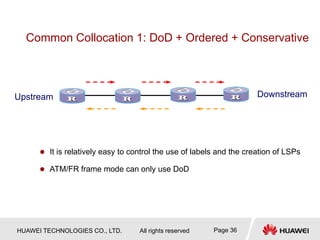
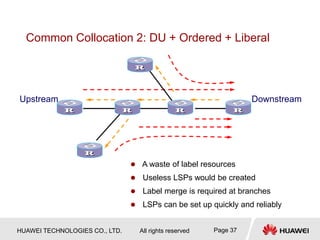
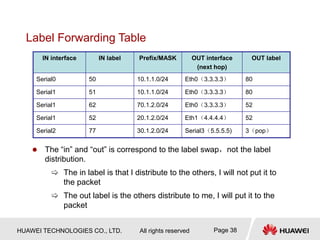
This document provides an overview of MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) concepts including label switching, label allocation, and label forwarding. It discusses MPLS label structure, label encapsulation, label spaces, label forwarding entries, and label distribution protocols. The key topics covered are:
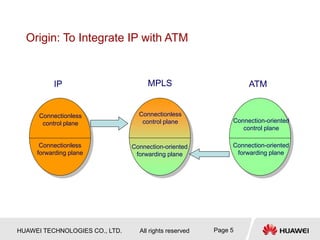
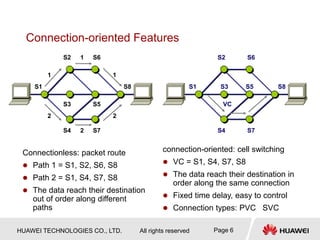
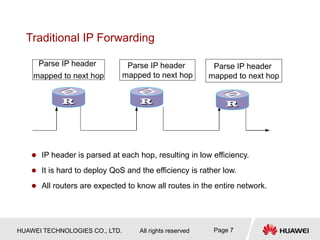
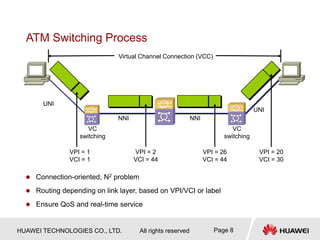
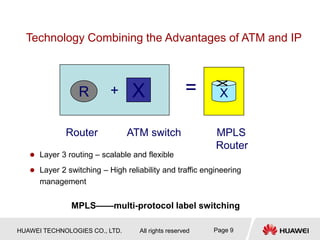
1) MPLS was developed to integrate connectionless IP networks with connection-oriented ATM networks for traffic engineering and QoS purposes. It works by encapsulating packets with labels and performing label switching instead of IP forwarding.
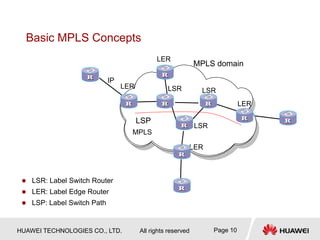
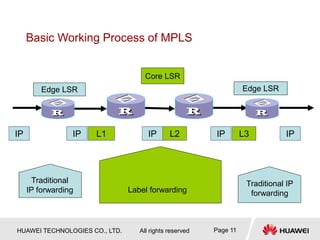
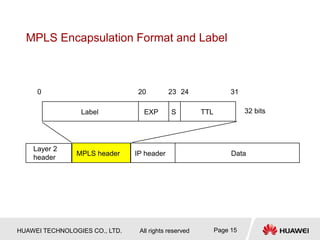
2) MPLS uses labels added to packet headers to forward packets. Label allocation can be downstream-on-demand or unsolicited. Label distribution protocols like LDP are used to establish label