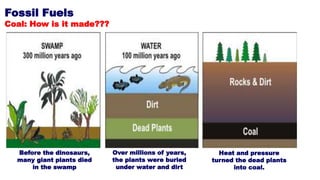
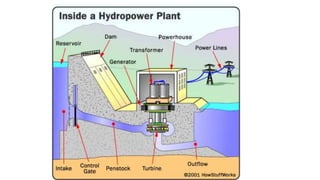
This document discusses various sources of energy. It describes conventional/non-renewable sources such as fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas which are formed over millions of years from remains of plants and animals. Nuclear energy from uranium fission or fusion is also considered non-renewable. Non-conventional/renewable sources mentioned include solar, wind, hydroelectric, tidal and geothermal energies which are naturally replenished. The document provides details on formation of fossil fuels and how different renewable sources like solar, wind and tidal are harnessed to generate energy.