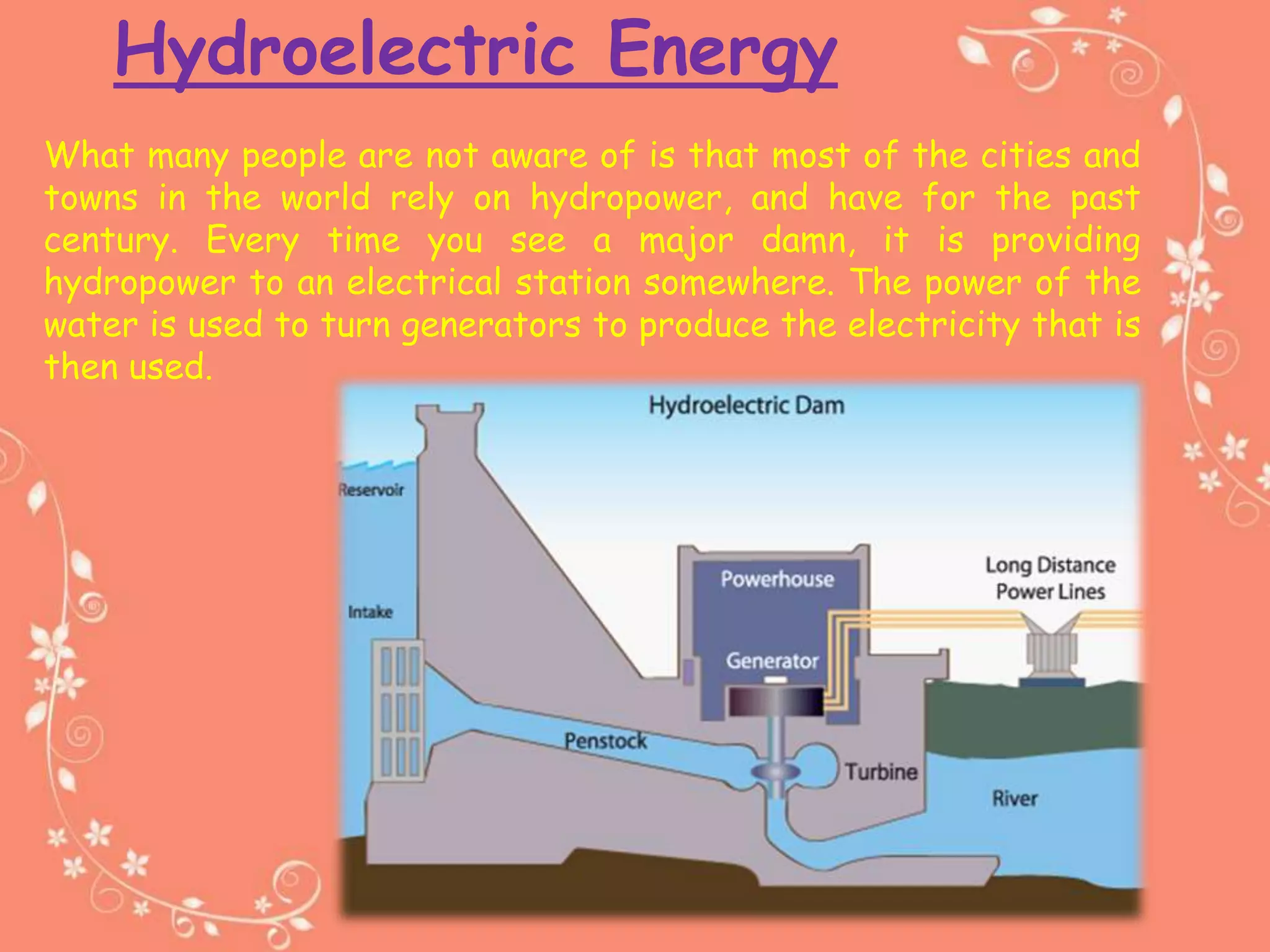
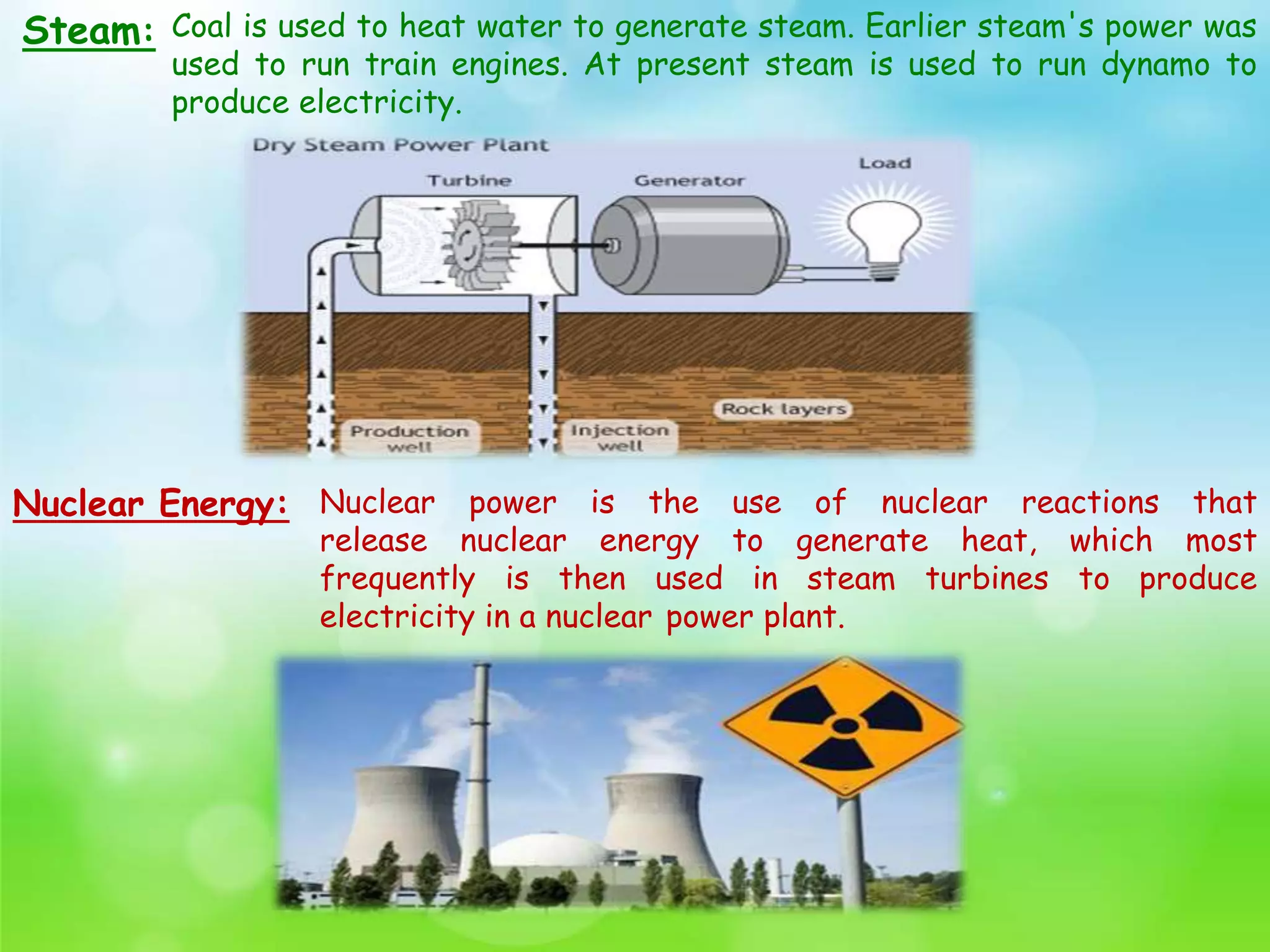
The document discusses various sources of energy, including solar, wind, geothermal, tidal, wave, hydroelectric, biomass, nuclear power, and fossil fuels. It outlines the characteristics of a good energy source as well as the risks and ecological problems associated with conventional energy sources. Finally, it emphasizes the role of technology in improving the efficiency of conventional energy sources.