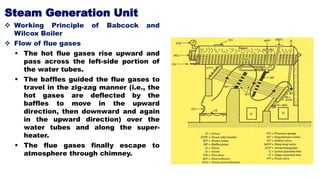
The document discusses steam generation units and their components. It describes how a boiler works to generate steam through the combustion of fuel and transfer of heat to water. Two common types of boilers are described in detail - the fire tube Cochran boiler and the water tube Babcock and Wilcox boiler. Their key components and working principles are explained. The document also covers boiler mountings such as safety valves, pressure gauges and blow-off cocks that are used to safely operate the boiler, as well as accessories like economizers and air preheaters that can improve boiler efficiency.