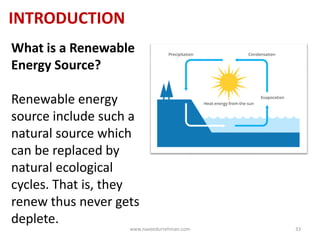
The document serves as an introduction to a detailed presentation on renewable energy systems covering various sources like solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, geothermal, and tidal energy. It highlights the historical significance of these energy forms, the challenges posed by fossil fuels, and the importance of sustainable and renewable energy sources. The document also provides links to additional resources and references related to renewable energy.