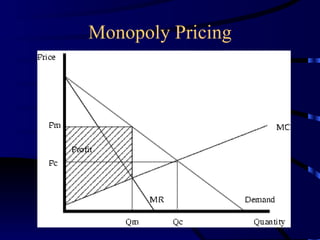
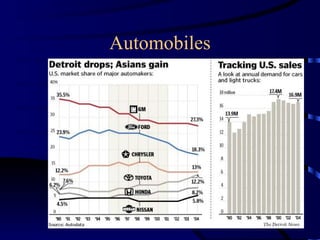
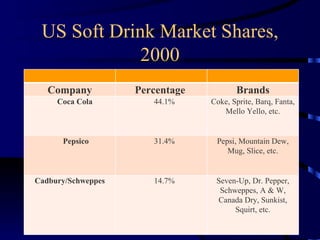
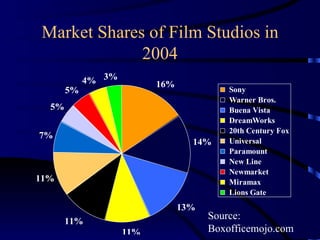
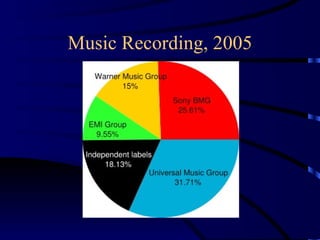
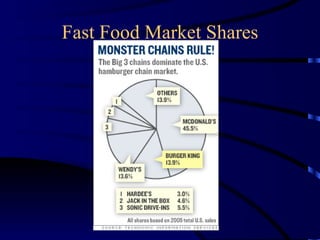
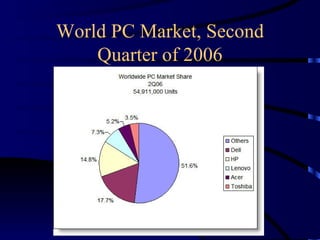
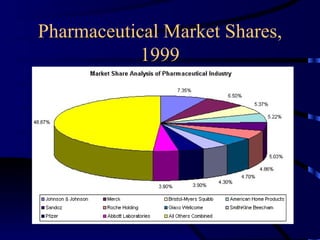
Multinational corporations (MNCs) can provide benefits to host countries such as capital, technology, marketing and management expertise, and increasing domestic competition. However, they are also criticized for engaging in anticompetitive behaviors, displacing domestic investment, undermining local cultures, and exploiting local workers. Industries dominated by a small number of large companies, called oligopolies, exist in sectors like automobiles, soft drinks, movies, music, pharmaceuticals, fast food, and personal computers. Public policies aimed at reducing the ill effects of monopolies and oligopolies include antitrust laws, fair trade laws, deregulation, and encouraging new competition through technologies.