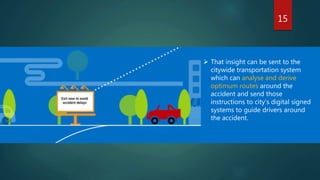
This document is a report on the Internet of Things (IoT) written by Rohit Mahali for his mentor Mr. Biswanath Sethi. The report defines IoT as connected devices that can collect and exchange data without human intervention. It discusses why IoT is useful for automation and remote control. Examples are given of applications in various industries. Challenges of IoT include connectivity, security, and managing large amounts of collected data in the cloud. The conclusion is that while complex, IoT has potential to transform many businesses and lives.