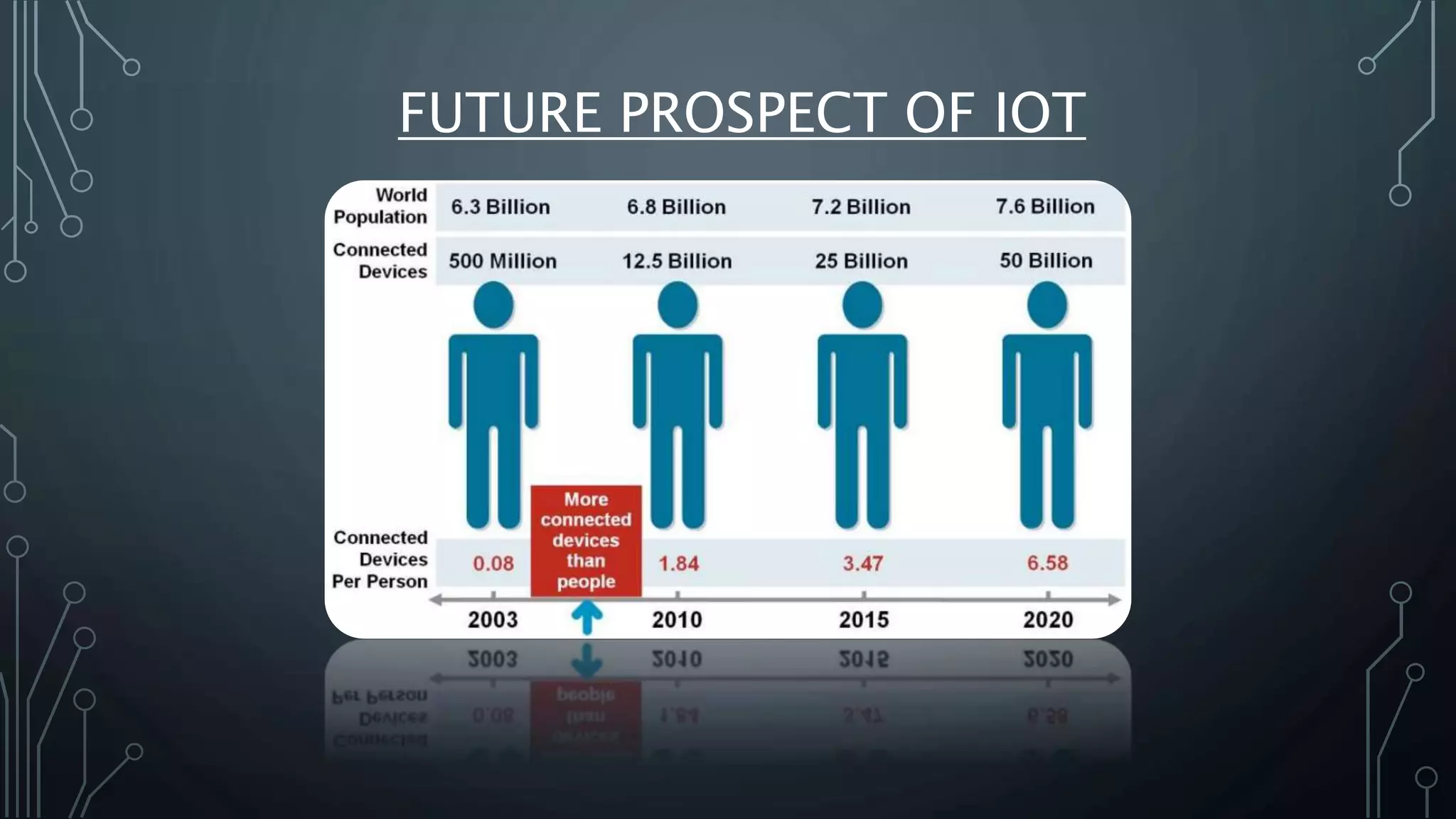
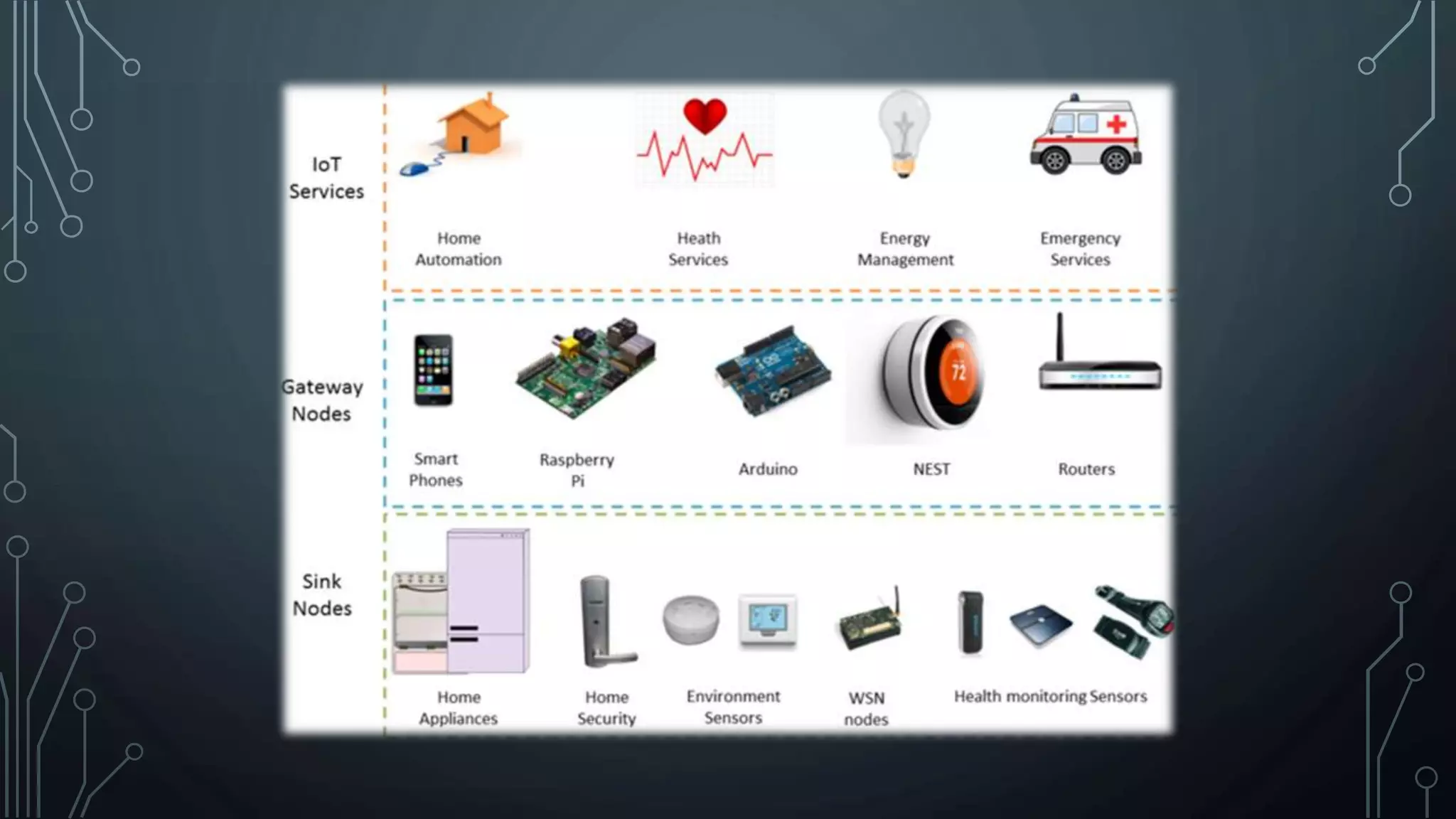
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects embedded with electronics, software, and sensors that allows them to connect, collect, and exchange data. IoT enables objects to be sensed and controlled remotely across existing network infrastructure, improving efficiency and economic benefit. Examples of connected devices include heart monitors, farm animal trackers, smart cars, and environmental sensors. These devices collect and share data using technologies like RFID, sensors, and networking. Major challenges to IoT adoption include issues with scalability, security, standardization, and software complexity, but solutions are being developed to address these challenges. Projections suggest IoT will have a $11 trillion economic impact by 2025 with 100 billion connected devices.