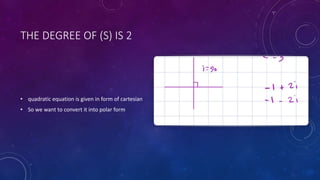
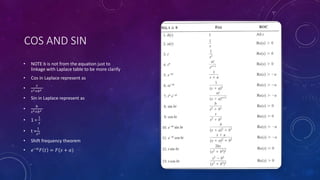
The document discusses the inverse Laplace transform focusing on converting functions from the s-domain to the time domain, particularly using complex roots and transformation rules. It elaborates on the simplification of quadratic equations from Cartesian to polar form and how coefficients affect the representation of sine and cosine in the Laplace transform. The process involves manipulating the equations through various operations to derive the inverse Laplace results related to specific terms like e^(-t) and integration techniques.