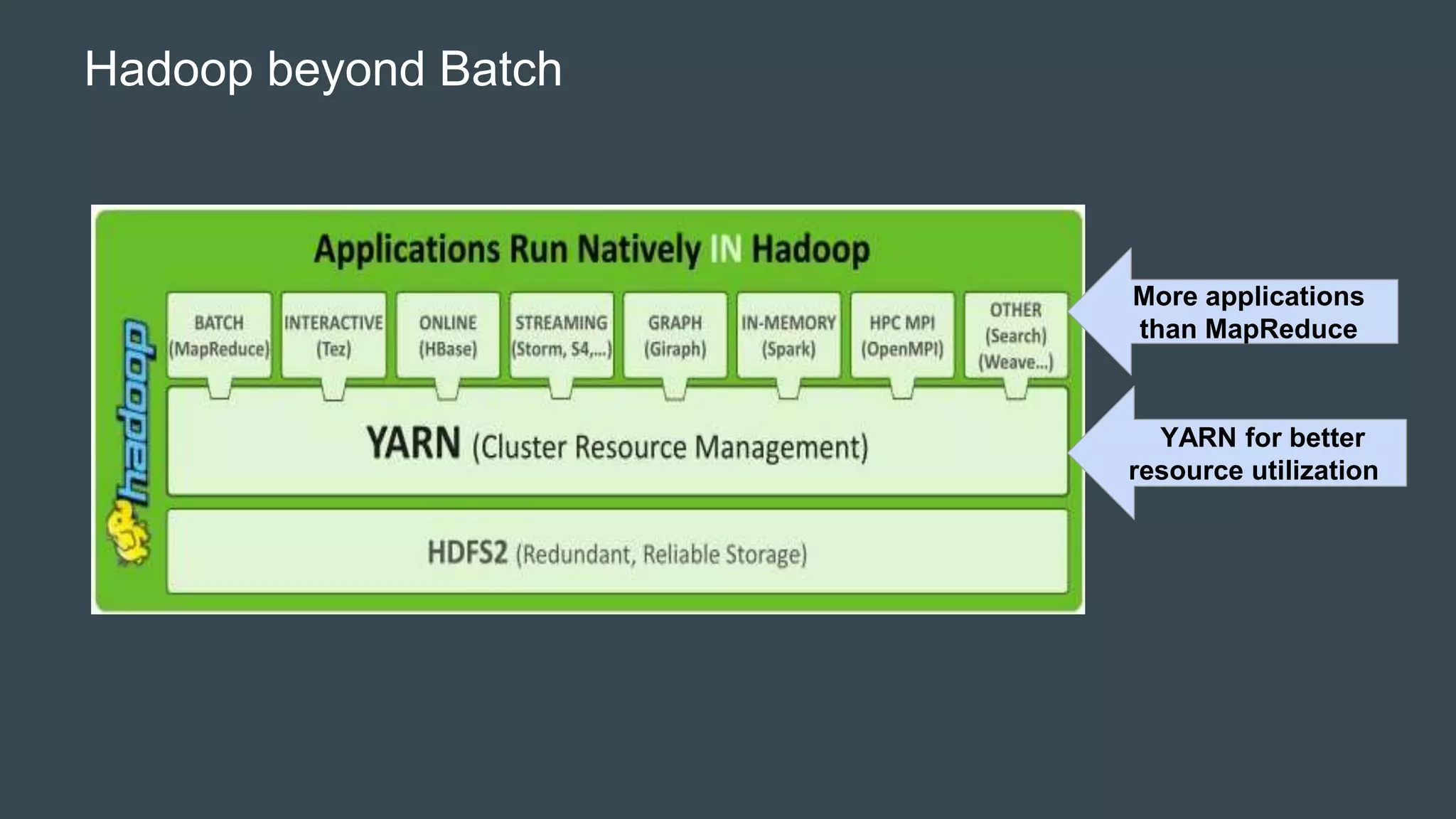
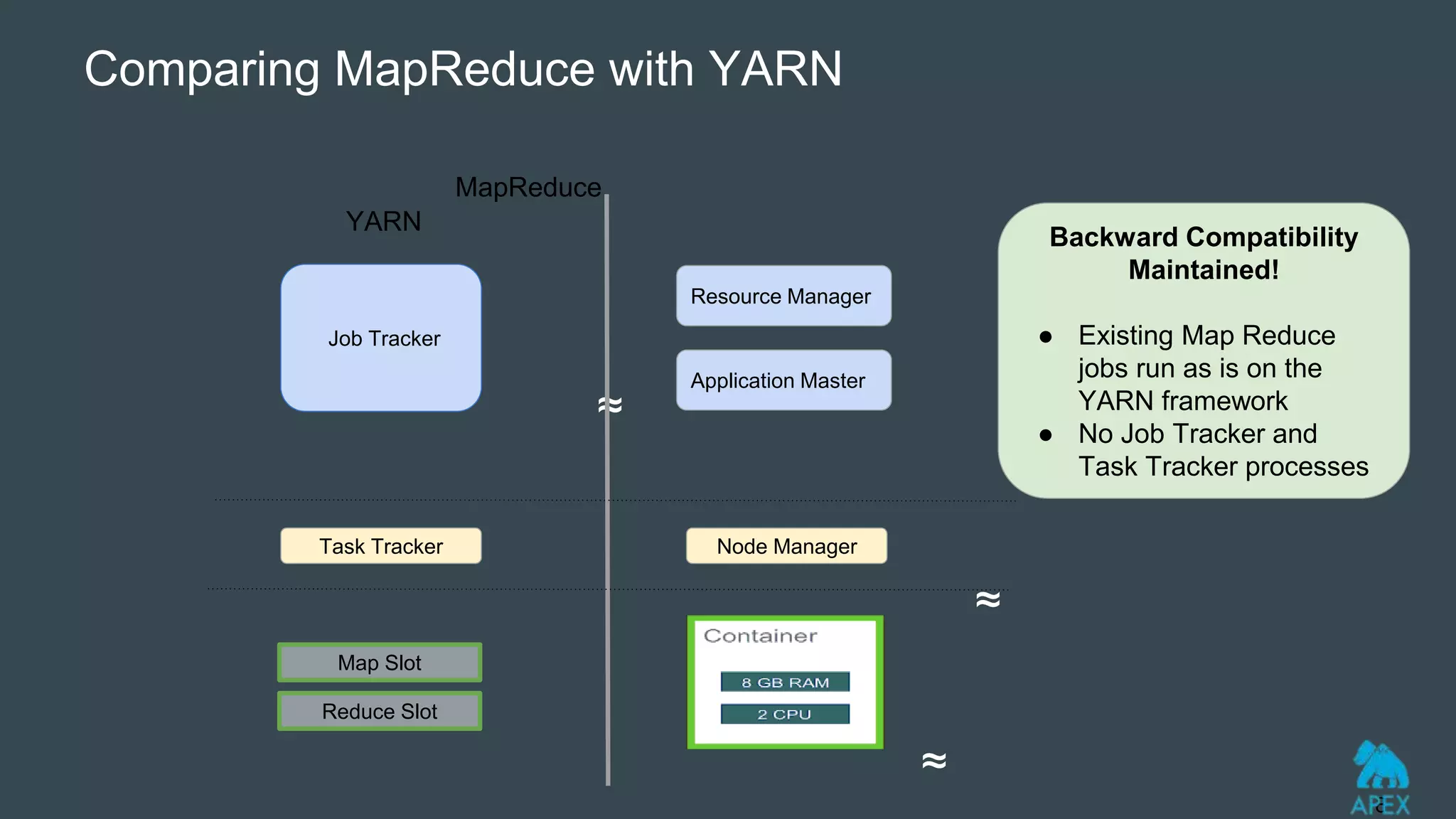
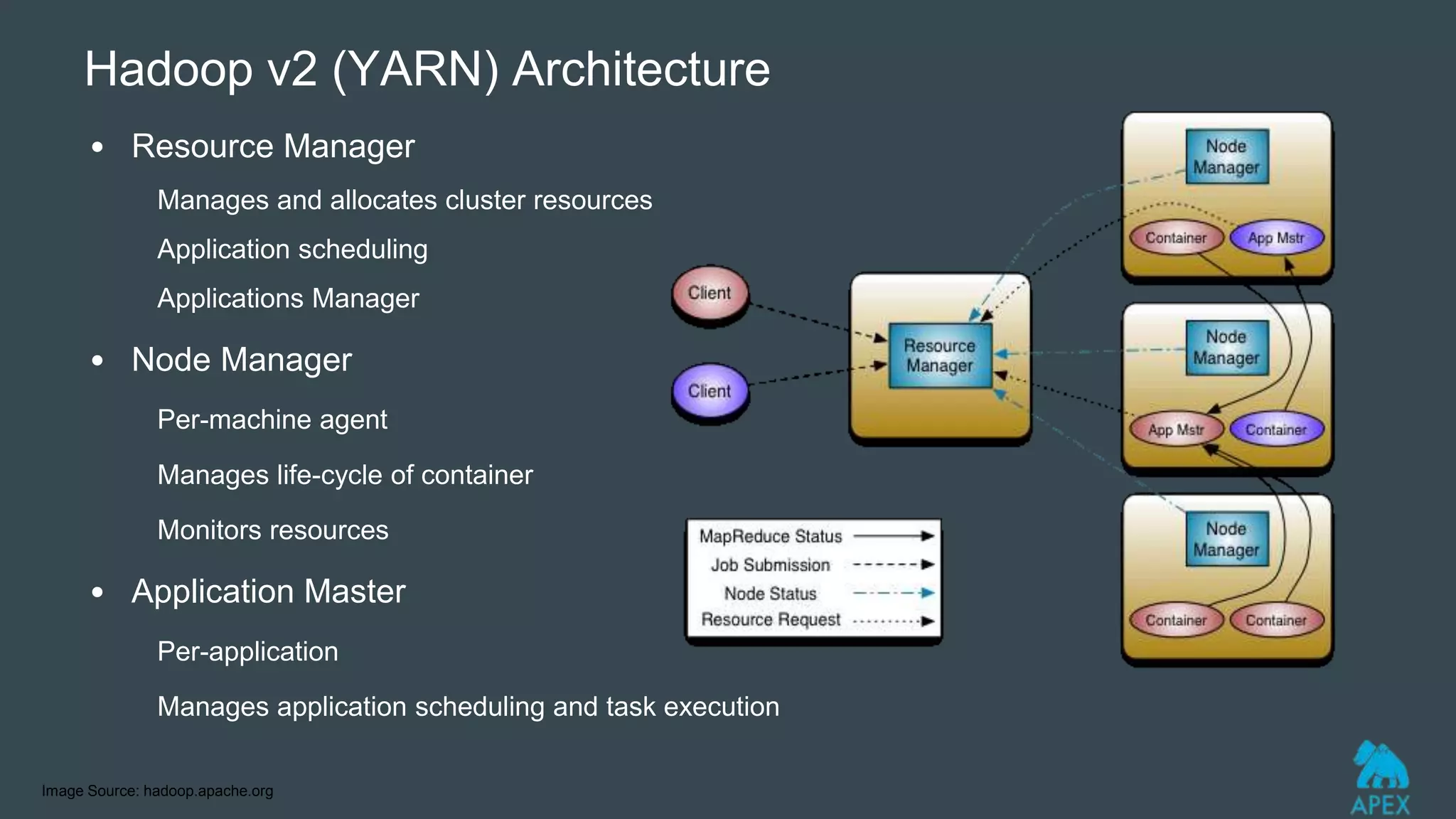
YARN was introduced as part of Hadoop 2.0 to address limitations in the original MapReduce (MR1) architecture like scalability bottlenecks and underutilization of resources. YARN introduces a global ResourceManager and per-node NodeManagers to allocate cluster resources to distributed applications. It allows various distributed processing frameworks beyond MapReduce to share common cluster resources. Applications request containers for ApplicationMasters that then negotiate resources from YARN to run application components in containers across nodes. Existing MapReduce jobs can also run unchanged on YARN.