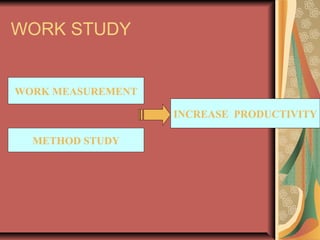
This document provides an overview of a training programme on work study for sewing floor staff. It discusses key aspects of work study including work measurement techniques, standard minute value calculation, efficiency calculation, and cost per minute calculation. The goal of the training is to increase productivity, output, and profitability through systematic analysis of work processes and setting fair productivity targets.