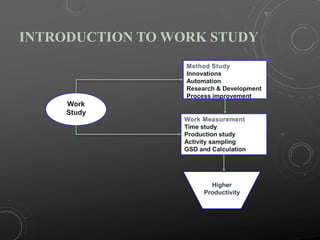
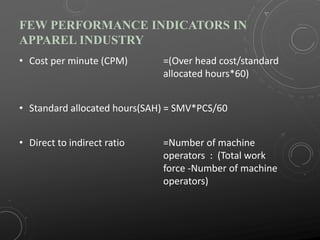
This document provides an introduction to work study and industrial engineering. It discusses work study as examining methods to improve resource use and set performance standards. Industrial engineering optimizes complex processes. The document then discusses specific work study techniques like method study, time study, and activity sampling that are used to improve productivity, efficiency, and reduce costs. It provides examples of calculating productivity and efficiency in industries. The key work study techniques of time study, production study, and activity sampling are explained. The document emphasizes using work measurement standards to set performance benchmarks and incentives.