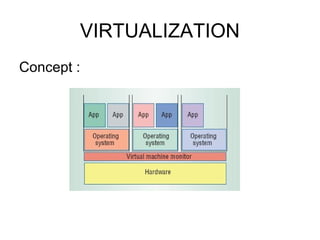
Virtualization was initially developed in the 1960s to improve usage of mainframe computers. It fell out of favor but was later successfully adapted by VMware in the 1990s to allow standard software to run on a multiprocessor system using middleware. VMware was founded in 1999 and released its first desktop and server products that year. VMware software provides virtual hardware that allows guest operating systems to run independently and be easily migrated between physical hosts. This allows for improved server consolidation and management in enterprises. Welch's Foods saw significant cost savings and efficiency gains through virtualizing over 80 servers on VMware infrastructure.