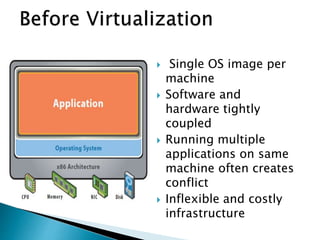
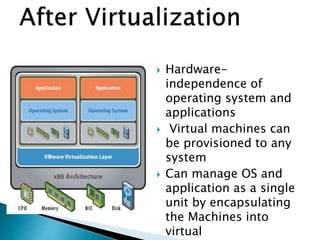
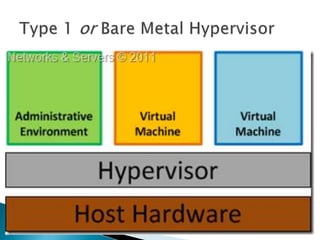
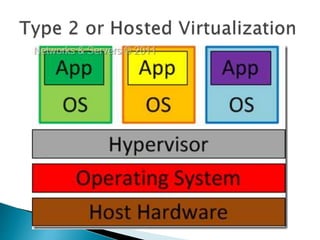
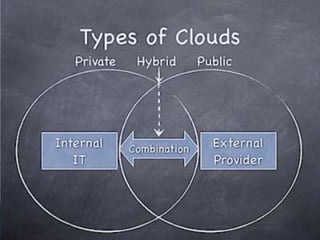
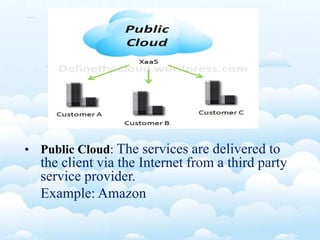
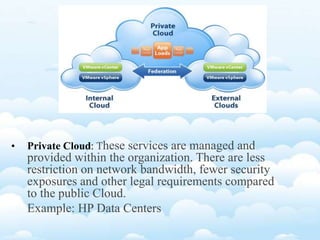
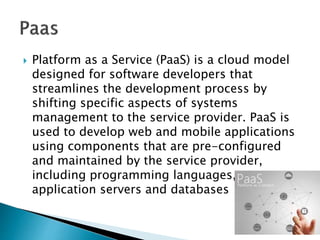
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on the same server simultaneously, improving hardware utilization. It reduces IT costs while increasing efficiency and flexibility. Virtualization provides hardware independence so operating systems and applications can run on any system, and virtual machines can be easily provisioned and managed.