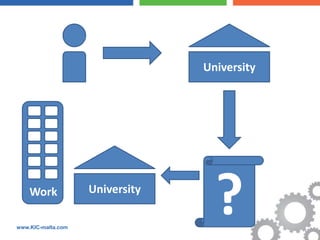
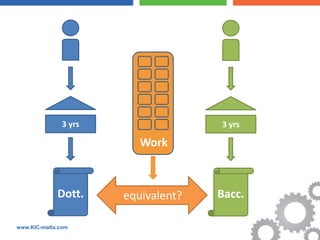
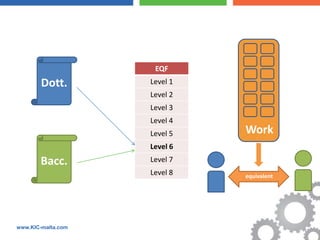
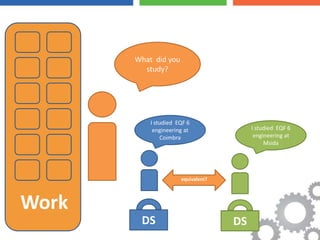
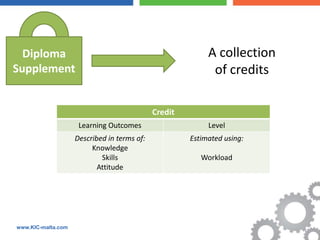
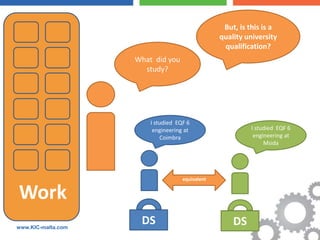
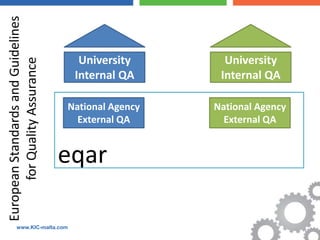
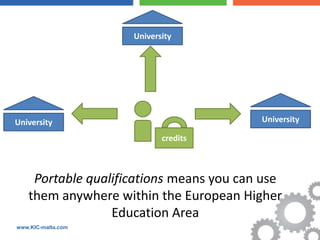
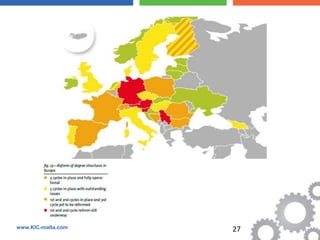
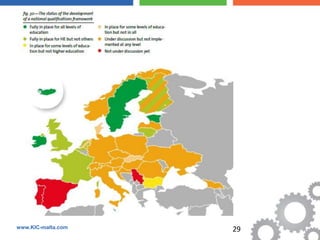
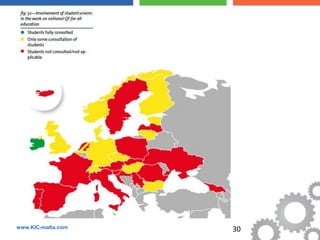
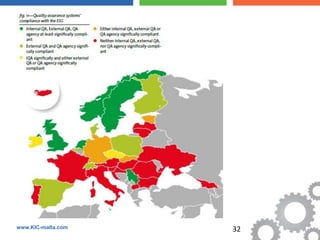
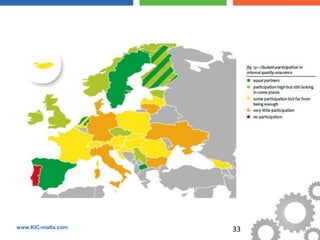
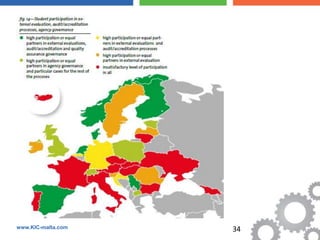
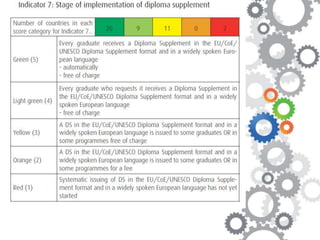
The document discusses the Bologna Process, which originated from the 1998 Sorbonne Declaration and aims to create a European Higher Education Area. It established structures and common tools to ensure comparability and compatibility of degrees based on a three-cycle system of bachelor's, master's and doctorate degrees. Key concepts introduced through the Bologna Process include the Diploma Supplement, ECTS credits, quality assurance standards, qualifications frameworks and a focus on mobility, lifelong learning and employability. The goal is to facilitate academic recognition between countries to allow students and graduates more flexible opportunities for studying and working across Europe.