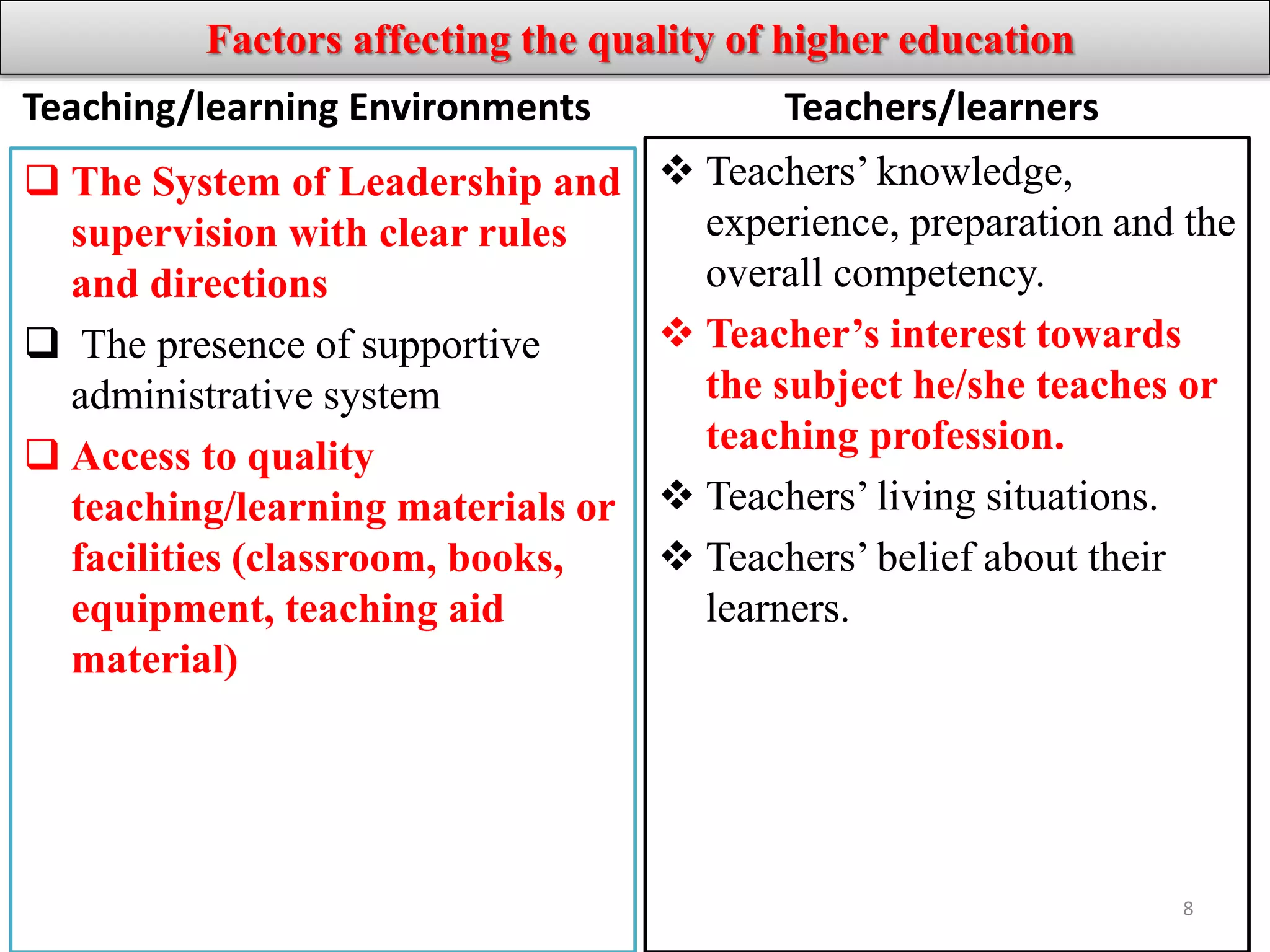
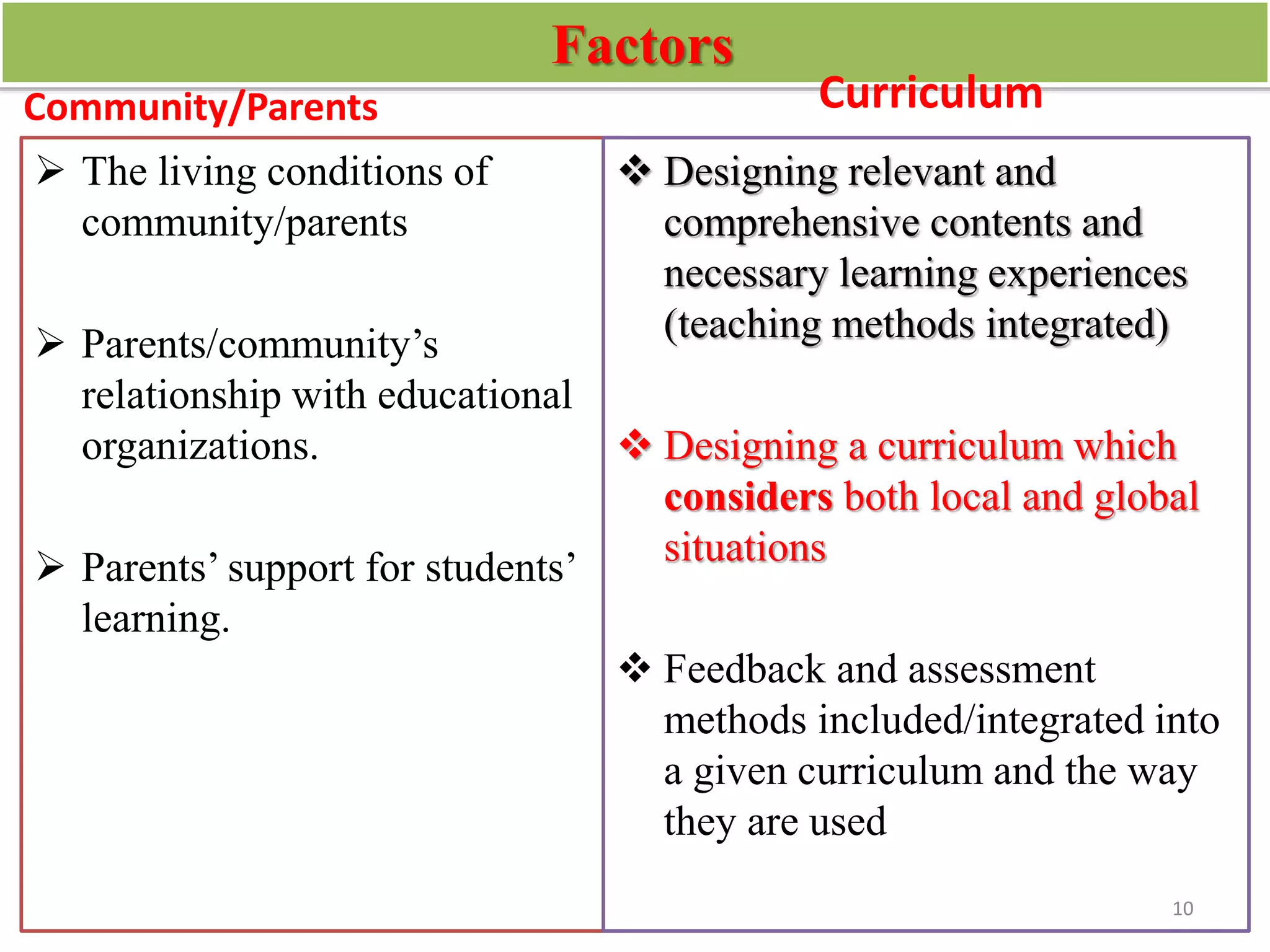
The document discusses factors that influence the quality of education, specifically higher education in Ethiopia. It begins by defining quality in the context of education and tracing the origins and evolution of the concept of quality from industry to education. It then identifies and describes major internal and external factors that can affect quality, including teaching/learning environments, teachers/learners, community/parents, and curriculum. The document concludes by having participants identify and rank the top four factors currently influencing higher education quality in Ethiopia.