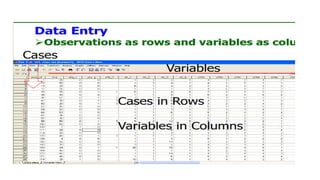
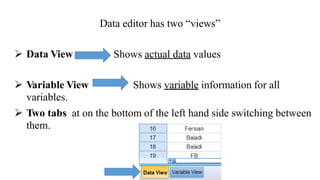
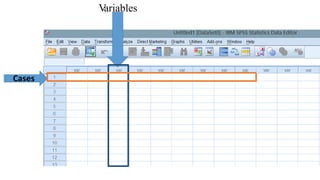
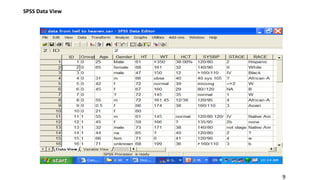
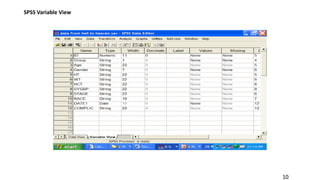
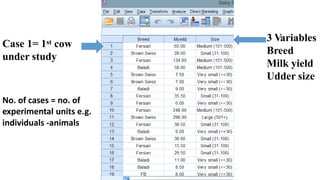
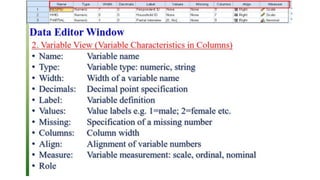
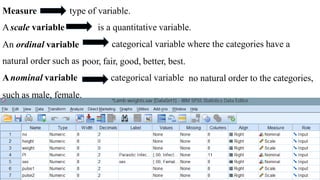
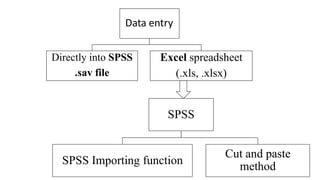
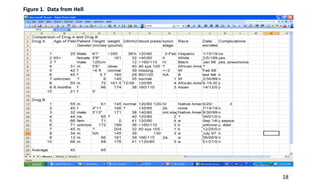
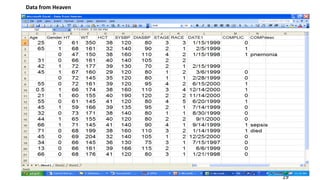
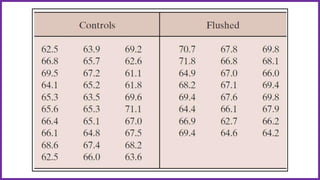
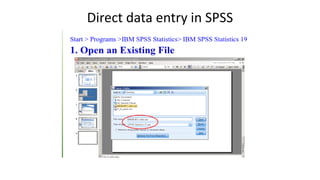
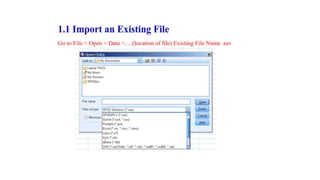
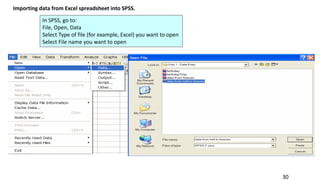
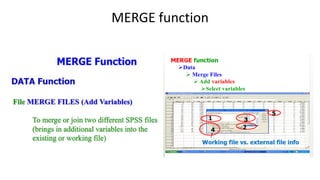
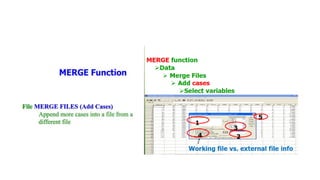
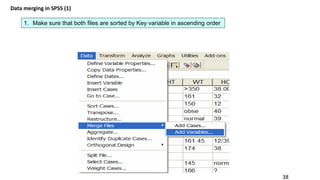
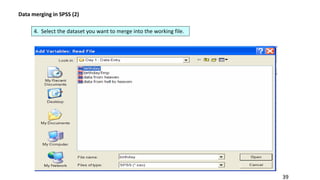
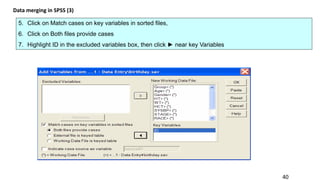
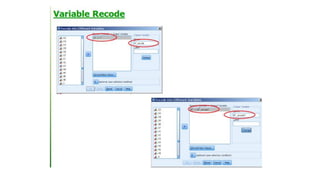
SPSS is a widely used statistical software package for analyzing social science and medical data. It allows users to easily enter, clean, transform, and analyze data through a graphical user interface with drop-down menus rather than commands. Data is organized in SPSS with variables and cases, and can be imported from Excel or directly entered. Common tasks include sorting, merging, and recoding data to prepare it for statistical analysis.