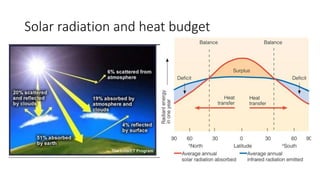
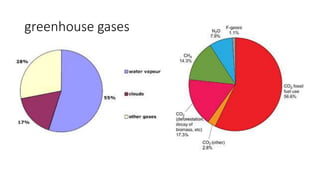
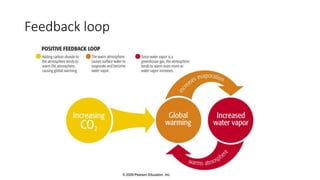
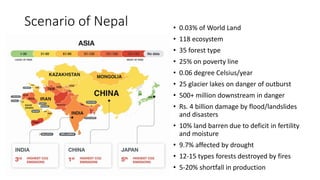
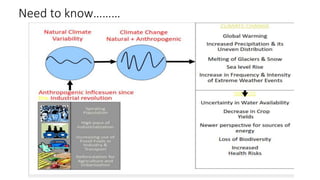
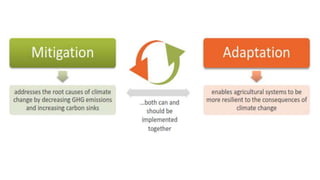
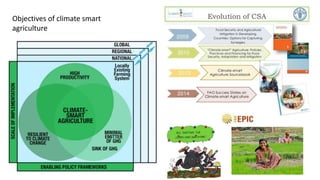
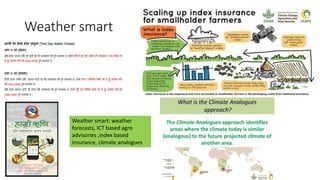
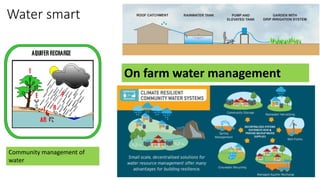
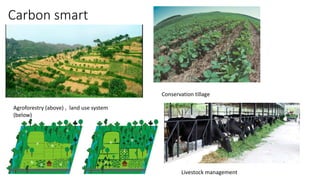
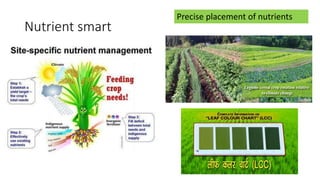
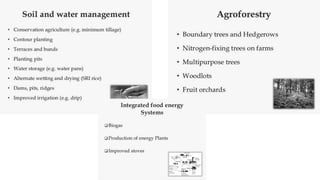
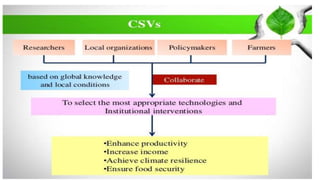
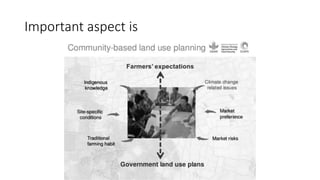
This presentation discusses climate smart agriculture. It defines key concepts like weather, climate, and the greenhouse effect. It explains how climate change is impacting Nepal's agriculture sector through increased temperatures, more extreme weather, and reduced crop yields. The presentation outlines the objectives of climate smart agriculture to develop practices that help farming adapt to climate change by being more resilient, productive, and low-carbon. Specific climate smart agriculture strategies discussed include conservation tillage, agroforestry, water management techniques, and ensuring gender inclusion in climate adaptation efforts.