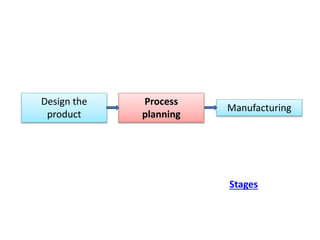
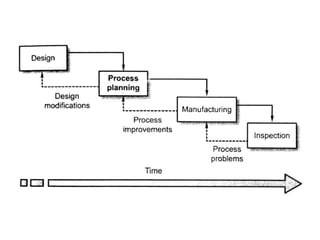
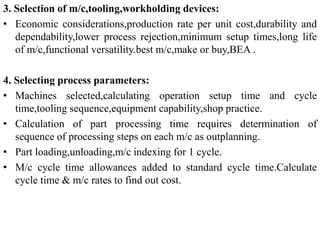
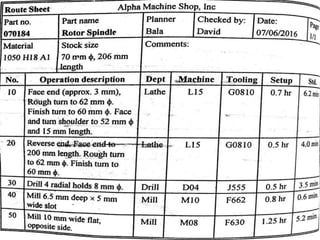
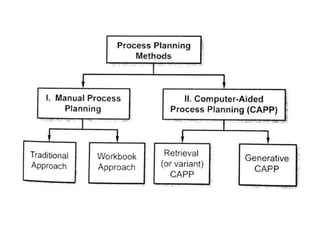
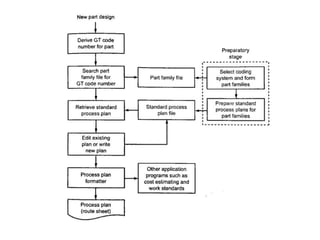
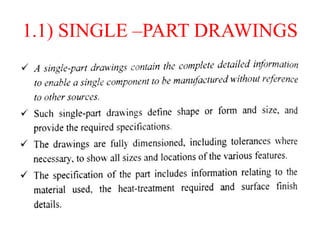
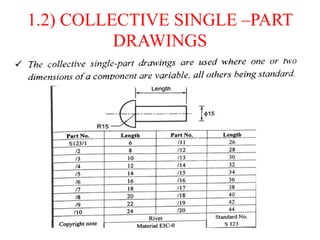
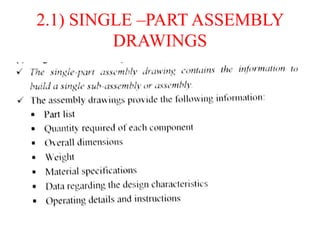
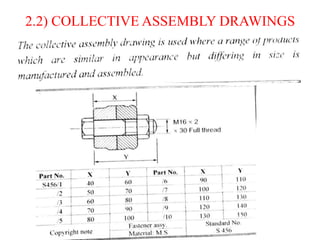
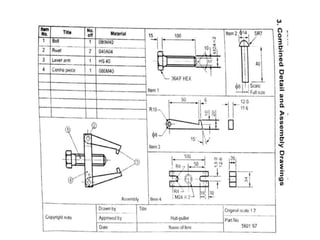
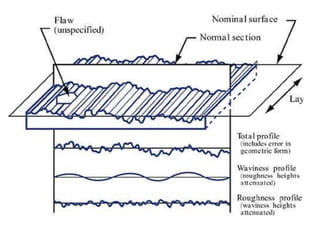
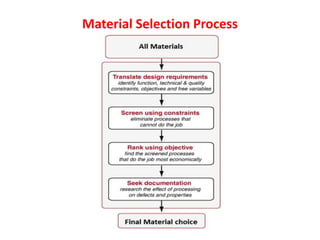
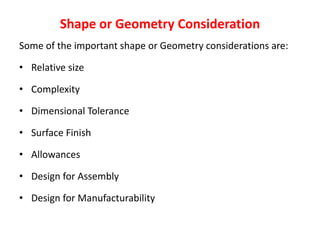
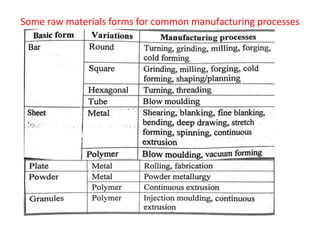
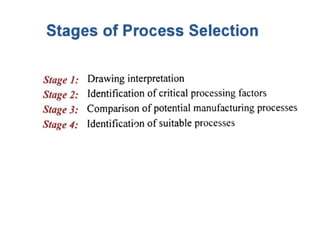
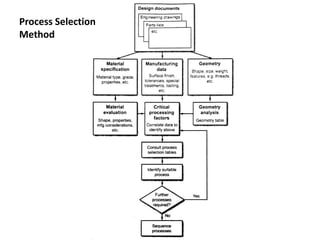
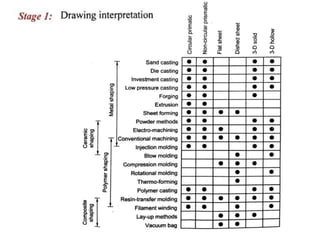
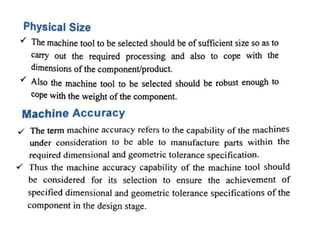
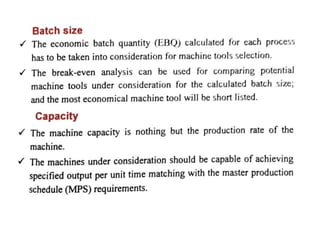
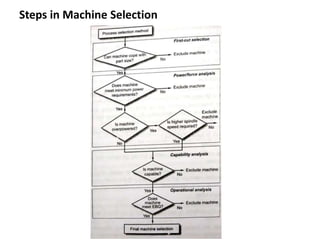
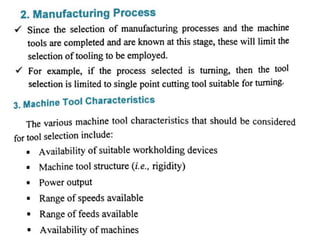
The document discusses the key activities in process planning which include drawing interpretation, material evaluation and selection of manufacturing processes, selection of machines, tools and workholding devices, determining process parameters and cycle times, quality assurance methods, and cost estimation. It also provides details on each of these activities and factors considered for machine and tool selection during the process planning stage of product development.