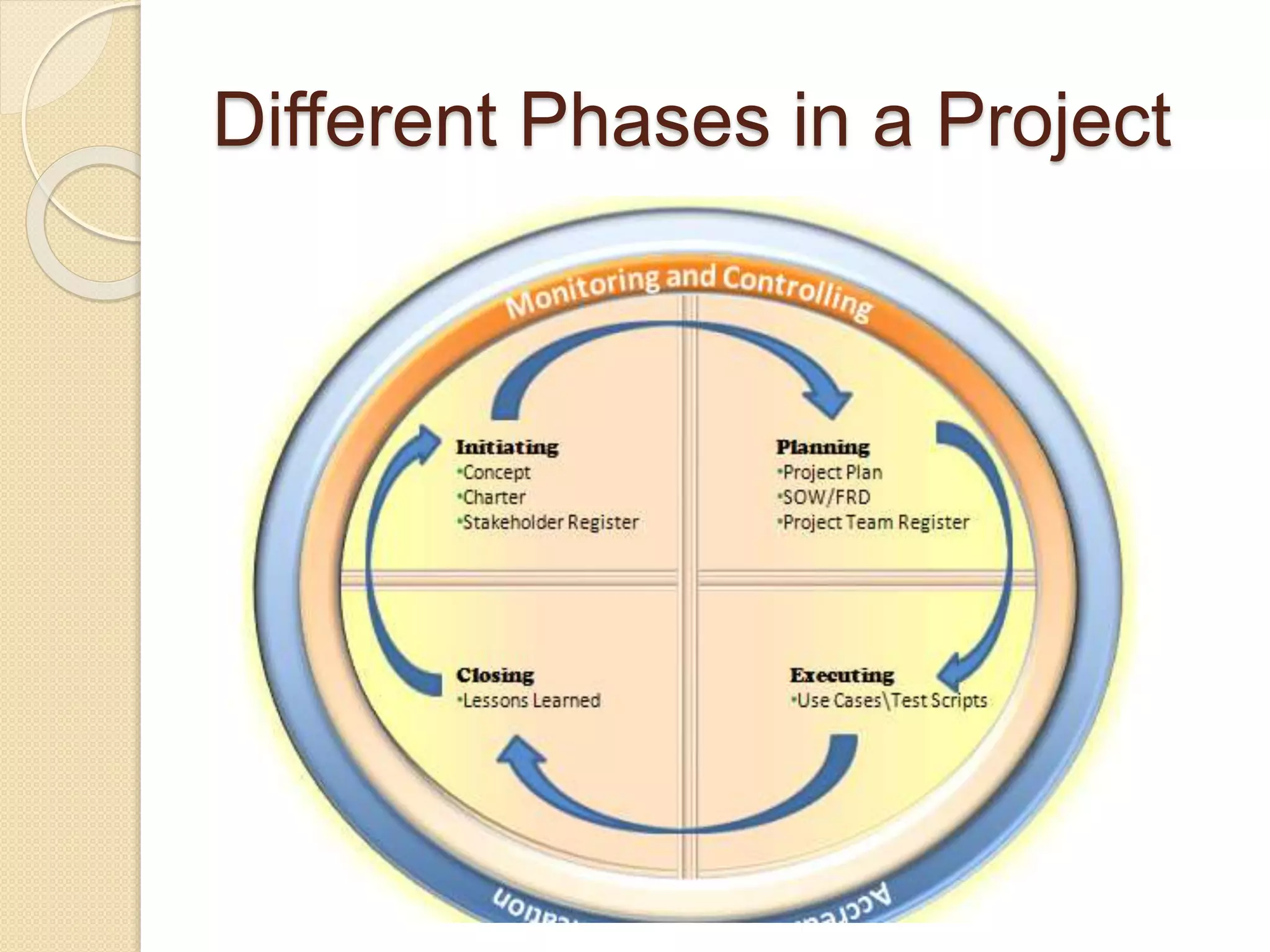
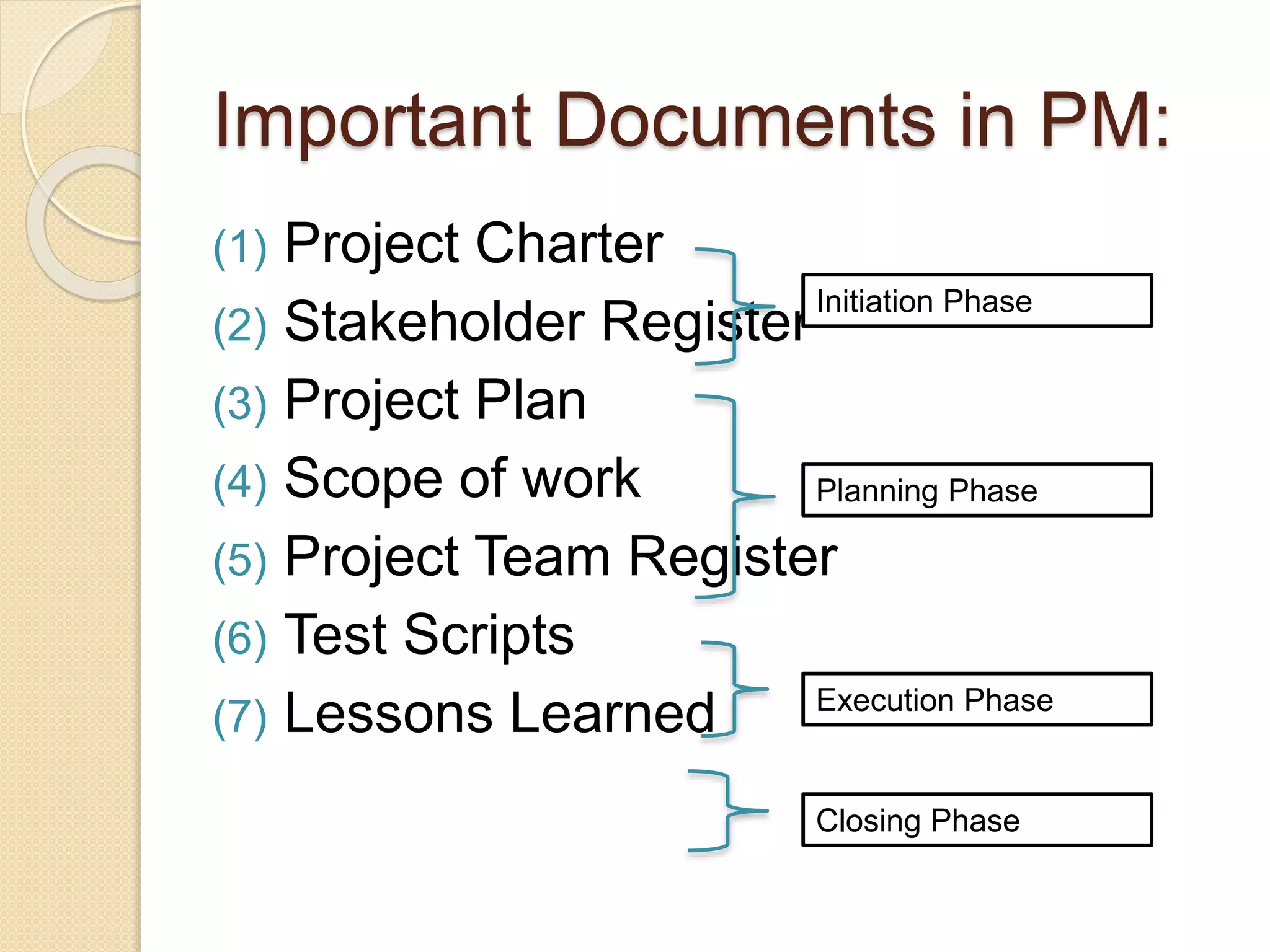
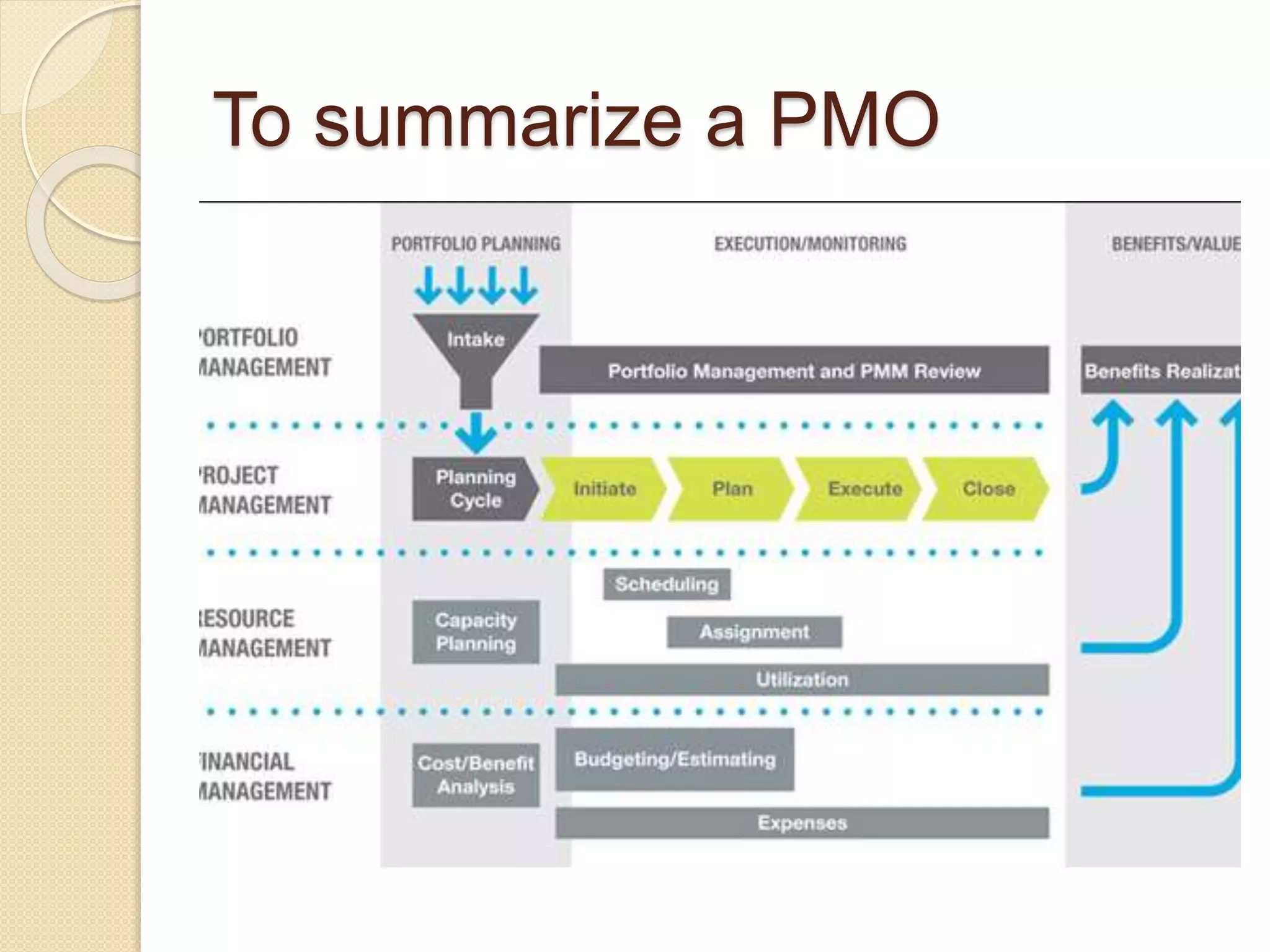
The document outlines the principles of project management, defining it as the application of knowledge and tools to meet project requirements. It details the project life cycle phases, including initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closing, and discusses the importance of a Project Management Office (PMO) to establish standards and support project management practices. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for documentation and templates to ensure efficiency and support within the organization.