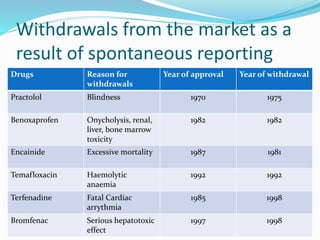
This document provides an overview of pharmacovigilance (PV), which is defined as monitoring the safety of medicines. It discusses the need for PV due to limitations of clinical trials and real-world use of medicines. Historical examples are given of drugs that were withdrawn from the market due to safety issues identified through spontaneous reporting. The PV process involves detecting, assessing and preventing adverse drug reactions through both spontaneous and mandatory reporting. India has a national PV program to improve patient safety. Narrative case reports are important for communicating individual safety cases and include details like medical history, events, and causality assessment. Various databases and reporting forms are used to support global PV activities.