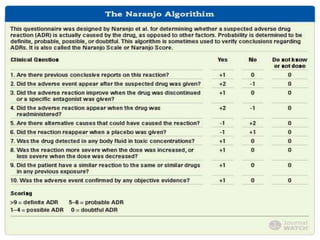
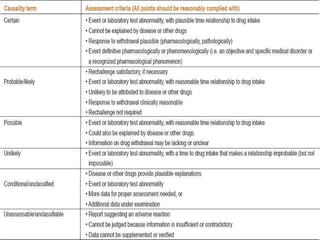
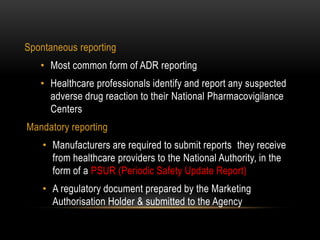
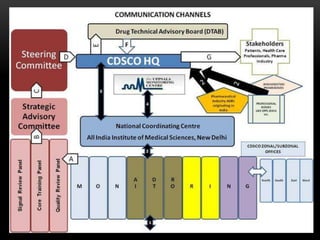
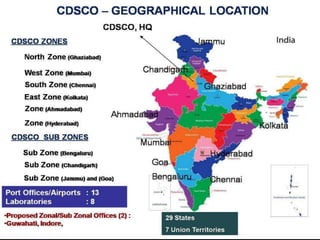
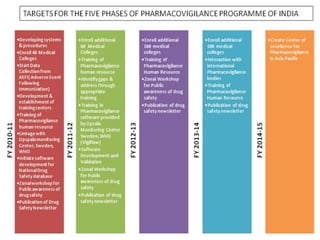
Pharmacovigilance is the science of monitoring the effects of medicines after they have been licensed for use, in order to identify new safety hazards and assess risks and benefits. It aims to improve patient care and safety in relation to medicine use. The thalidomide disaster in the 1960s demonstrated the need for formal pharmacovigilance systems to detect adverse drug reactions. Spontaneous reporting by healthcare professionals and mandatory reporting by manufacturers are key methods for collecting information on adverse drug events. Reports are assessed for causality and contribute to the ongoing evaluation of medicines to ensure their safe and effective use.