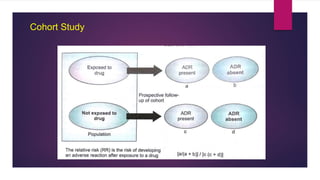
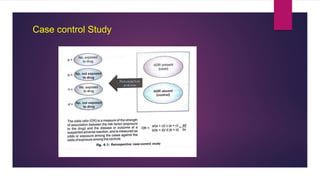
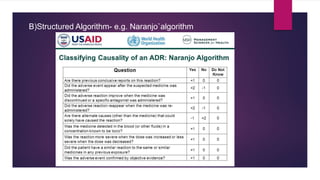
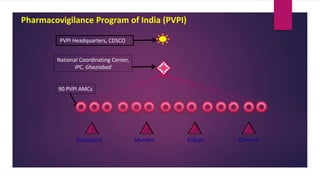
The document discusses pharmacovigilance and adverse drug reactions (ADRs). It provides historical context on important events that increased focus on pharmacovigilance like the Thalidomide disaster. It describes the need for pharmacovigilance due to limitations of preclinical and clinical trials. It outlines the aims, methods like spontaneous reporting and causality assessment, and programs in India and by the WHO. It defines ADRs and provides classifications. In summary, the document overviews the importance and process of pharmacovigilance in monitoring drug safety post marketing.