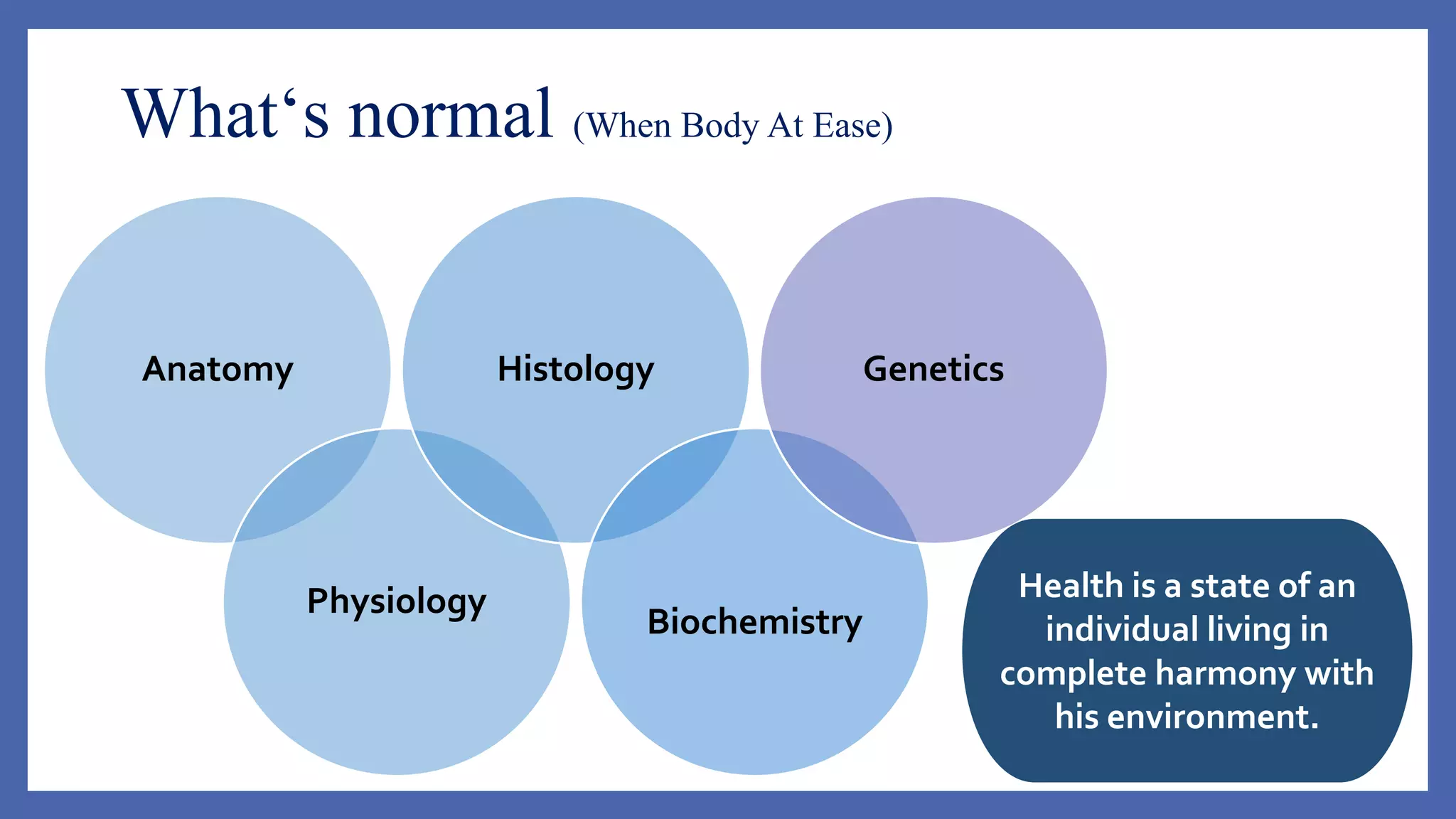
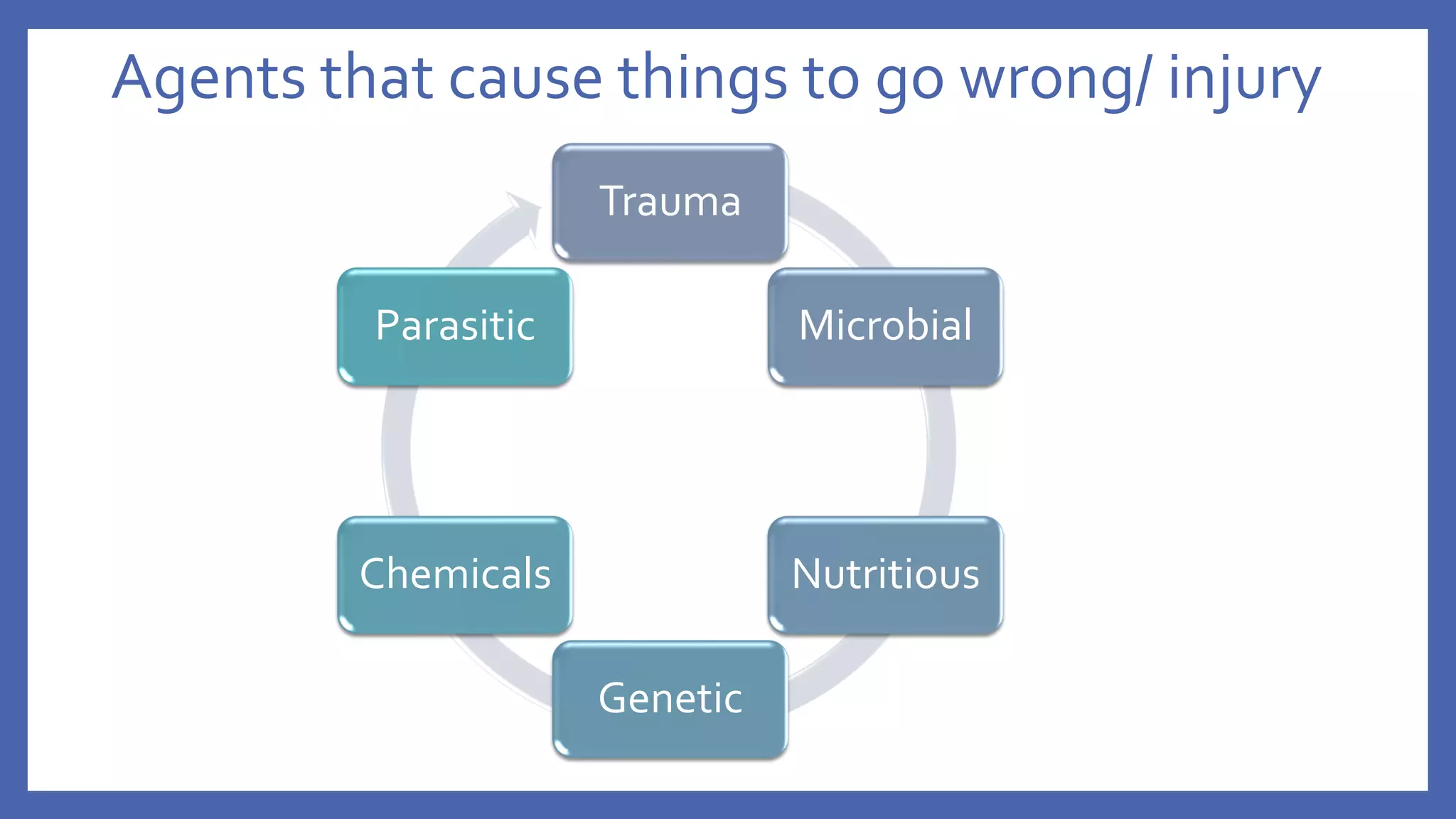
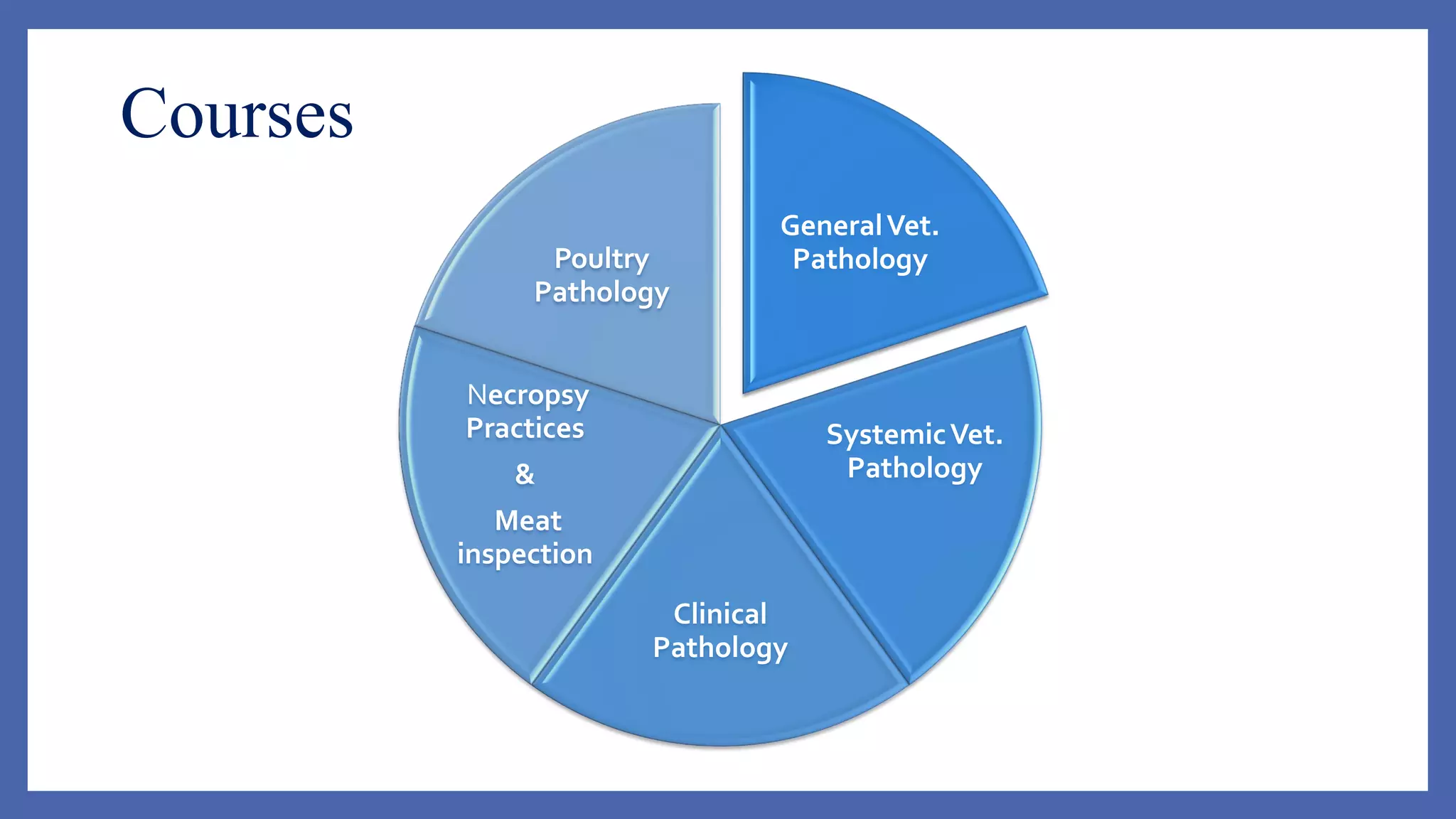
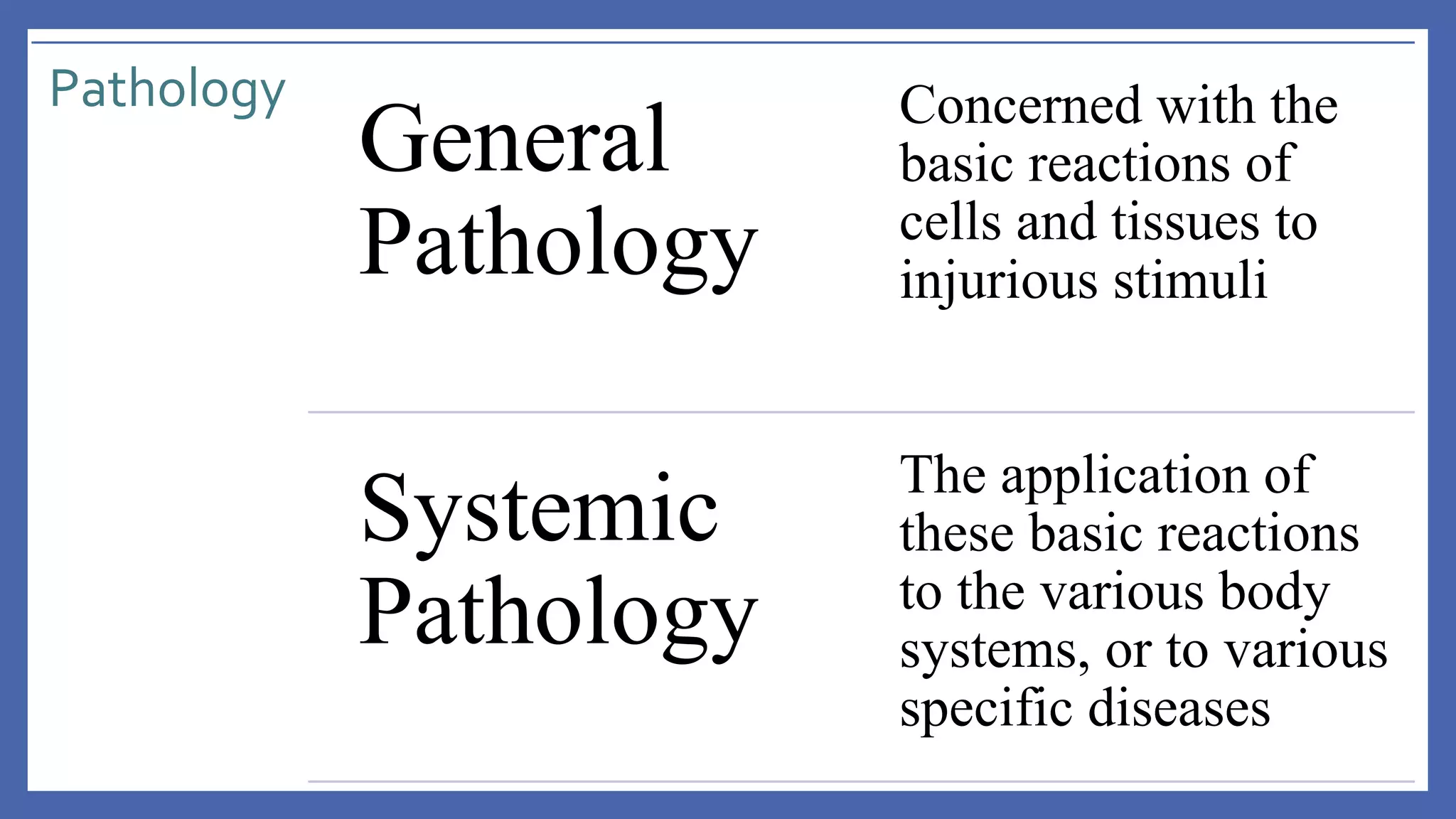
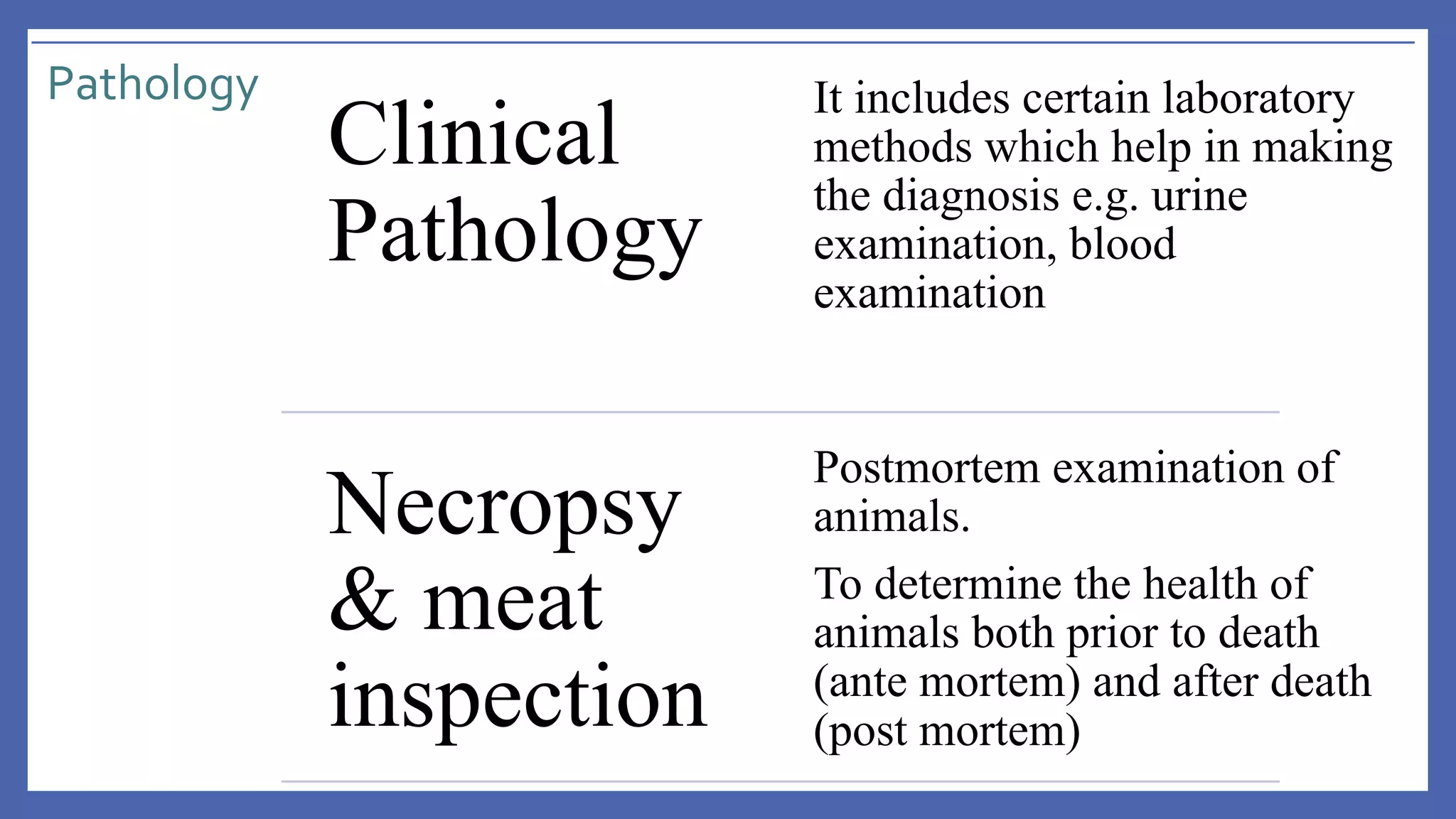
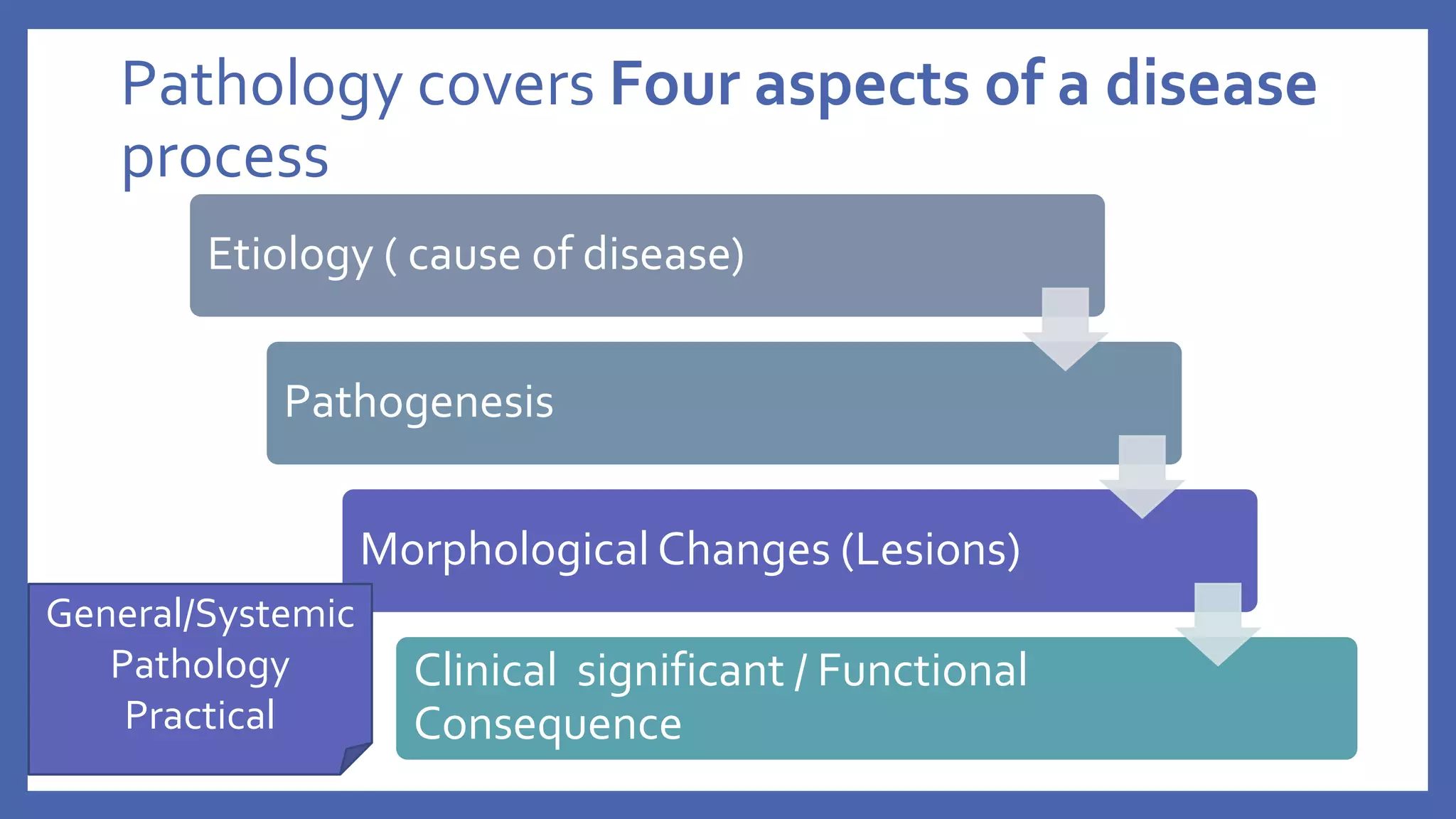
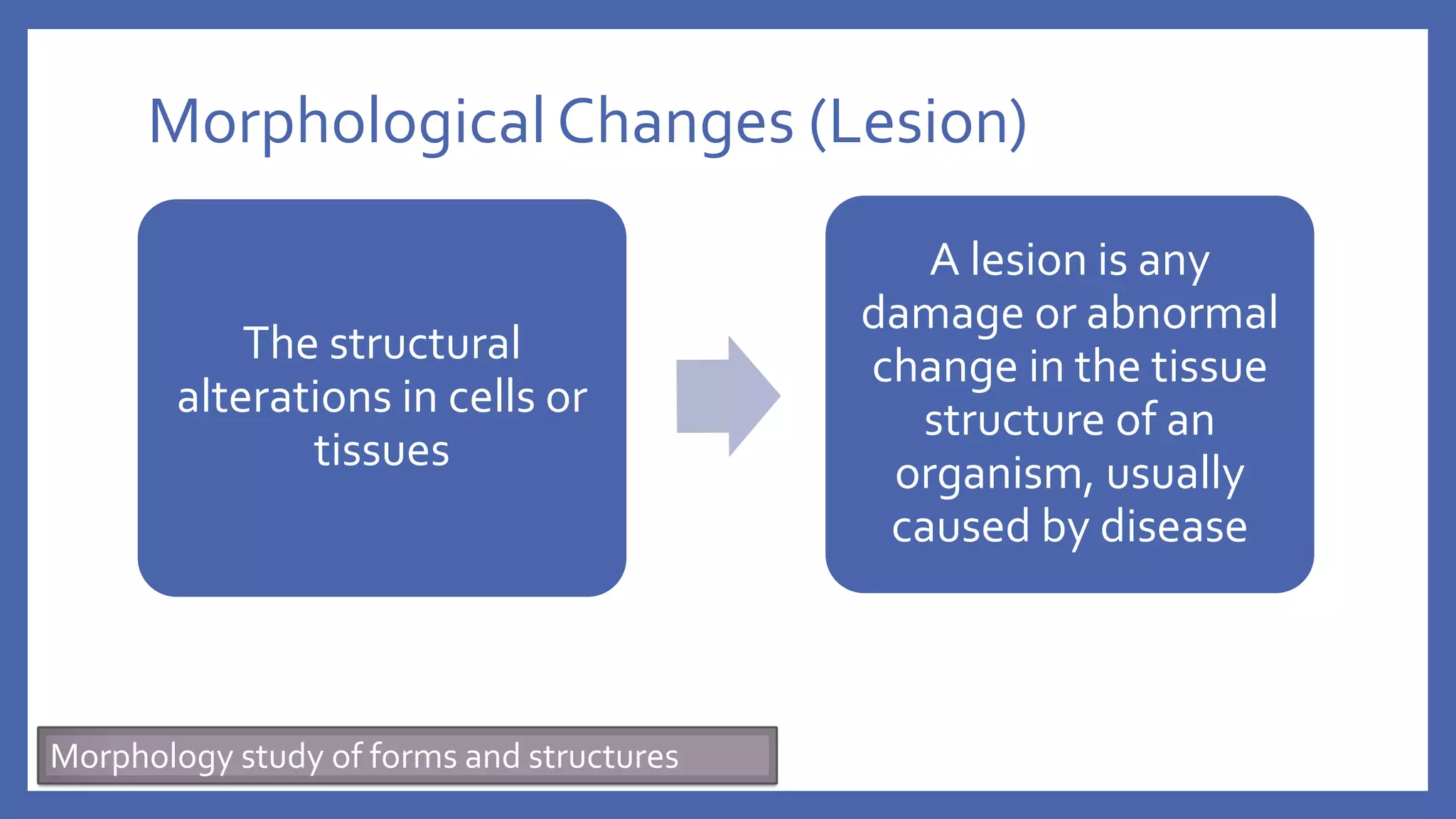
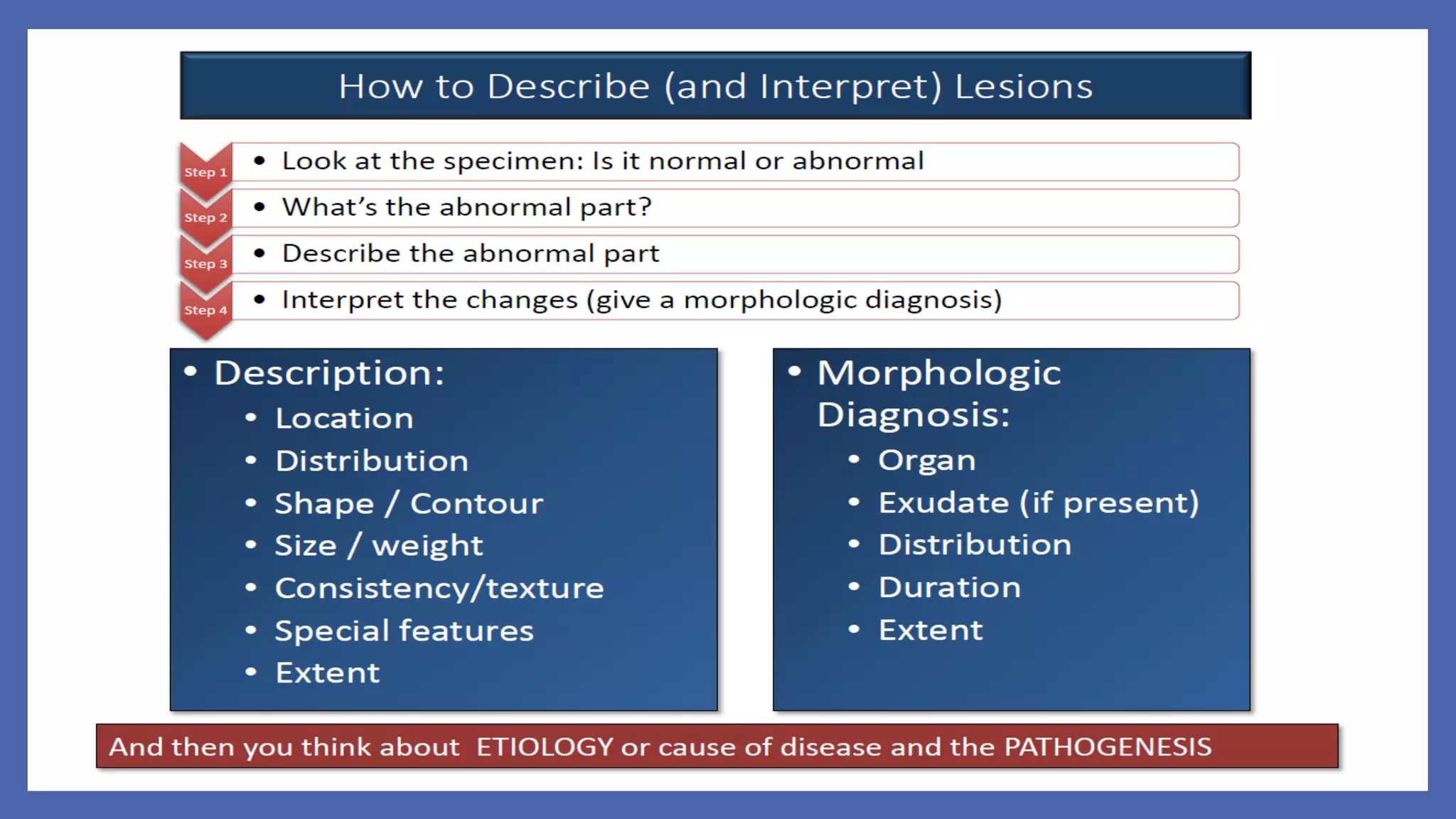
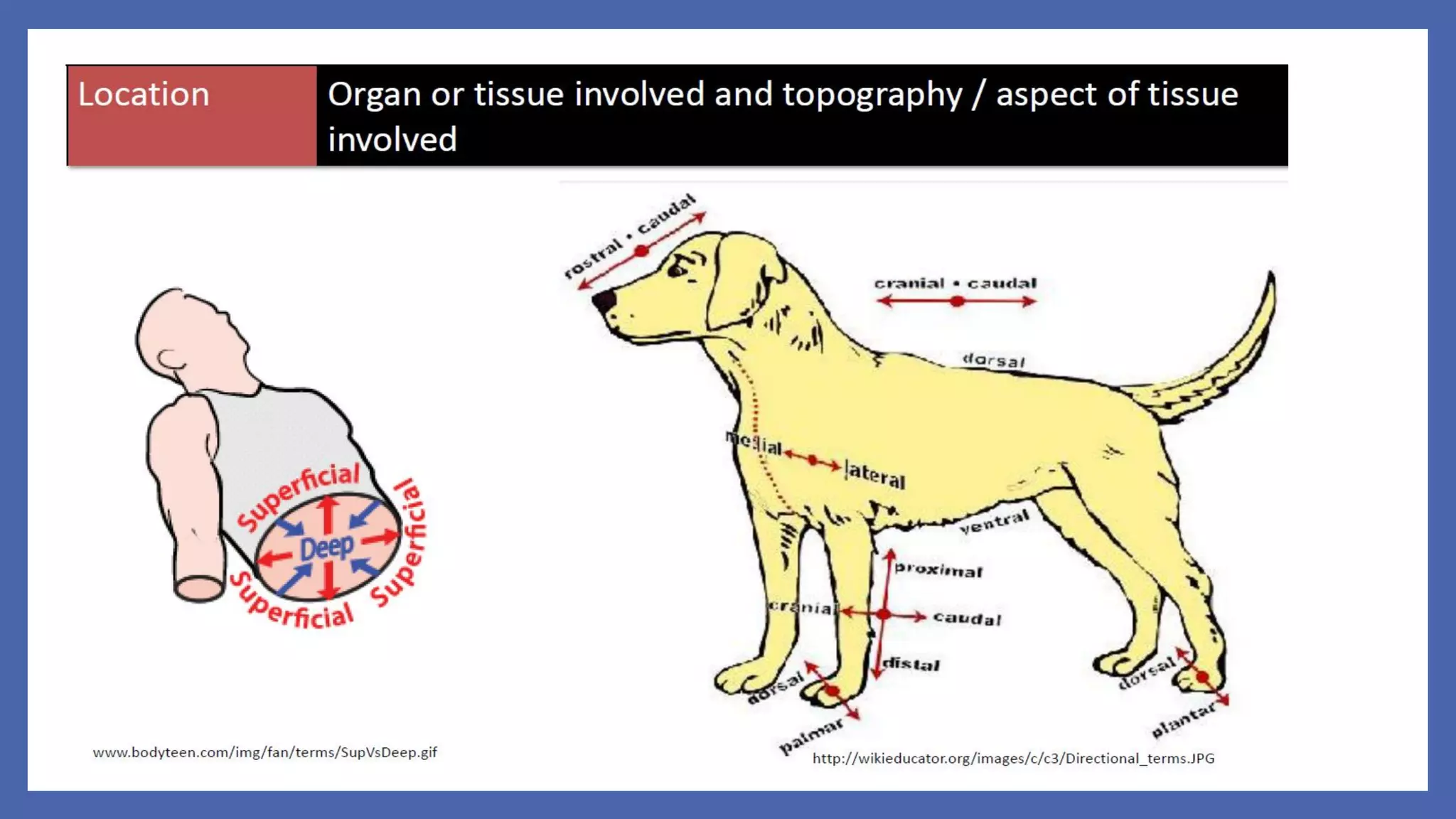
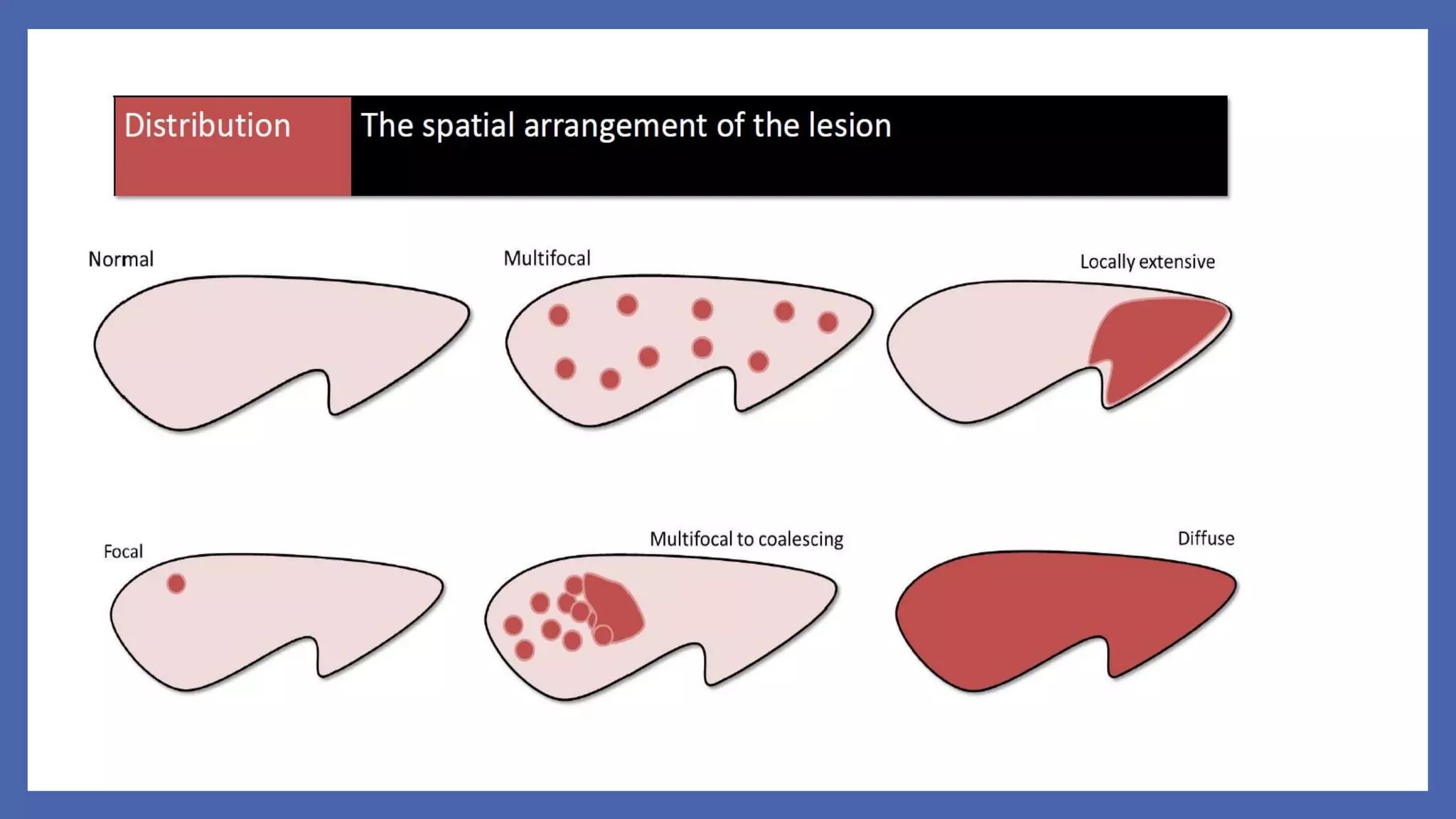
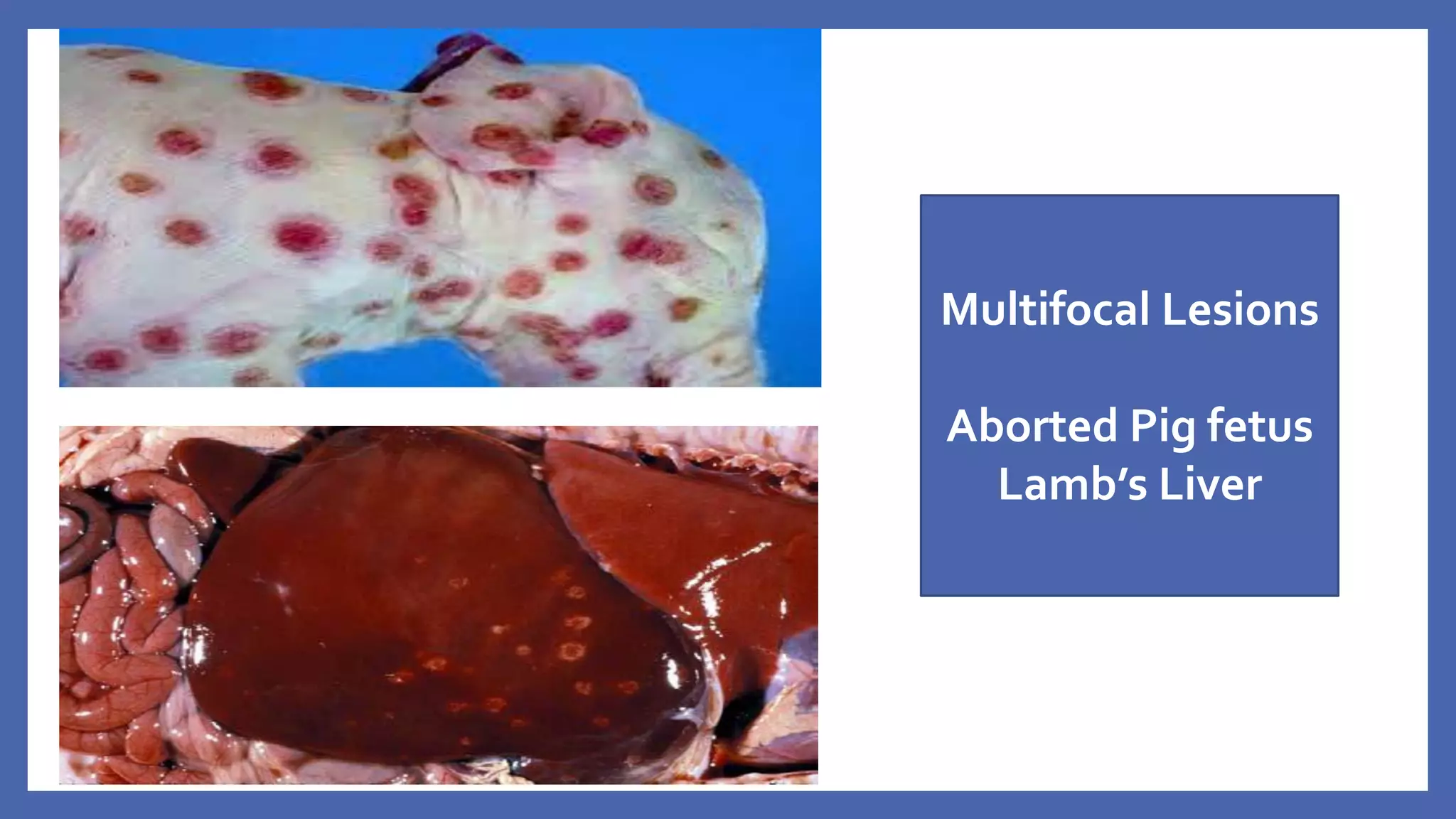
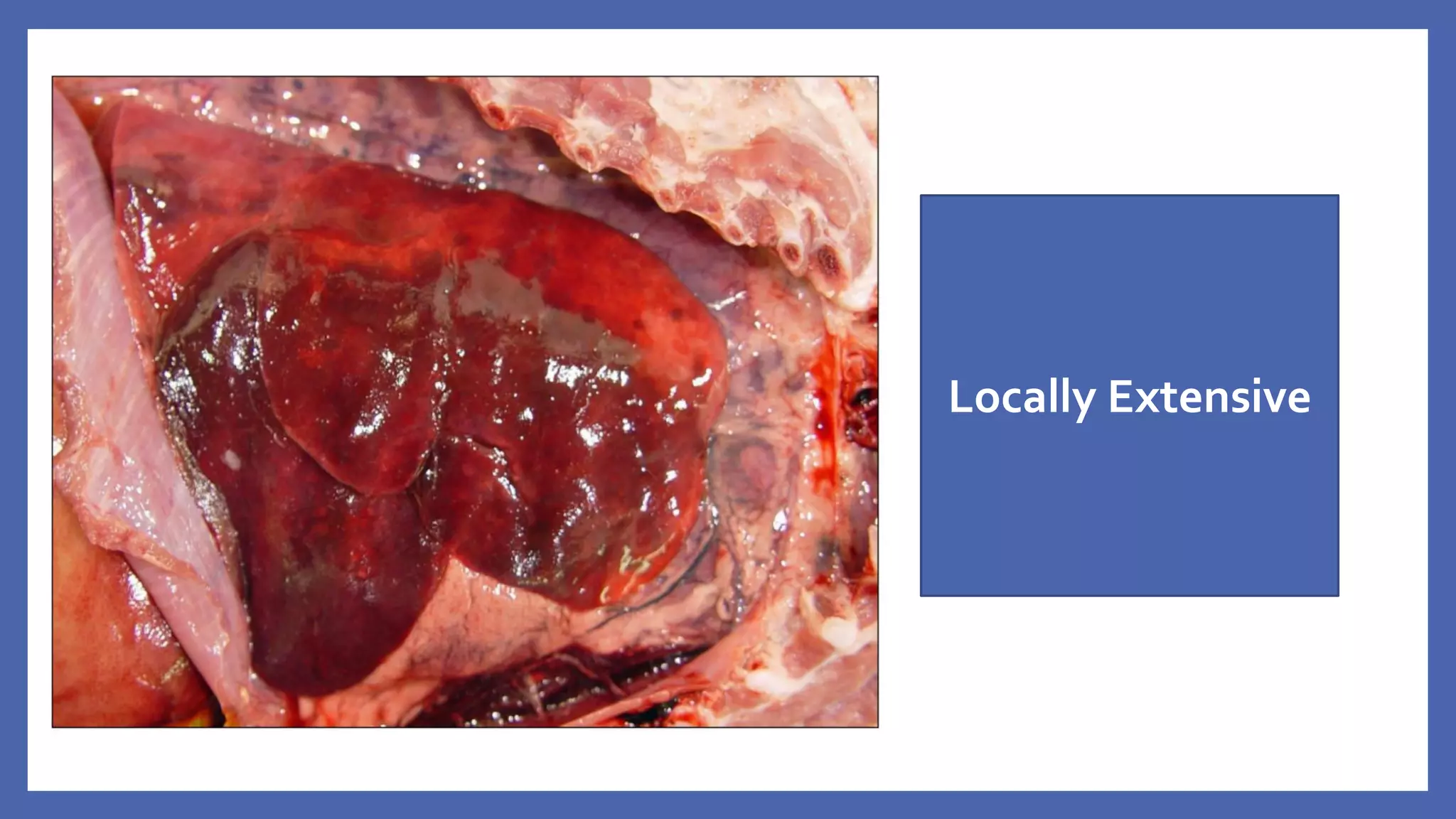
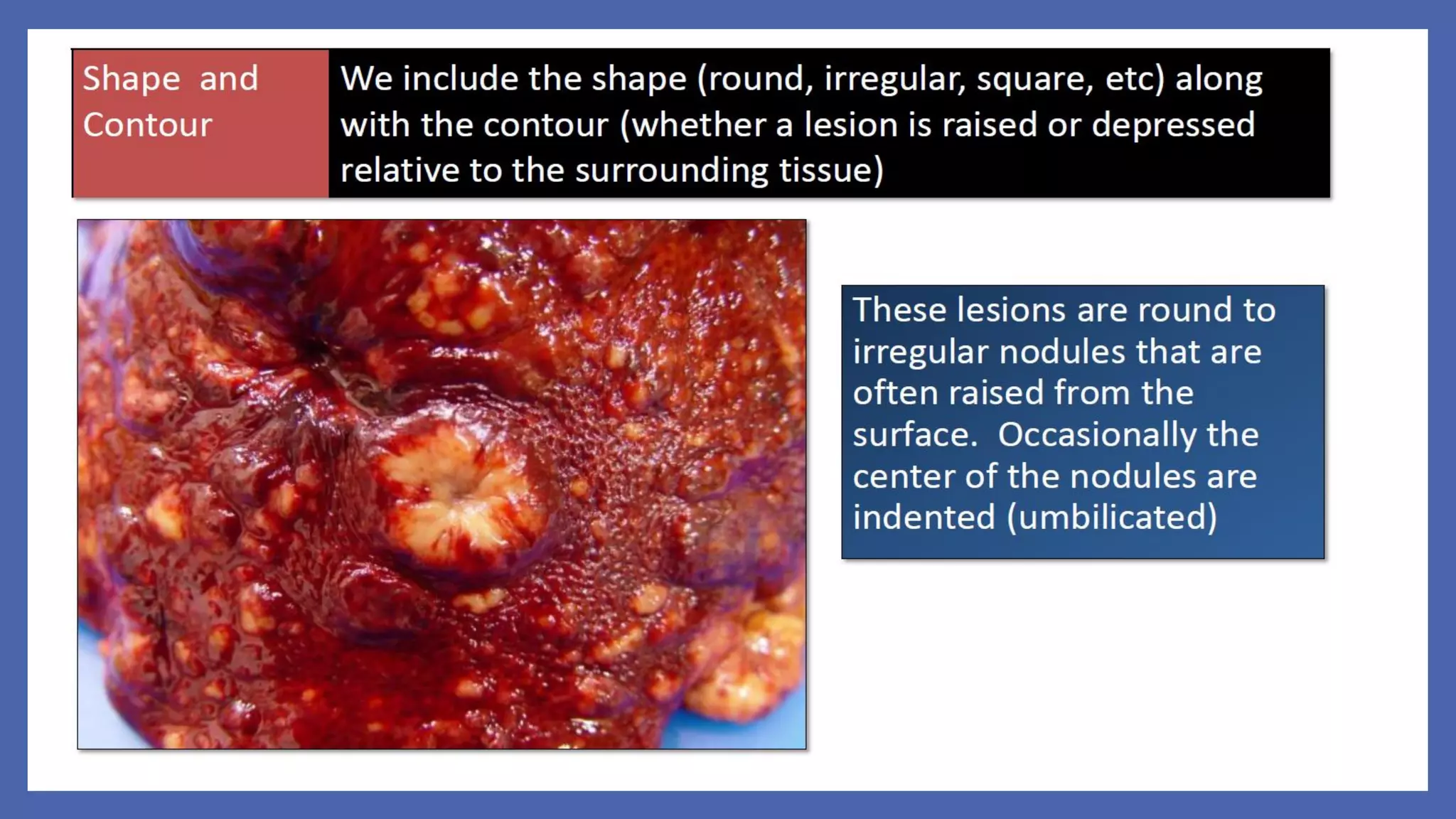
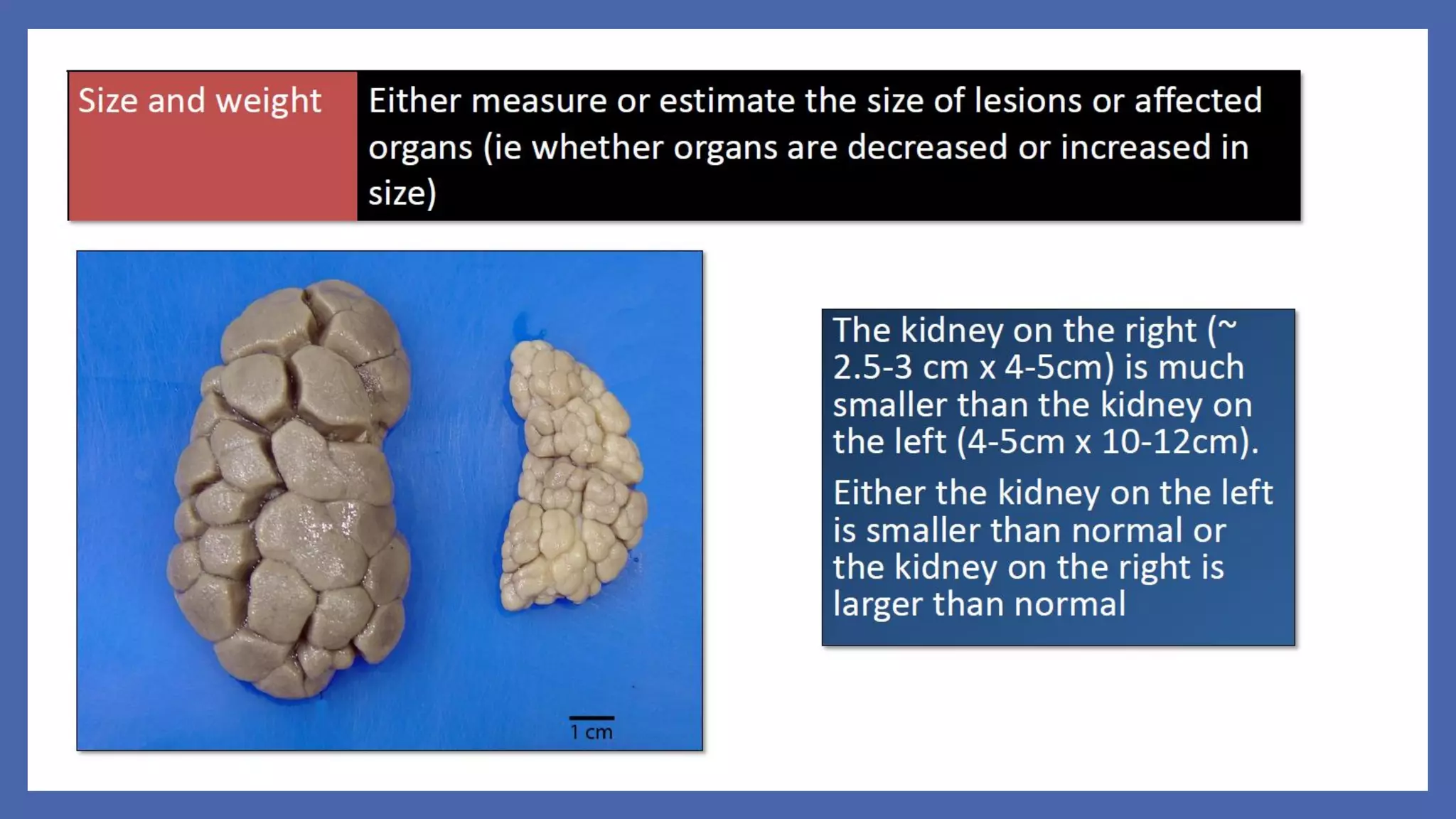
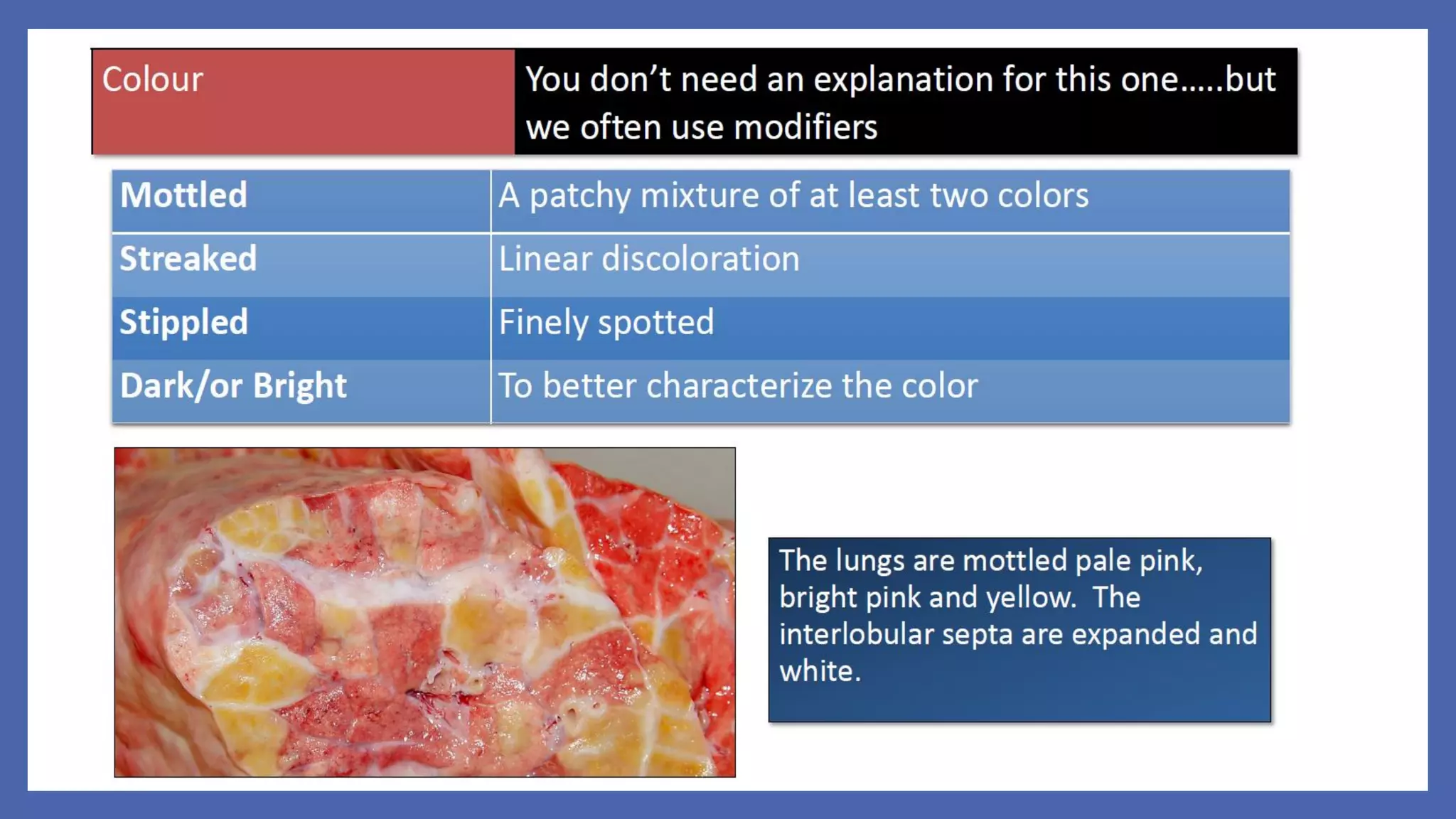
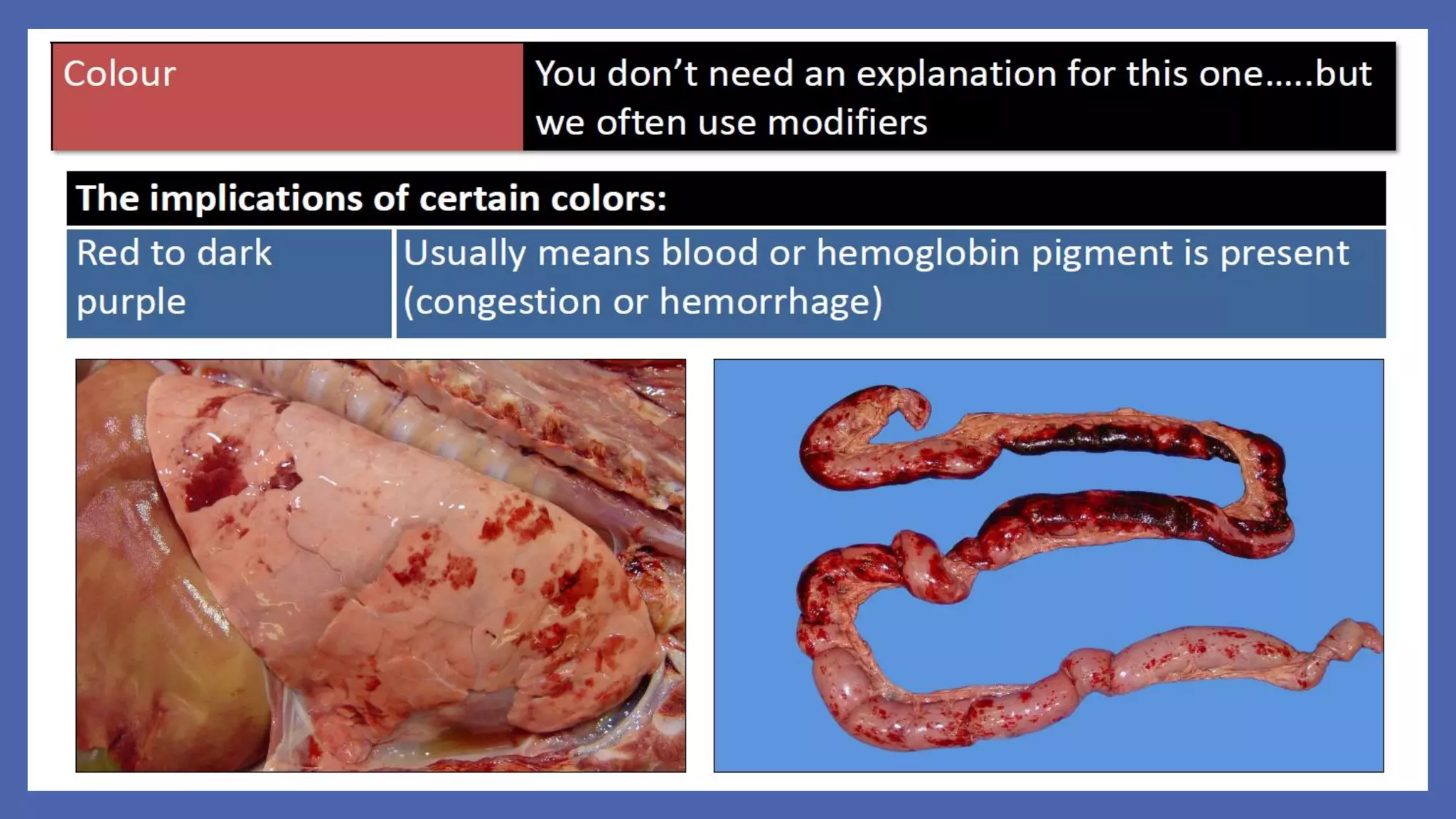
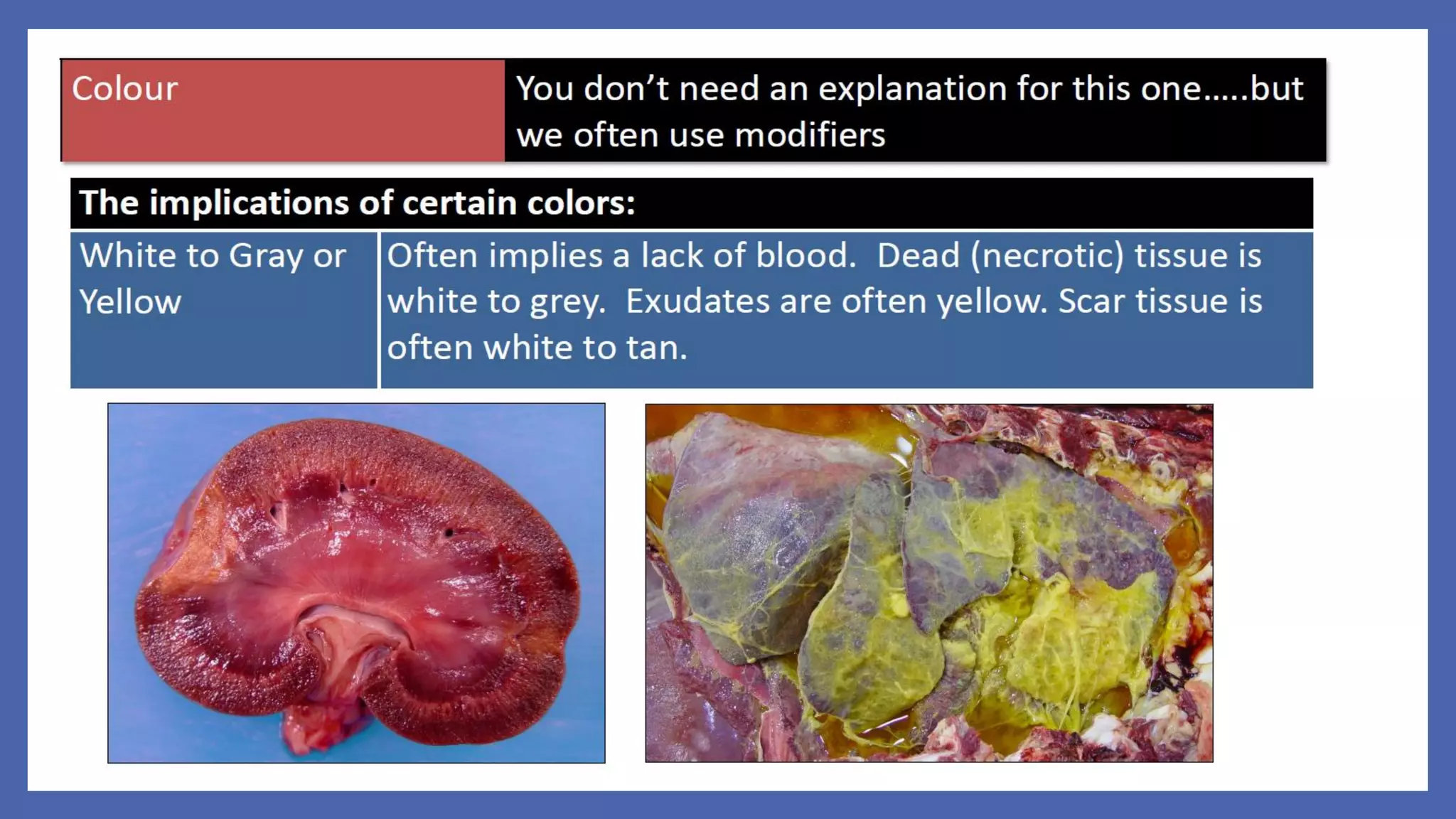
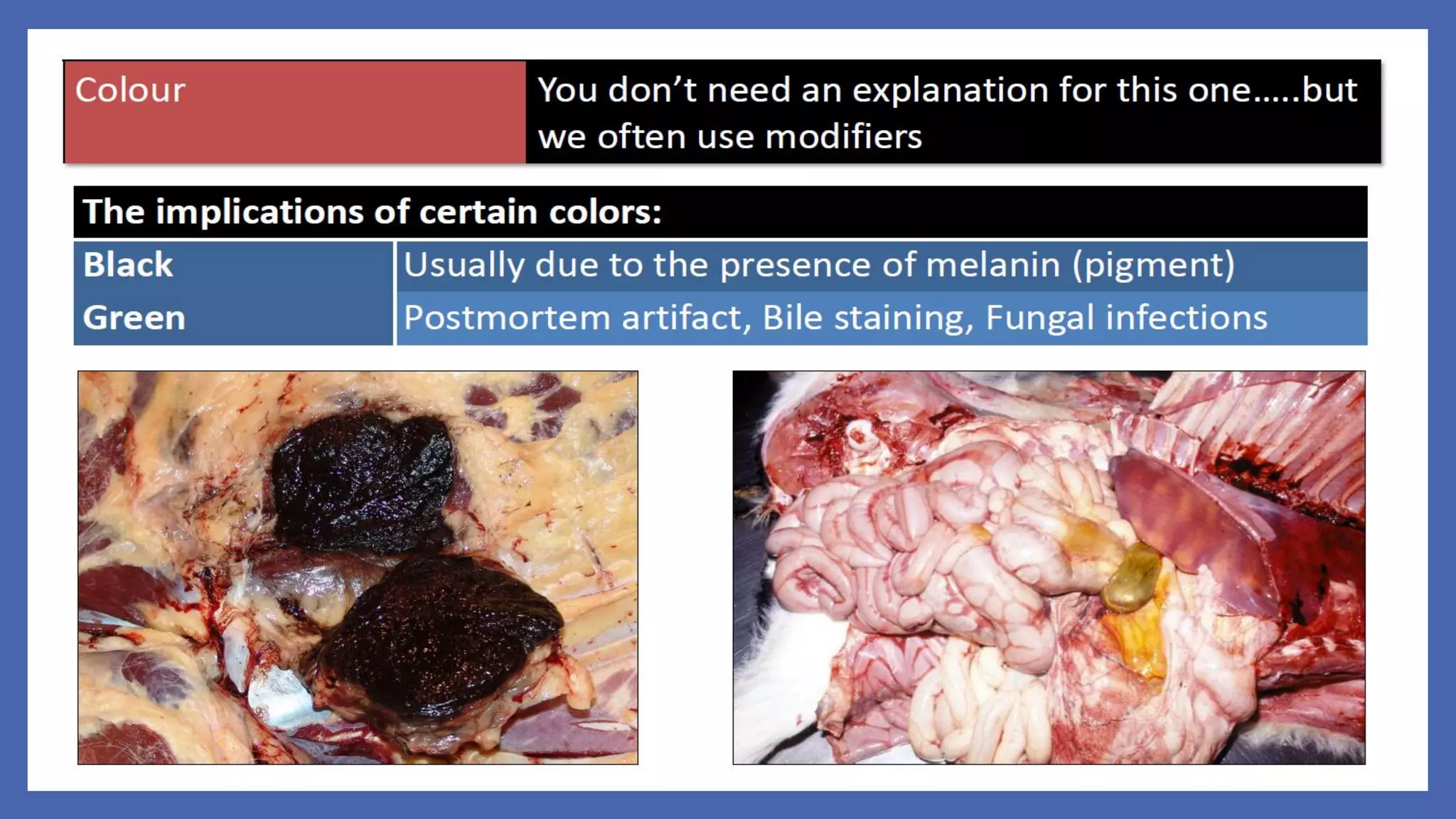
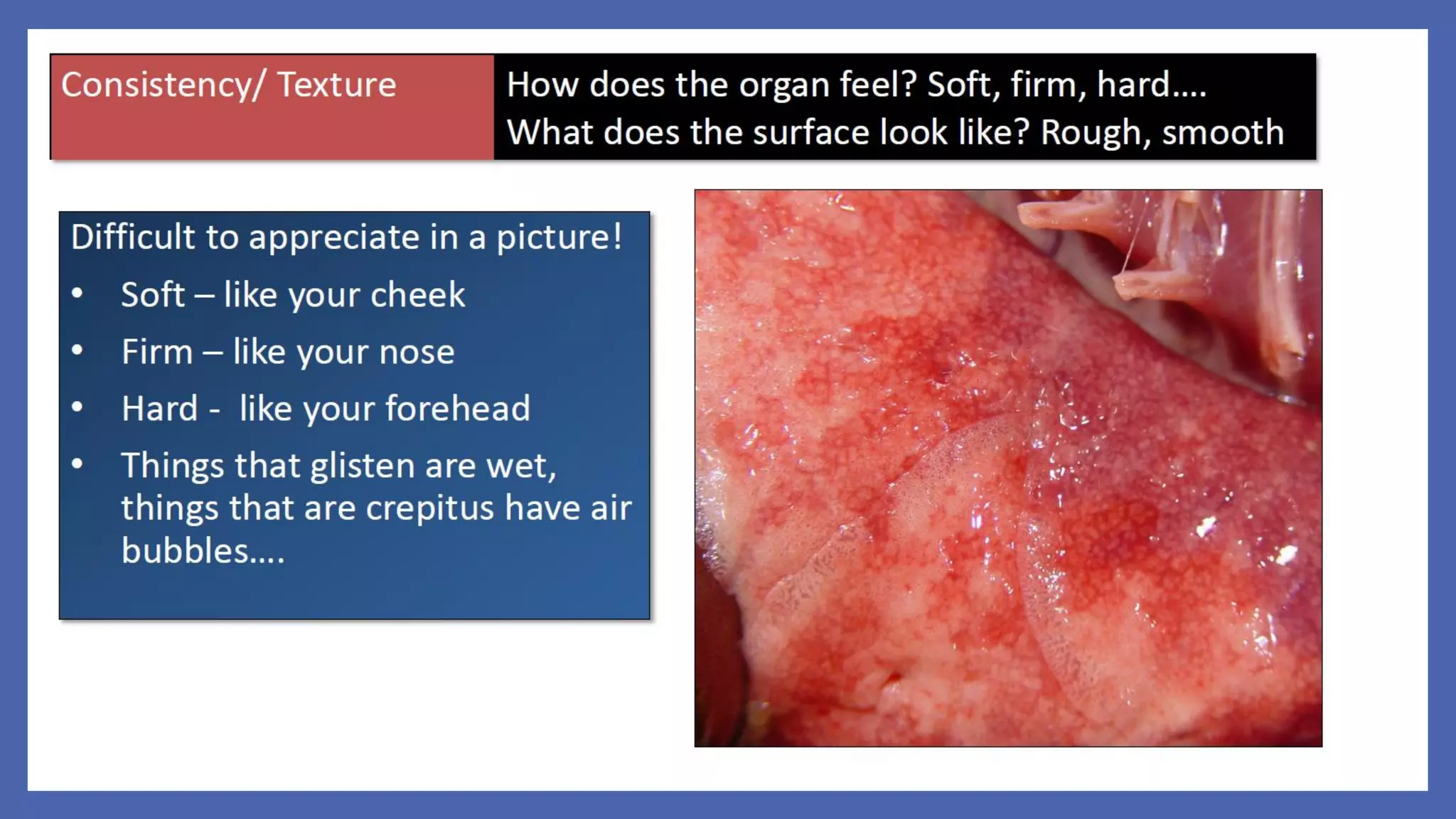
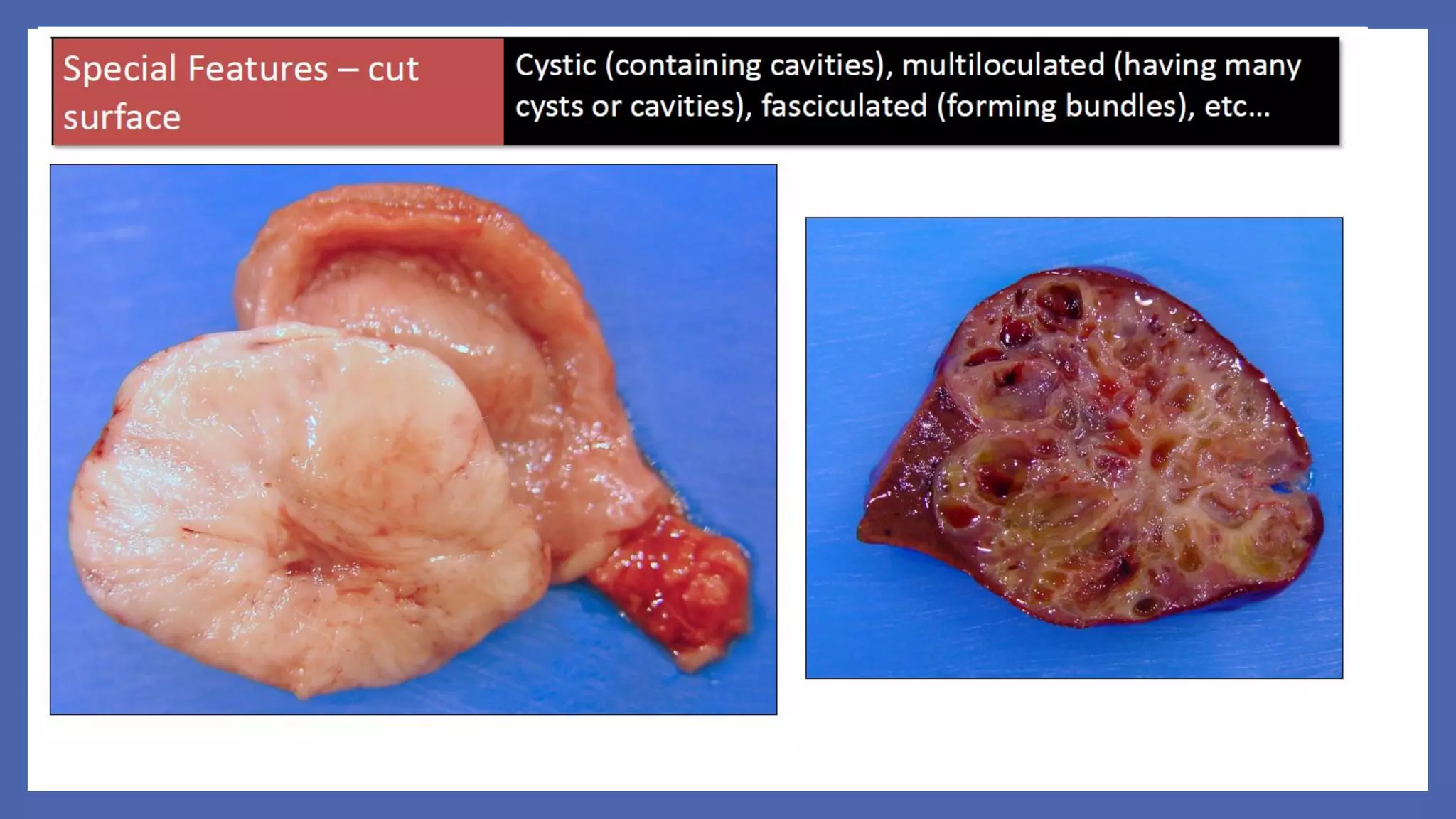
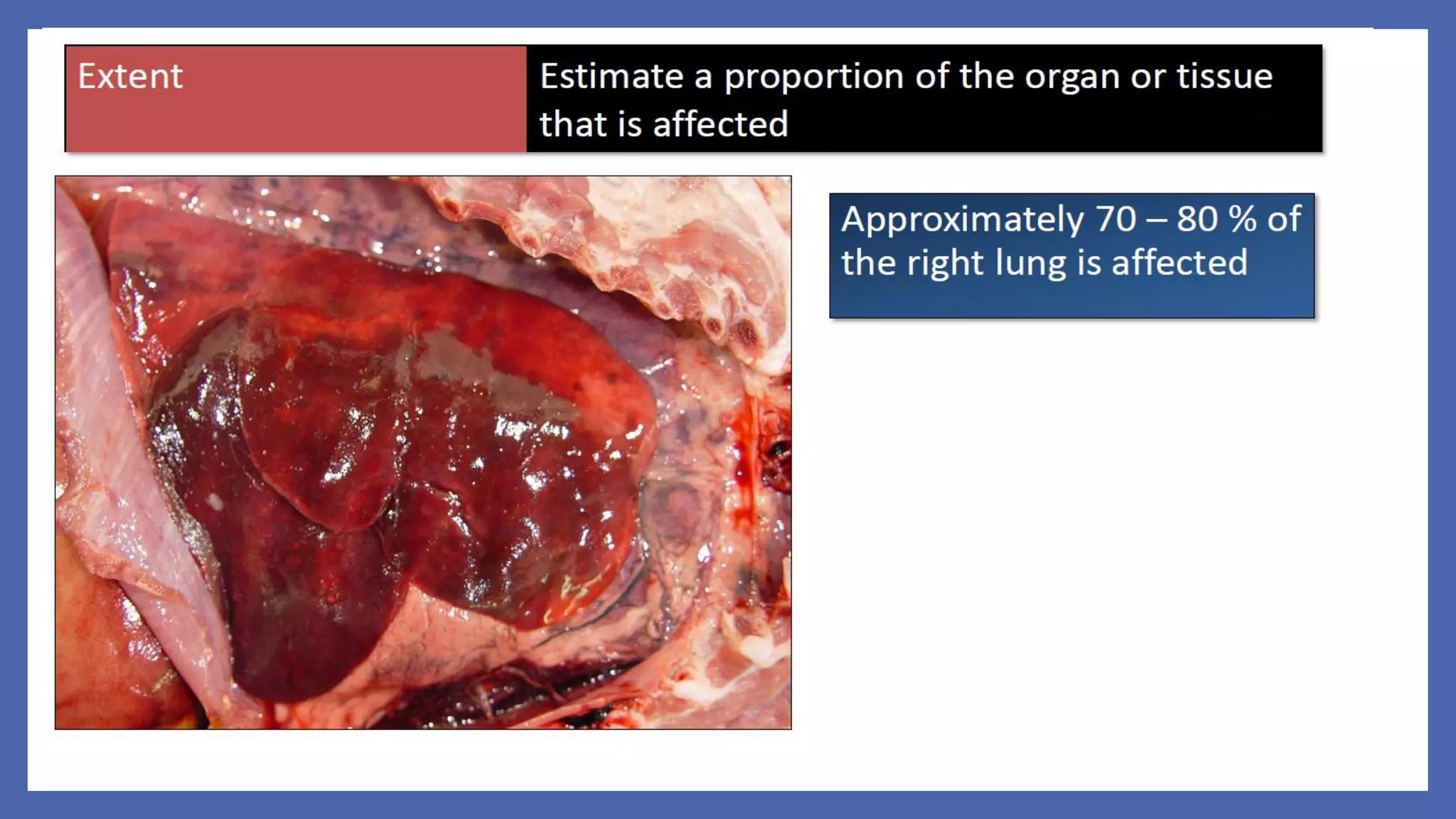
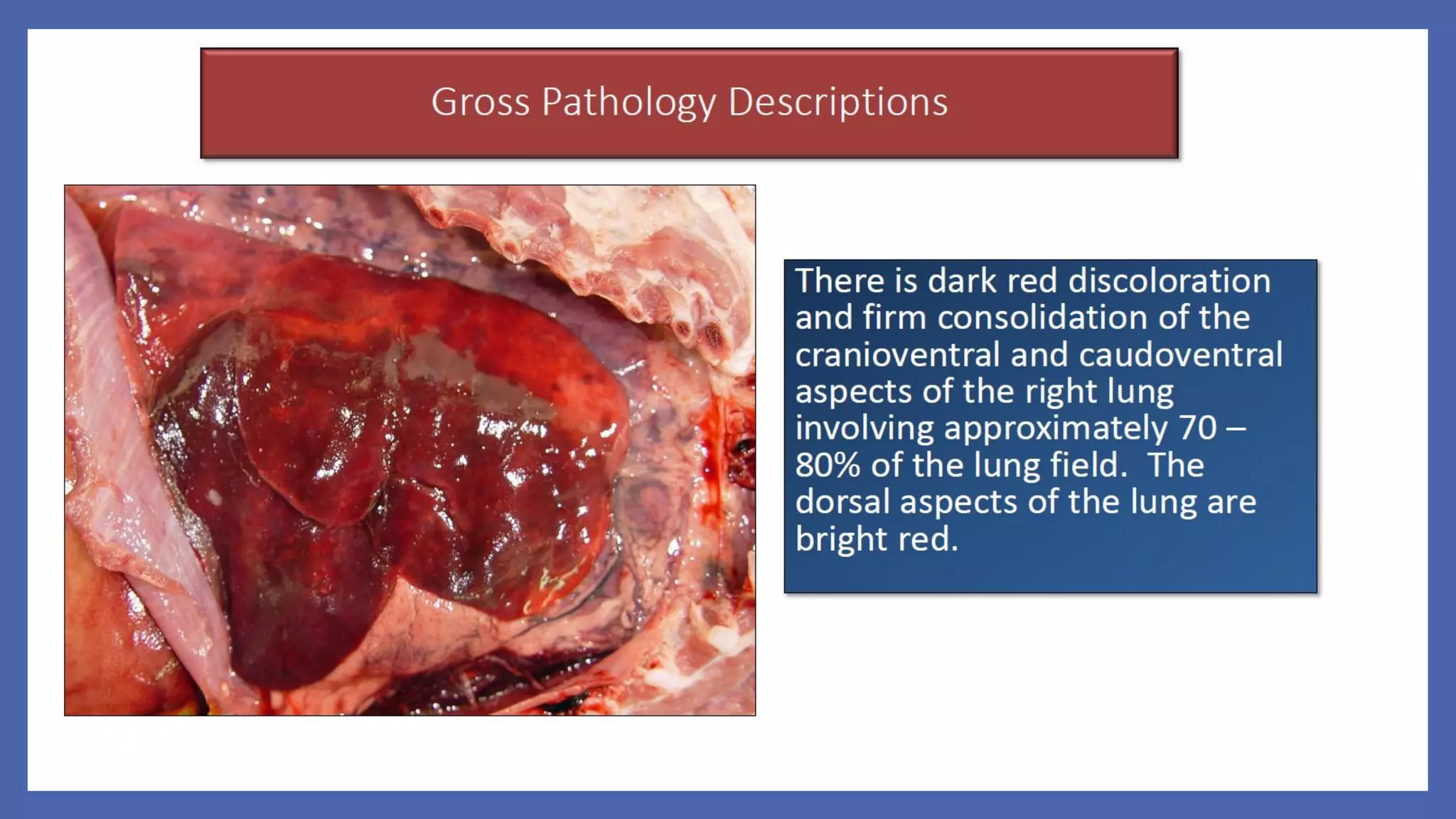
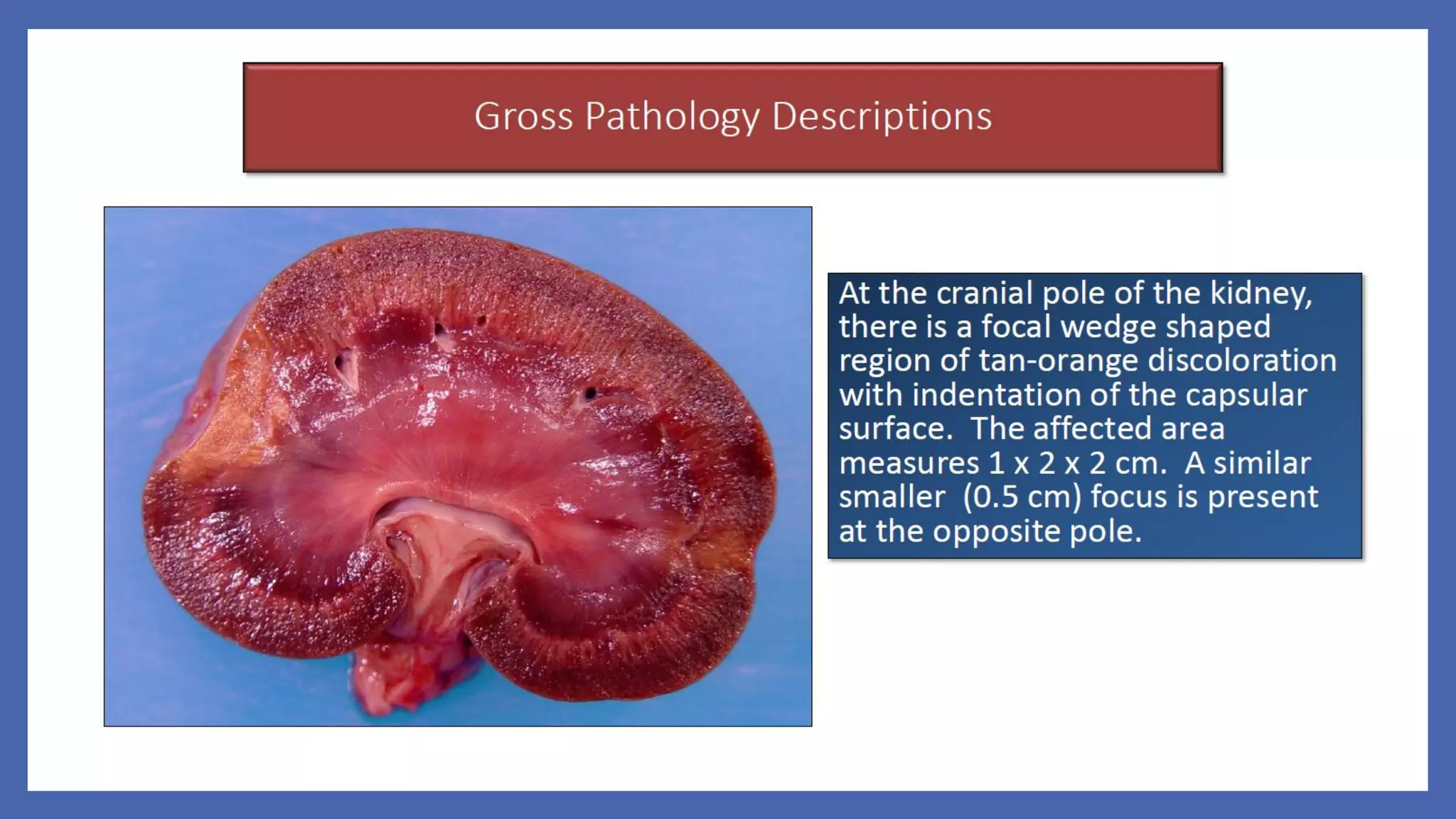
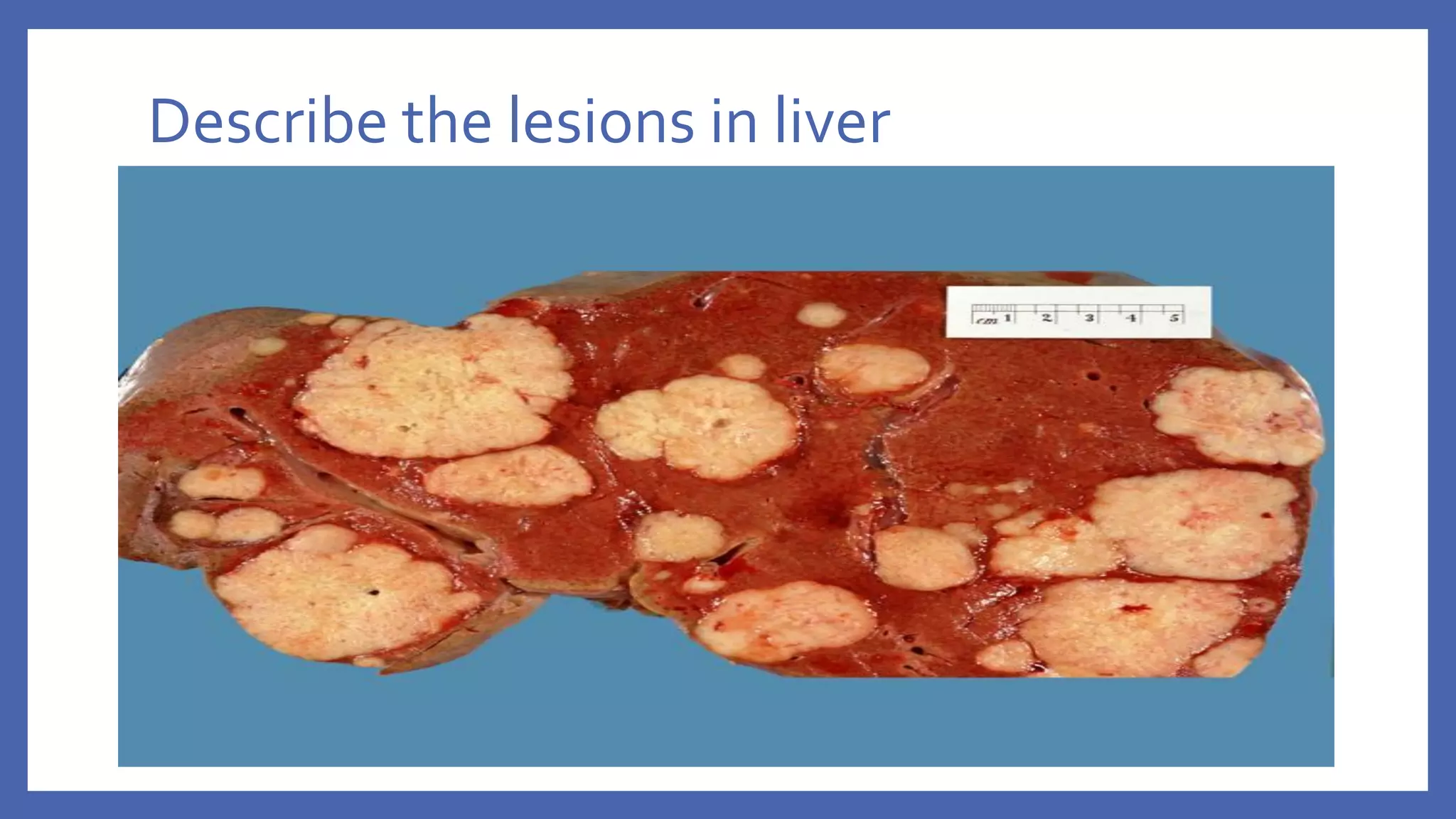
The document outlines the learning outcomes for a veterinary pathology lecture, focusing on defining pathology, general pathology, and abnormal morphological changes in tissues. It highlights the significance of understanding disease processes and various aspects of pathology including clinical and systemic pathology. The lecture emphasizes the importance of gross and microscopic examination of lesions to improve diagnosis and treatment in veterinary medicine.