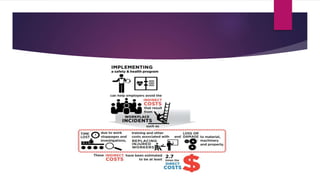
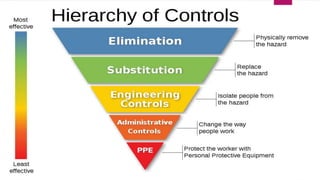
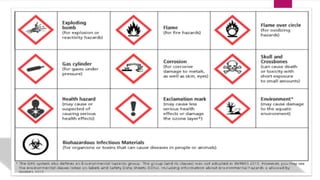
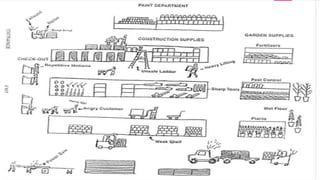
The document outlines essential information regarding OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and workers' rights to a safe workplace. It highlights employers' responsibilities to maintain hazard-free working conditions and details specific rights for workers, including the ability to request inspections and report hazards. Additionally, the document discusses methods for reducing workplace hazards and the importance of collective action in addressing safety concerns.