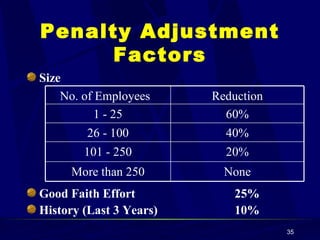
OSHA was created in 1970 to ensure safe and healthful working conditions. It aims to prevent work-related injuries, illnesses, and deaths. OSHA sets and enforces standards and provides compliance assistance through inspections, citations, and penalties. It covers most private sector employers and some public sector employers. OSHA standards address hazards in various industries and a general duty to provide hazard-free workplaces.