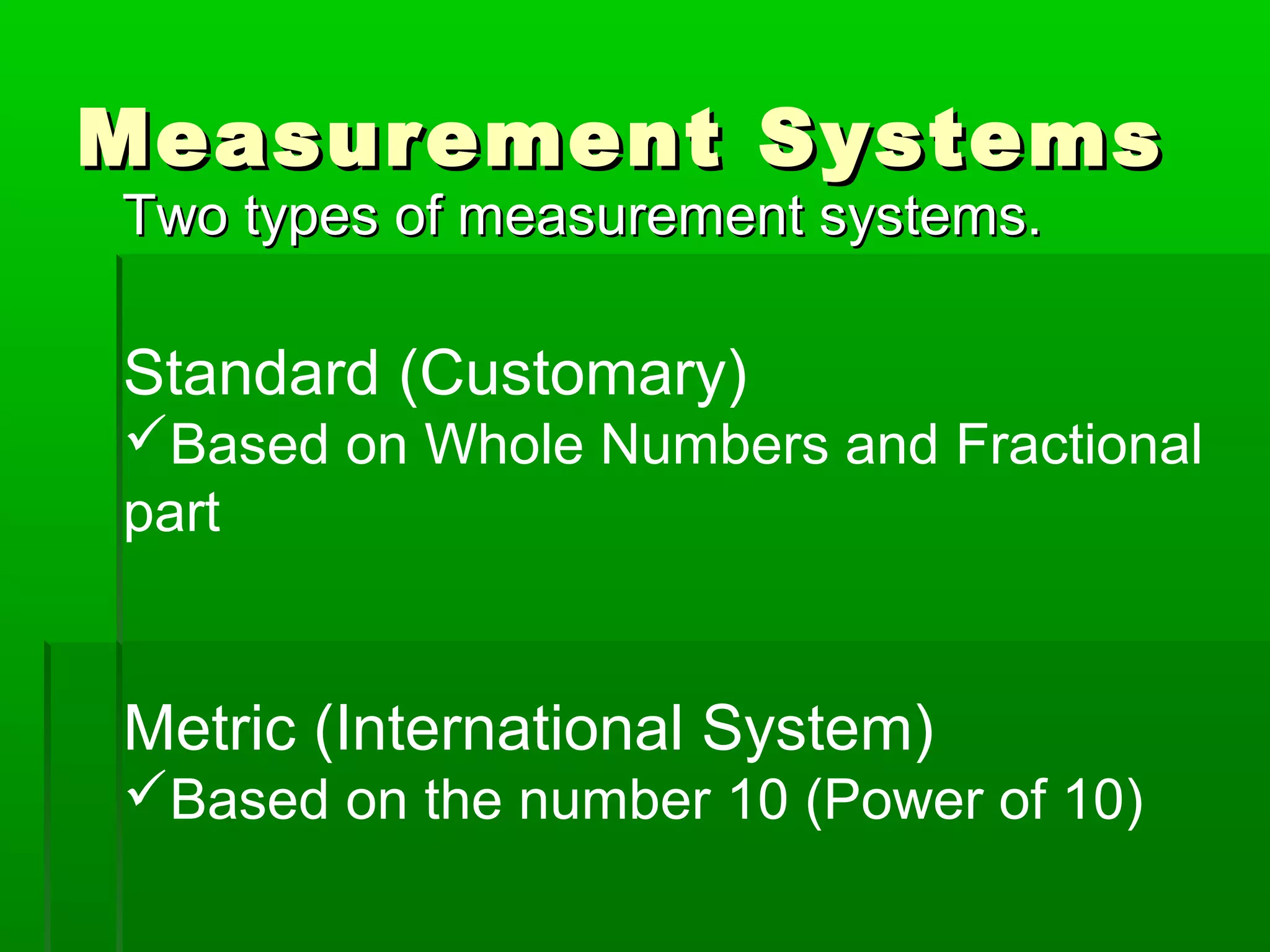
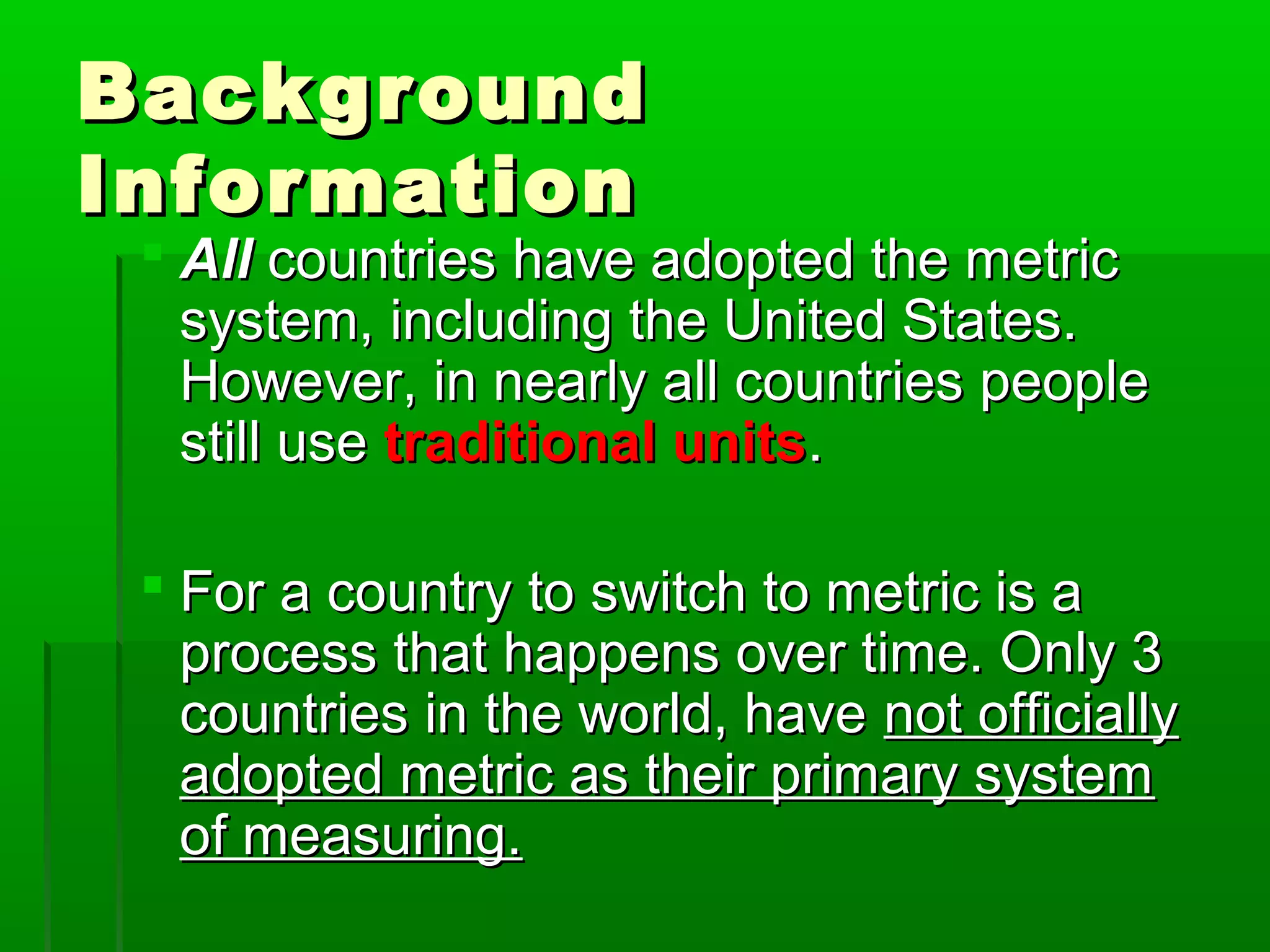
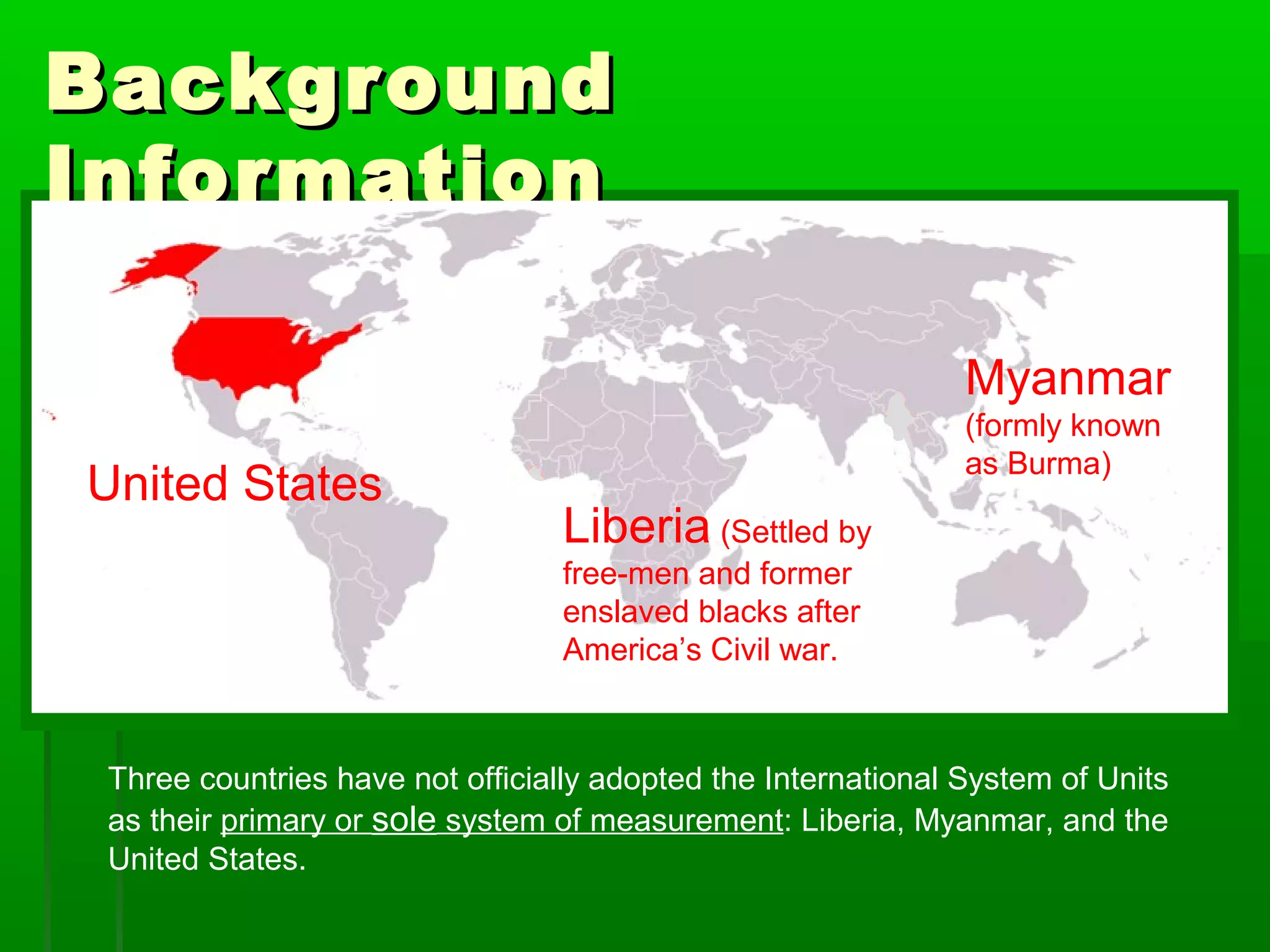
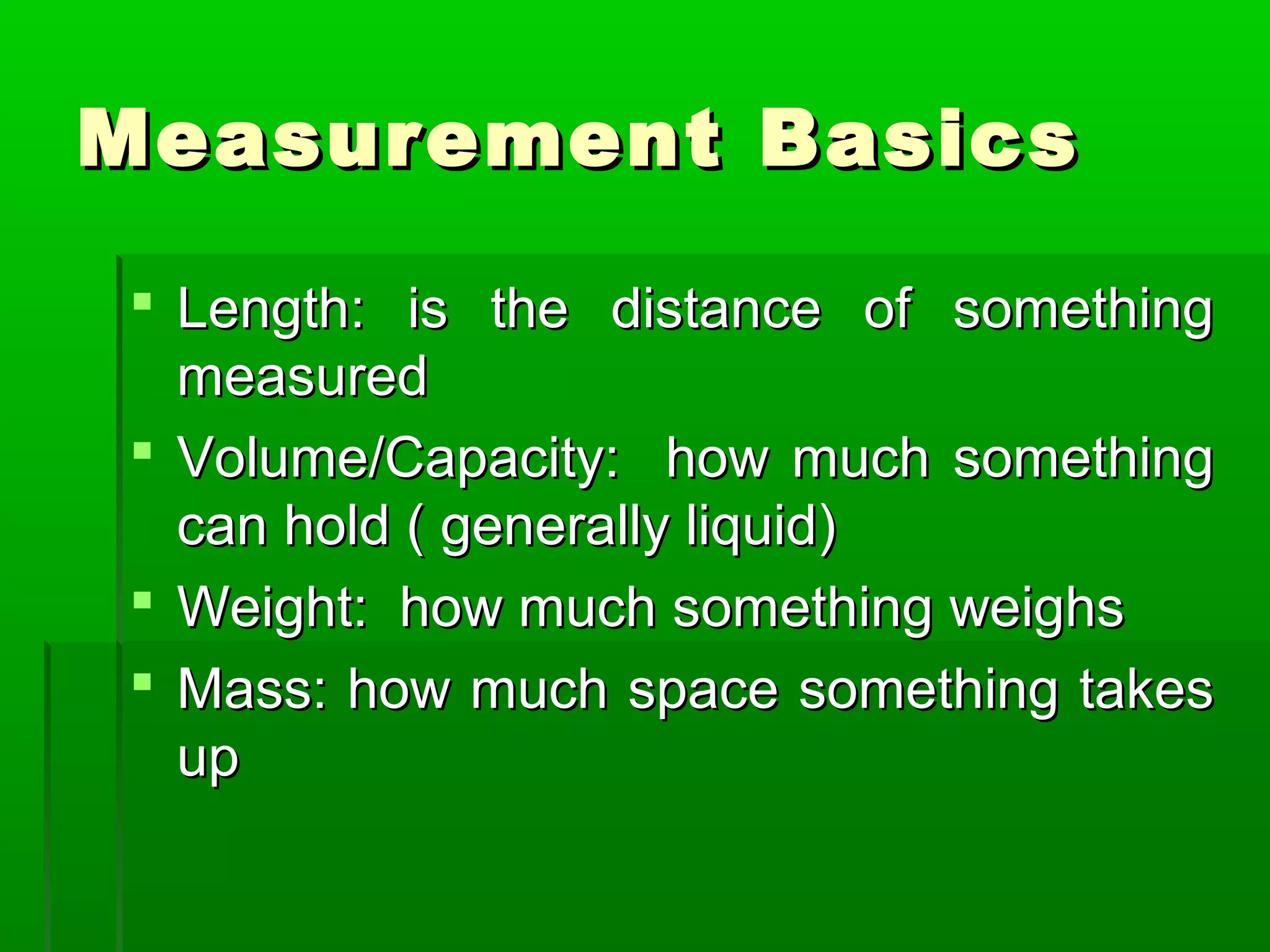
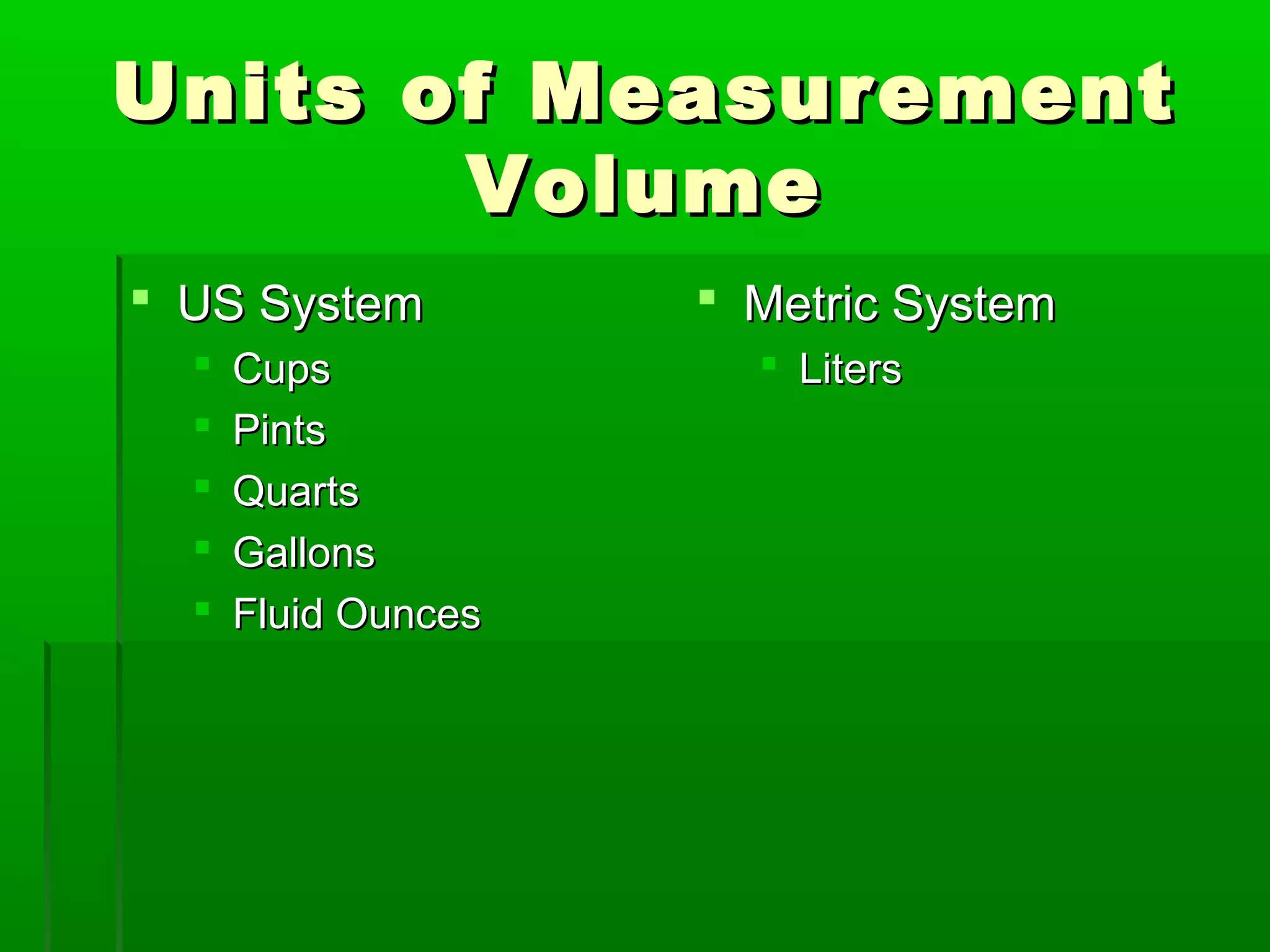
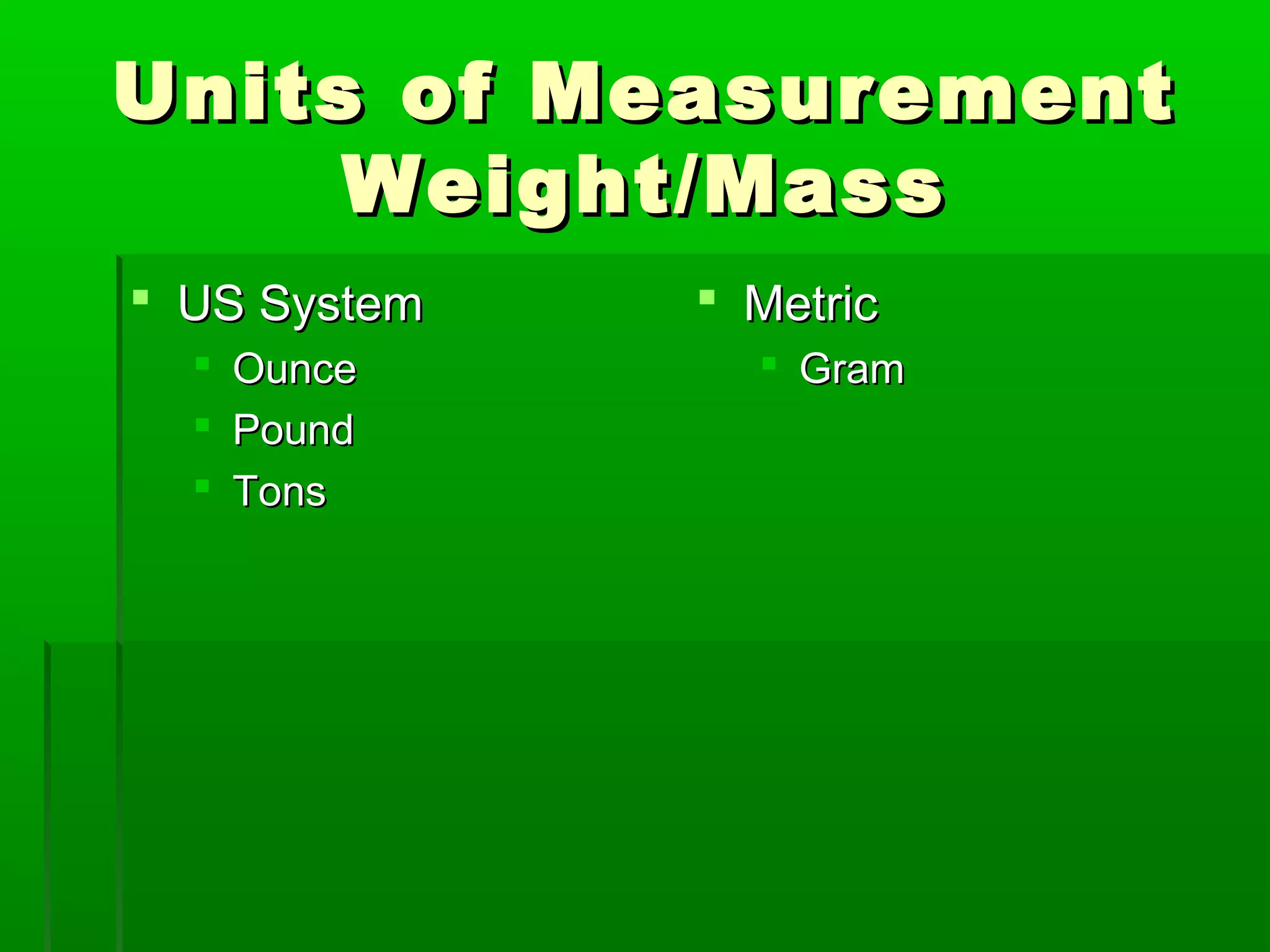
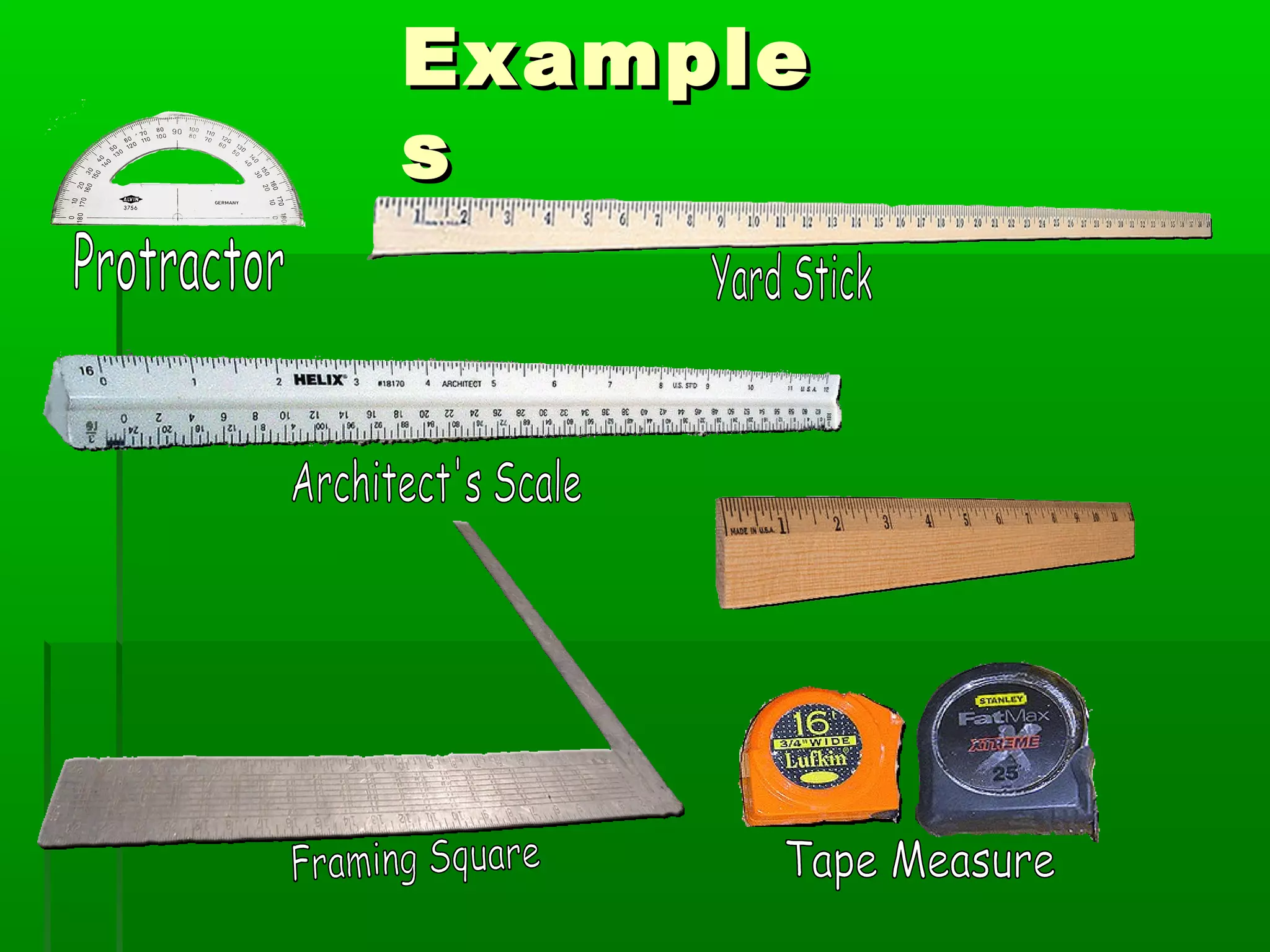
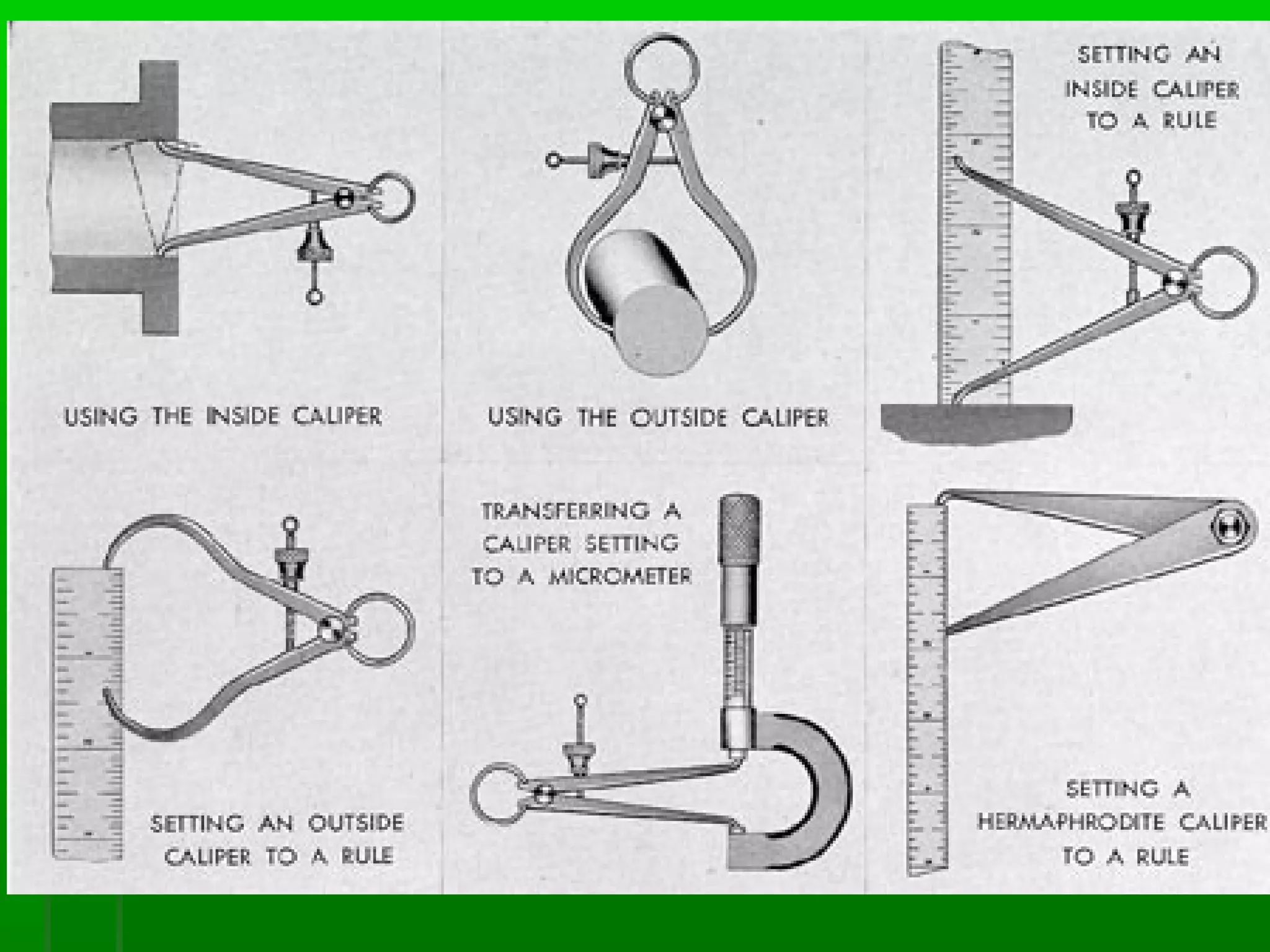
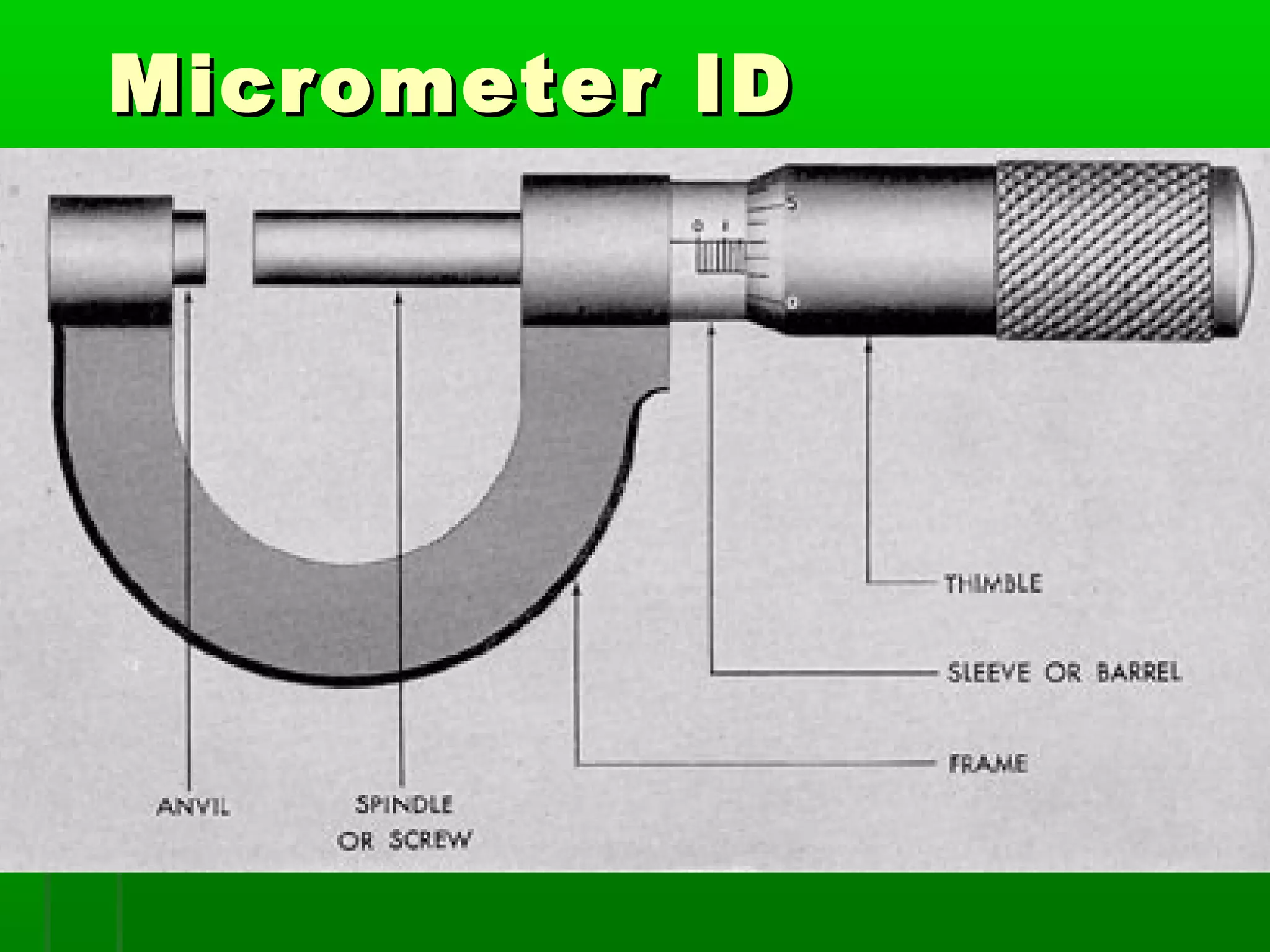
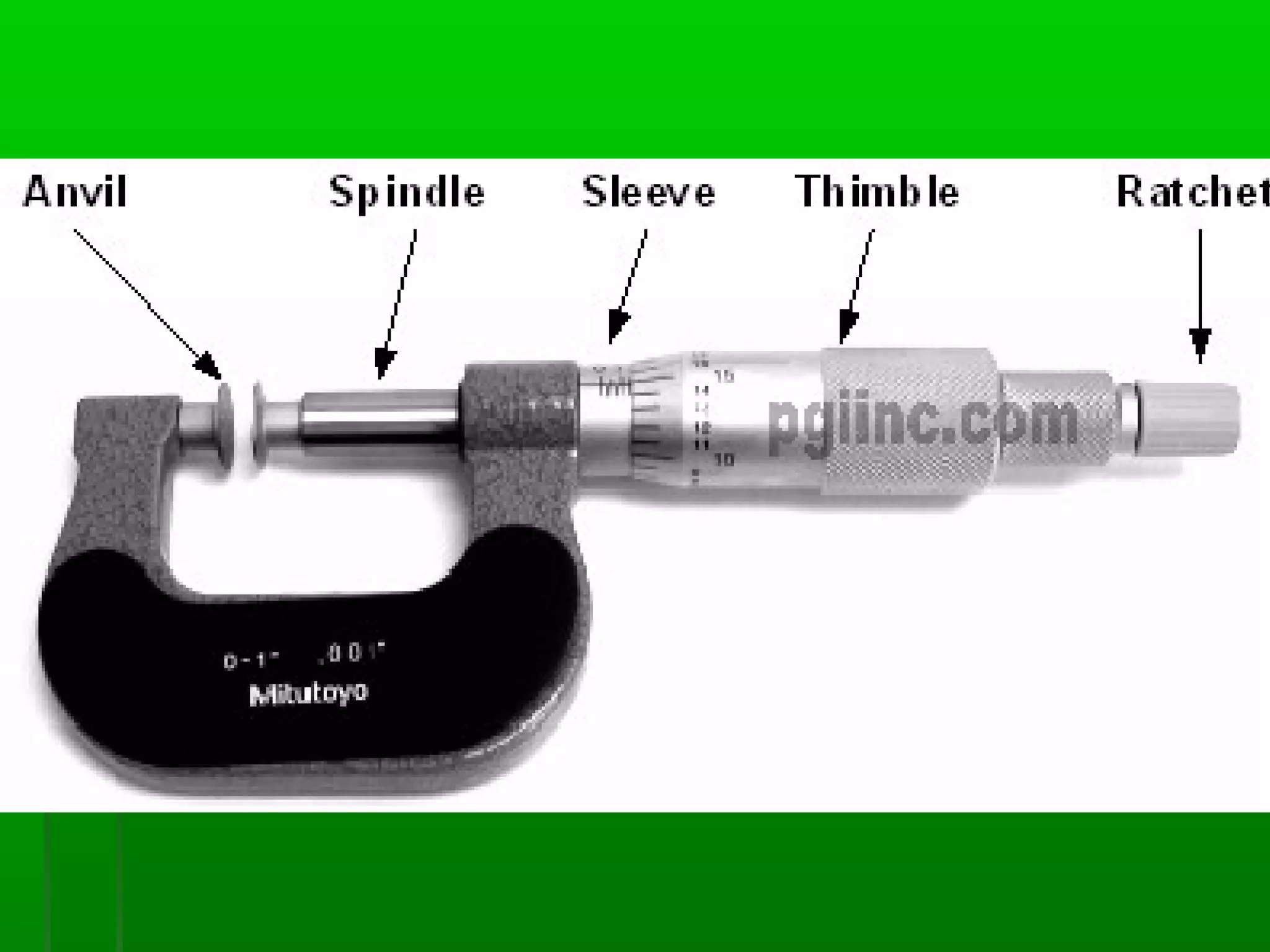
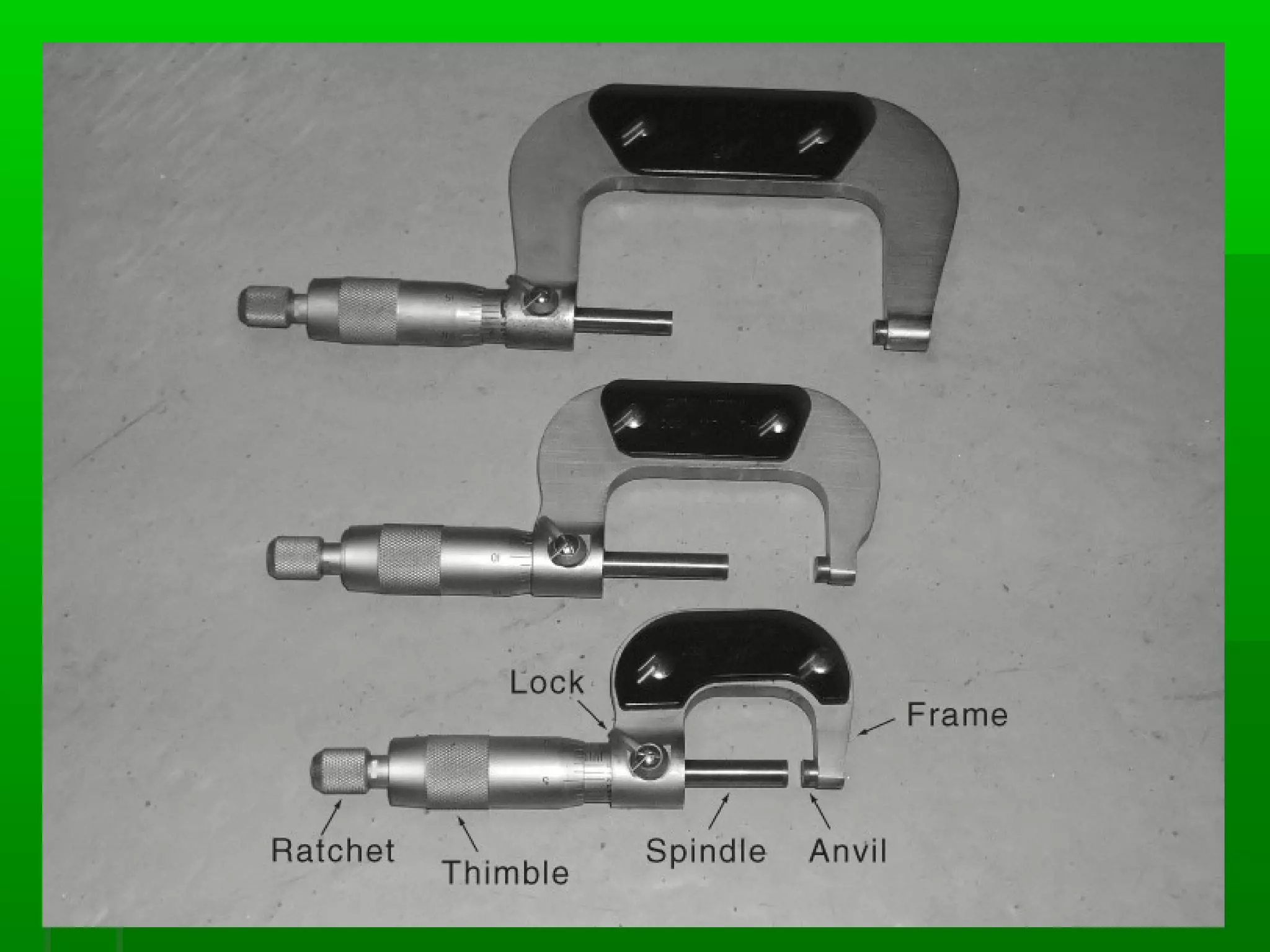
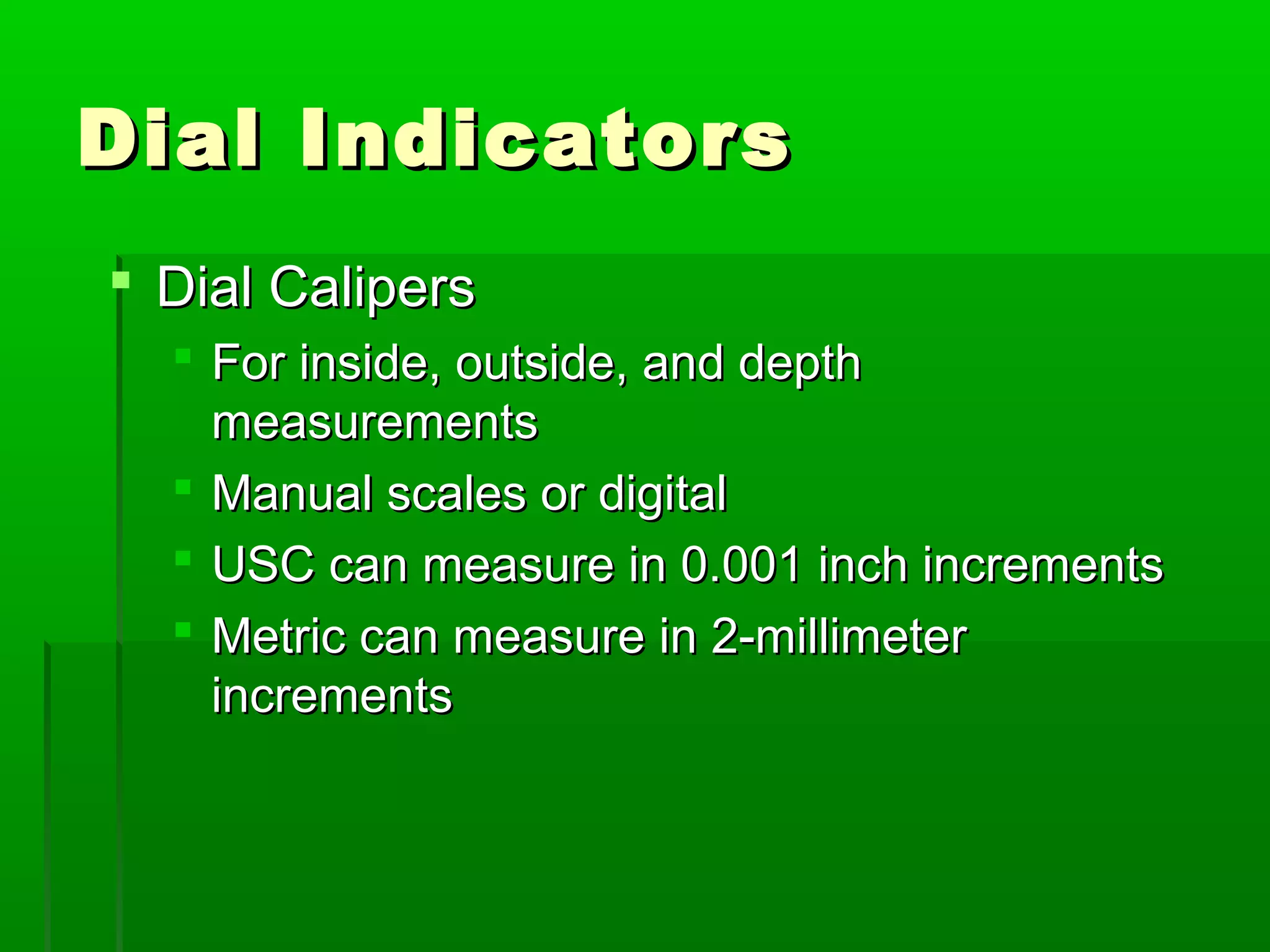
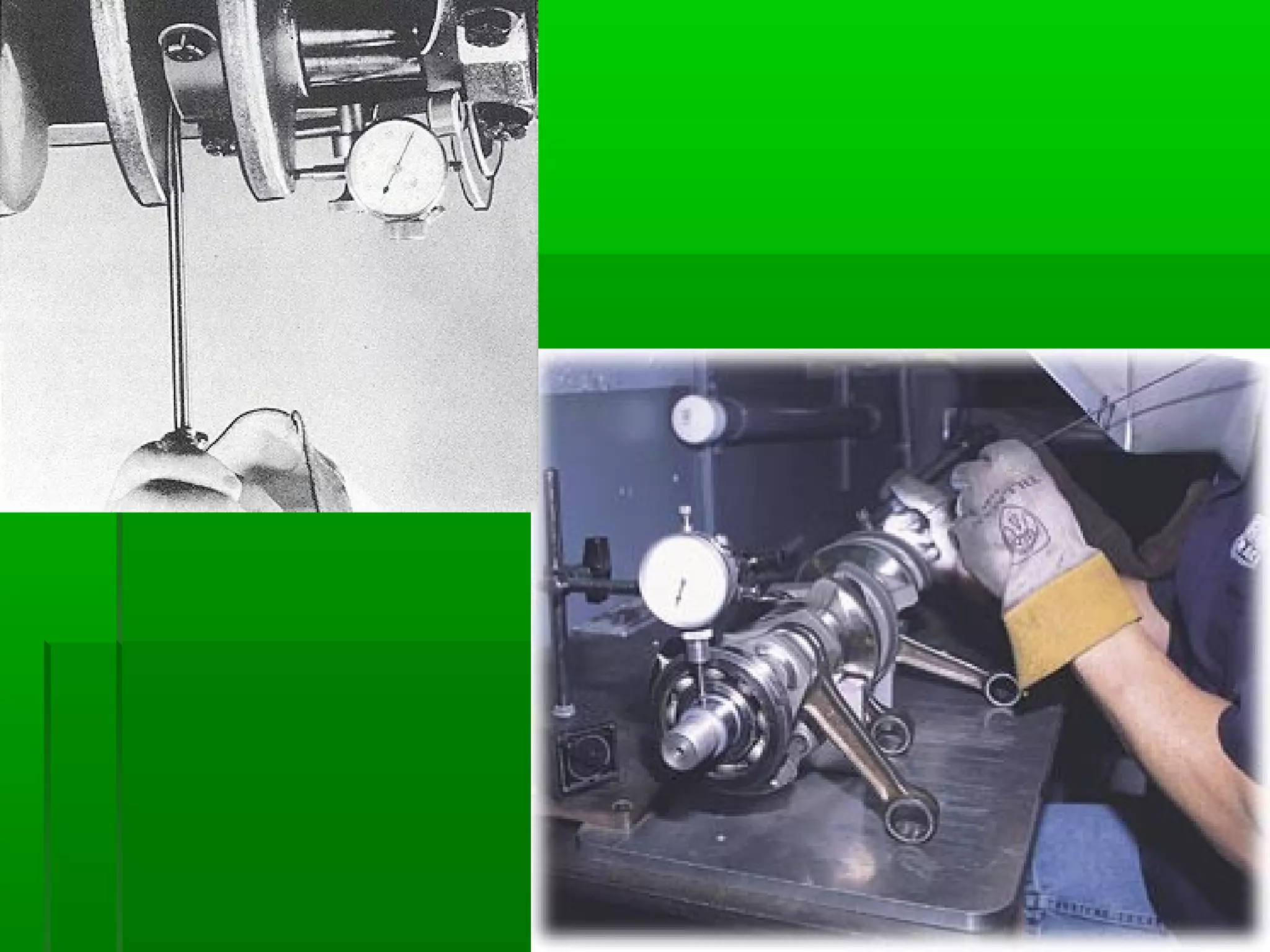
The document provides information on different measurement systems and tools used for measurement. It discusses the two primary systems - the US Customary system and the metric system. The metric system is based on powers of 10 and is used globally, while the US Customary system uses various unrelated units. The document then describes various tools for measuring length, volume, weight, and other quantities like rulers, tape measures, calipers, micrometers, gauges, and indicators.