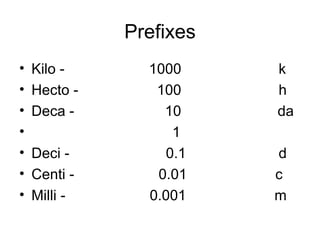
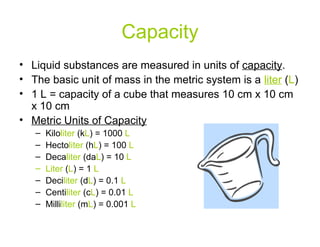
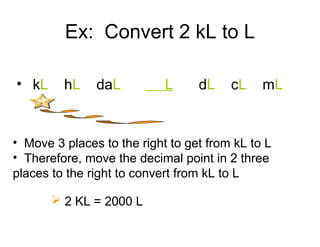
The document discusses the metric system of measurement. It explains that the metric system is based on a base unit and prefixes that are used to denote powers of ten. It provides the prefixes for the metric system and gives the base units and conversions for length, mass, and capacity. Examples are given for converting between metric units by moving the decimal point right or left based on the prefixes.