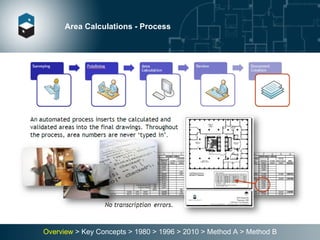
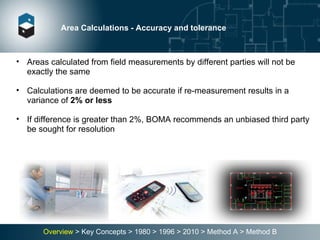
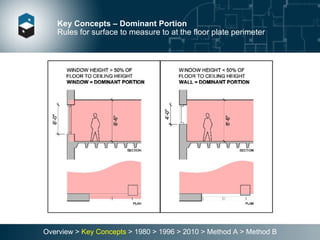
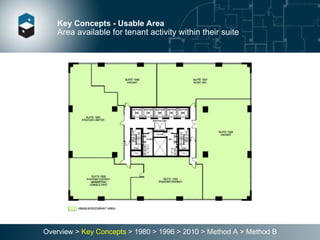
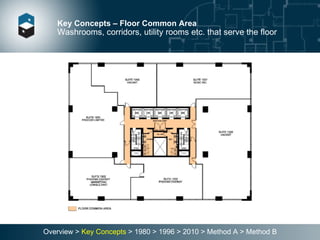
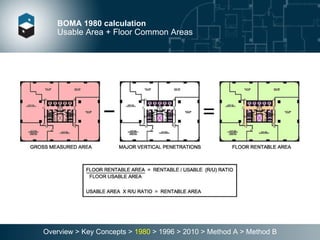
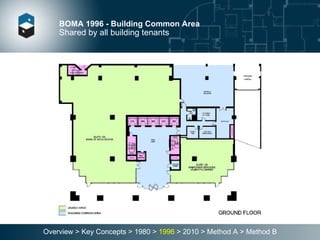
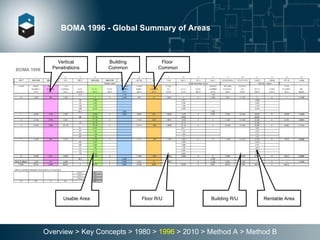
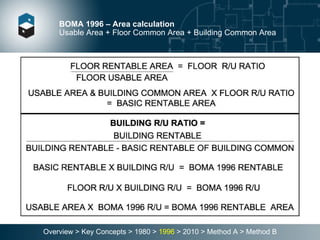
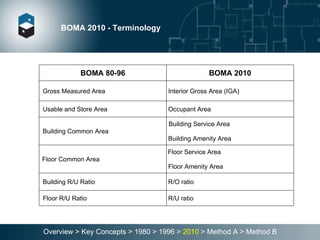
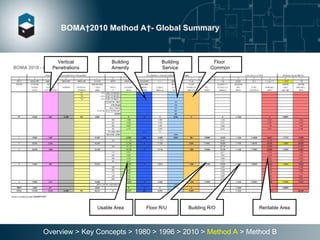
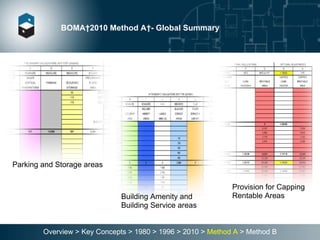
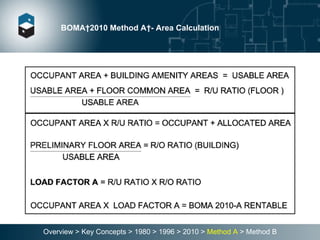
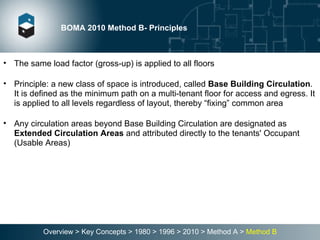
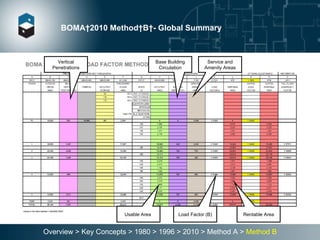
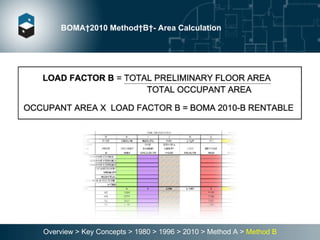
The document summarizes the Building Owners and Managers Association (BOMA) standards for measuring office building space over multiple revisions from 1980 to 2010. The 1980 standard calculated rentable area as usable area plus floor common areas. The 1996 standard added building common areas distributed to all tenants. The 2010 standard offers two methods - Method A is similar to 1996, while Method B applies a single gross-up ratio to all floors by defining base building circulation assigned to each floor.