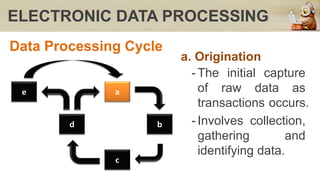
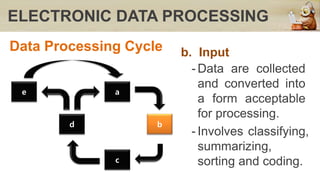
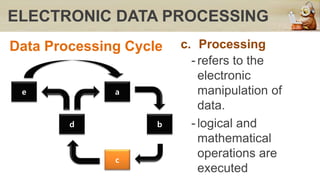
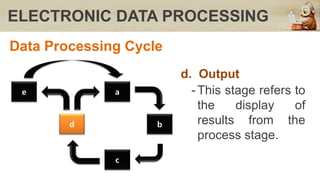
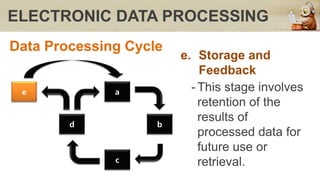
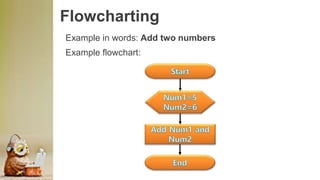
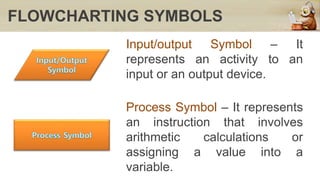
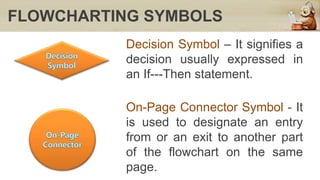
This document discusses computers in daily life and electronic data processing. It begins by stating the objectives of understanding data processing principles, computer system elements, algorithms, and flowchart creation. It then defines electronic data processing as utilizing computers for processing data. It distinguishes between data and information, and describes the five stages of the data processing cycle: origination, input, processing, output, and storage and feedback. The document concludes by explaining what a flowchart is, providing an example, and listing the basic flowchart symbols used to represent elements like terminal, input/output, decision, and flowlines.