Embed presentation
Downloaded 80 times









Eclipse is an integrated development environment used primarily for Java development. It contains components like an editor, compiler, and plugins for additional functionality. Eclipse loads plugins like the workbench graphical user interface and manages resources for projects. Users can work with Eclipse by creating Java projects and classes, writing and refactoring code, importing and exporting projects, and using features like CVS integration.
Basic introduction to the presentation.
Eclipse is an IDE with Java Development Tools, a compiler, and various plugins, and is open source.
Requirements to install Eclipse include the Eclipse installer, Java Development Kit (JDK), and Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
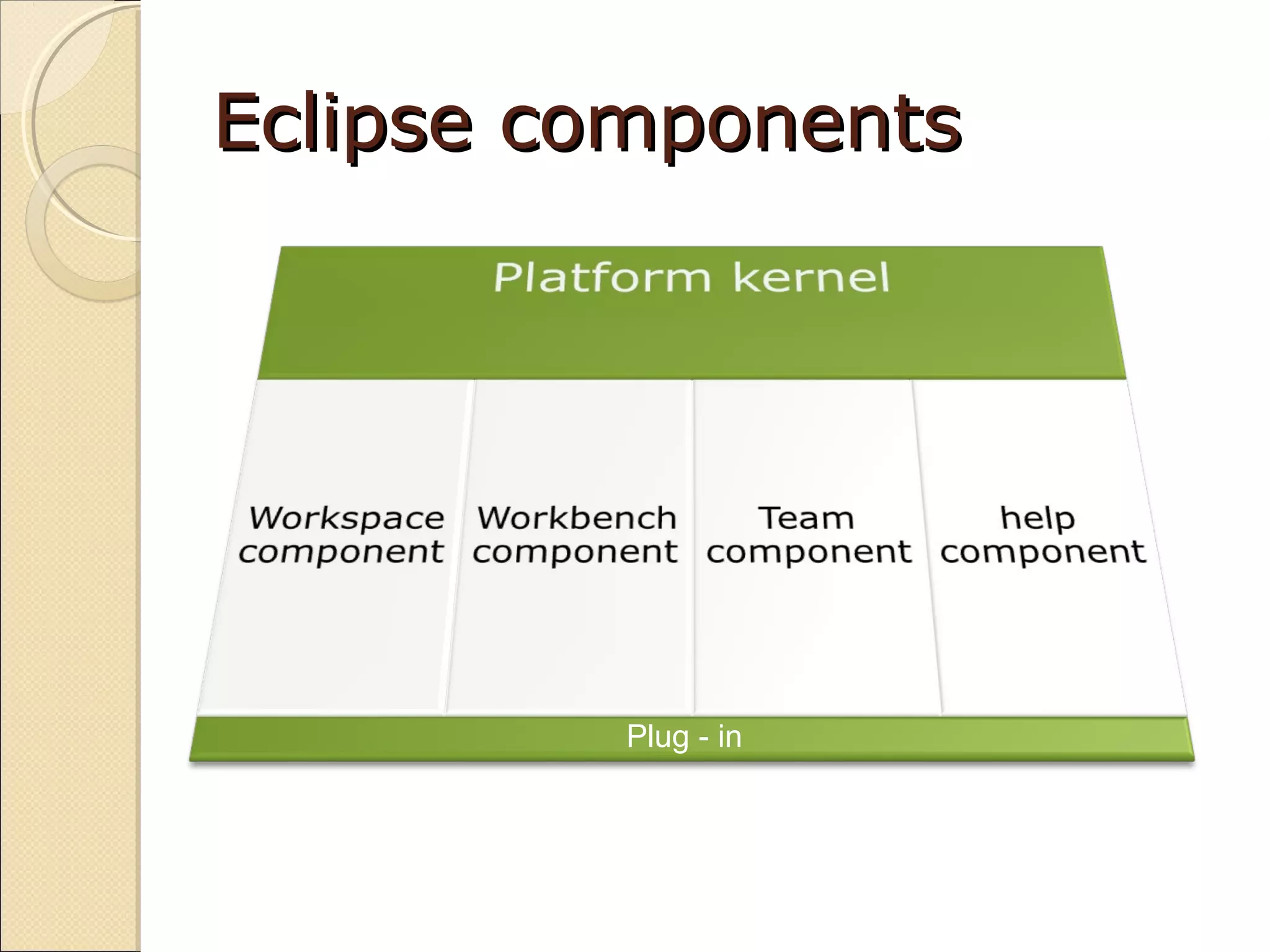
Overview of Eclipse components concerning plug-ins.
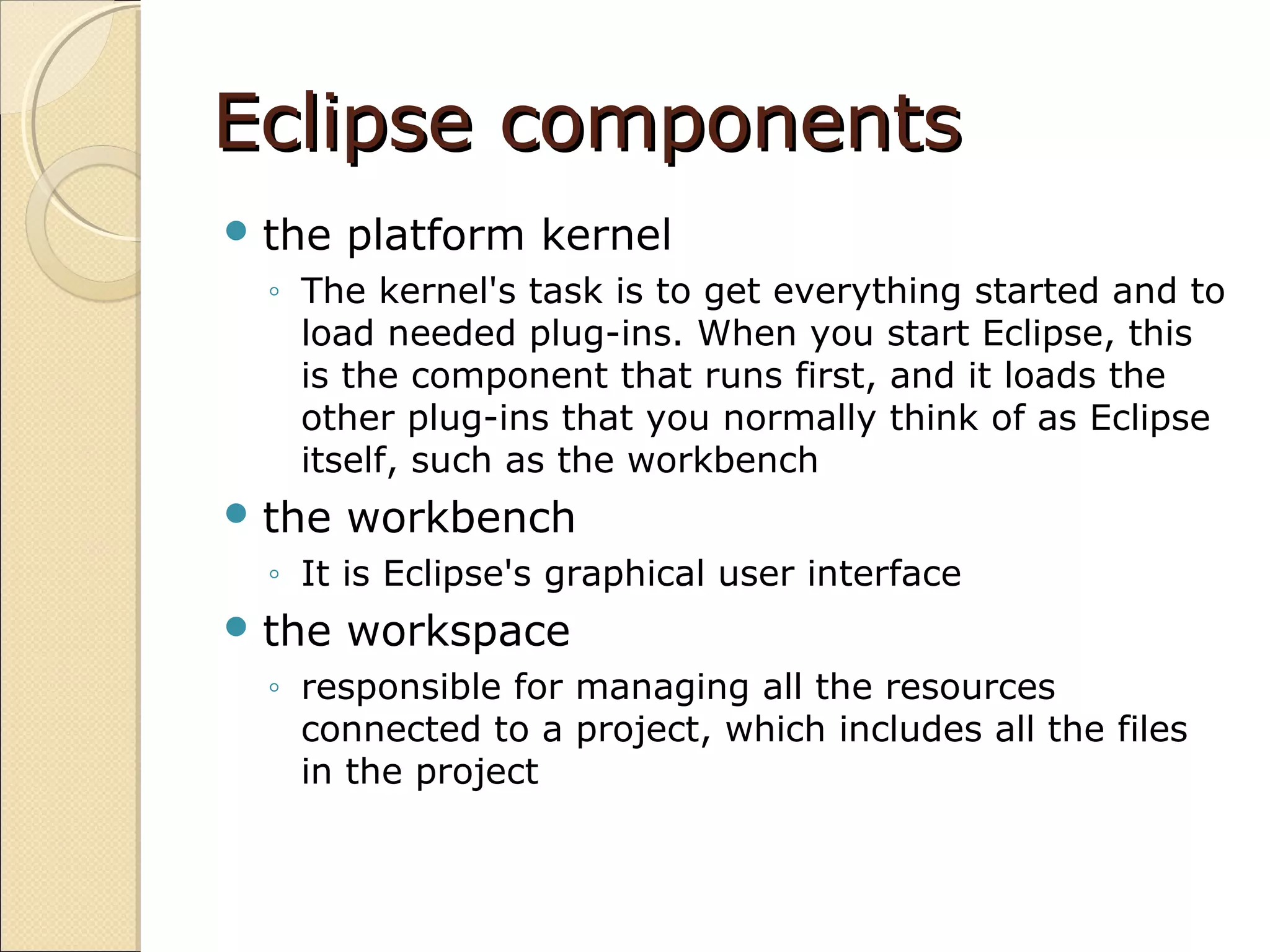
The kernel, workbench, and workspace manage resource management and UI for Eclipse.
Features like the team component for versioning and the help component for user assistance.
Guidance on how to access and select views in Eclipse.
Setting up a workspace, creating/deleting projects and Java classes, and writing code.
Creating, overwriting methods, managing JRE selection, refactoring, and customizing code.
Managing CVS repositories, checking out, committing, updating, and synchronizing code.









