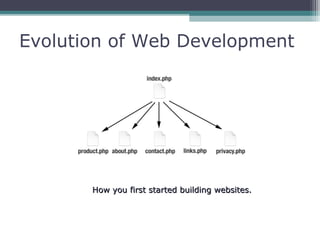
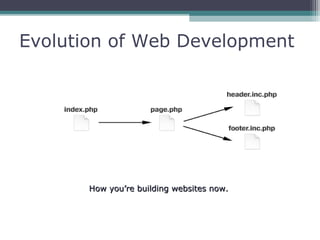
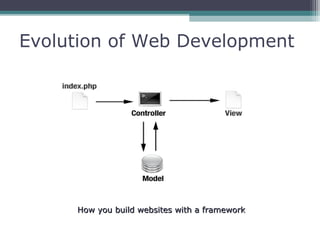
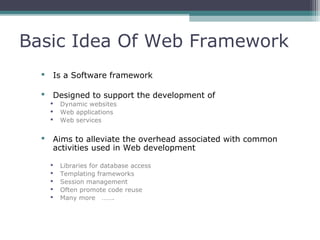
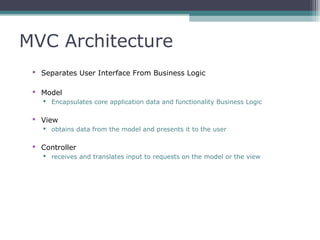
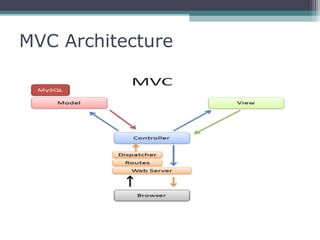
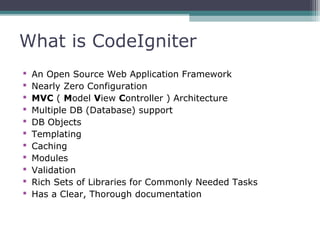
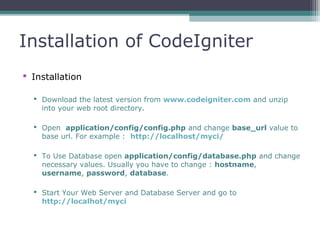
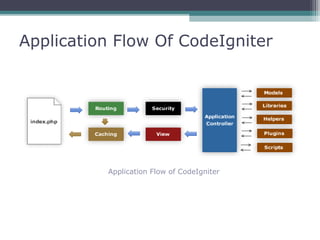
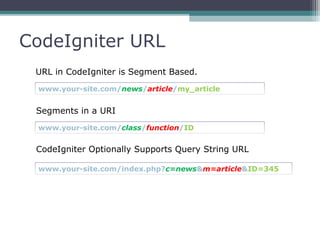
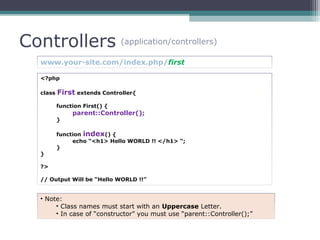
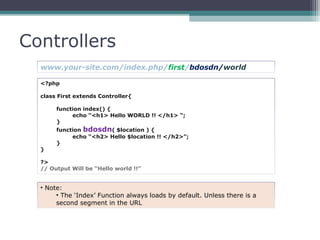
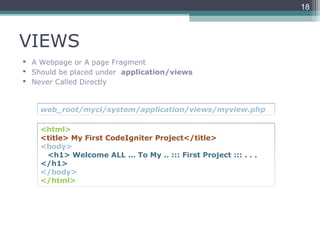
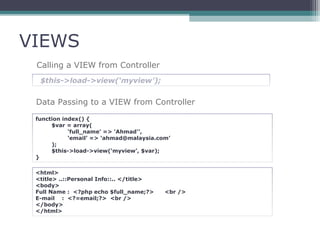
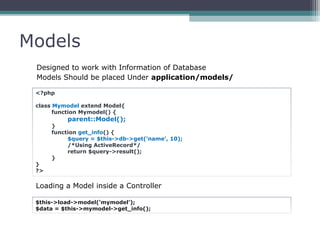
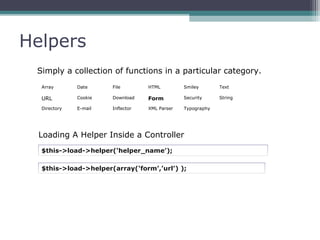
This document provides an introduction and overview of CodeIgniter, an open source PHP web application framework. It outlines the prerequisites of OOP, PHP and MySQL. It then covers the installation of CodeIgniter including Apache, PHP and MySQL. The core components of CodeIgniter are explained - the MVC architecture with Controllers, Views and Models. CodeIgniter libraries, helpers and the application flow are also summarized. Lastly, some example lab work topics are listed such as database selection, CRUD operations and file uploads.