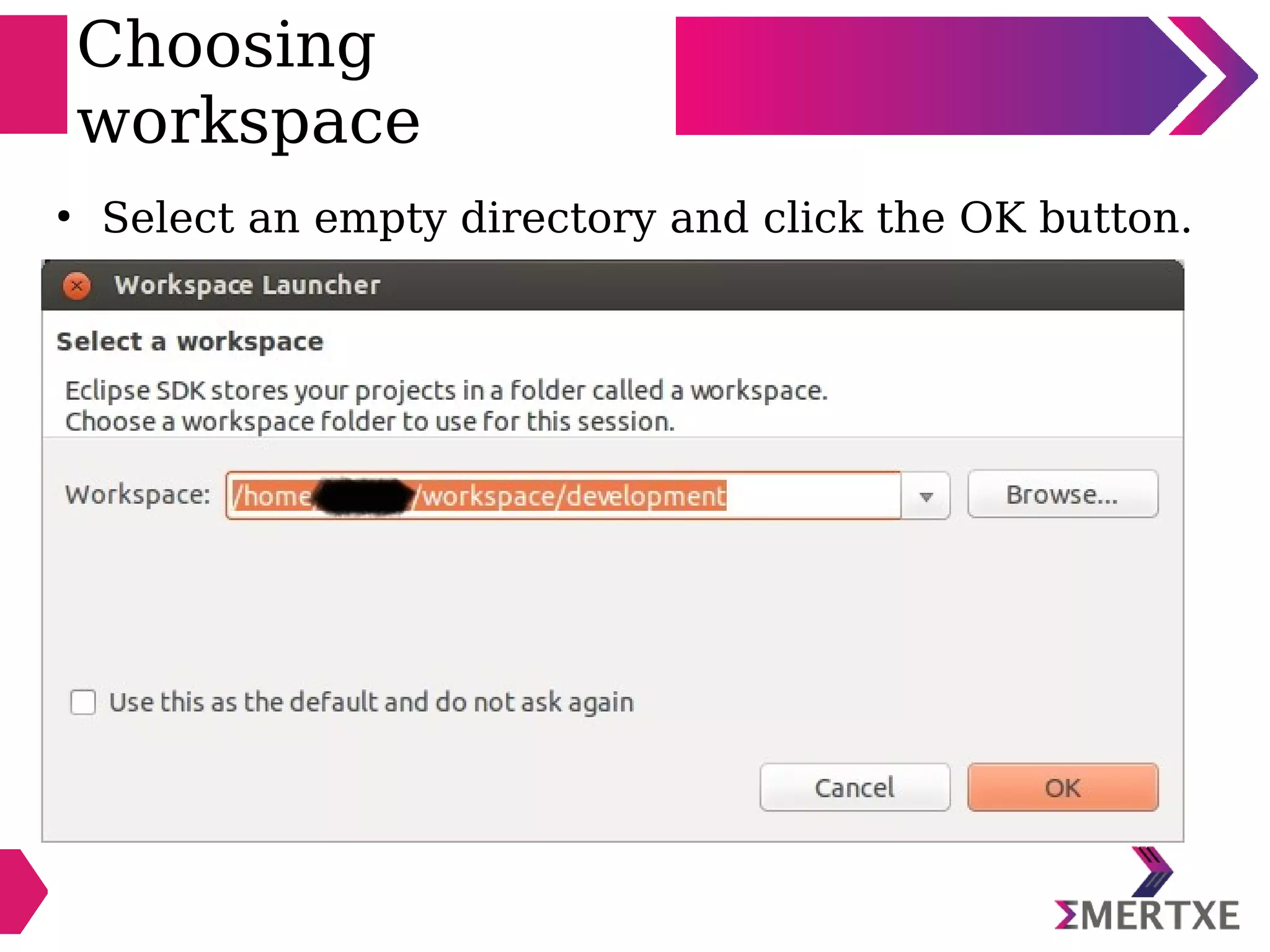
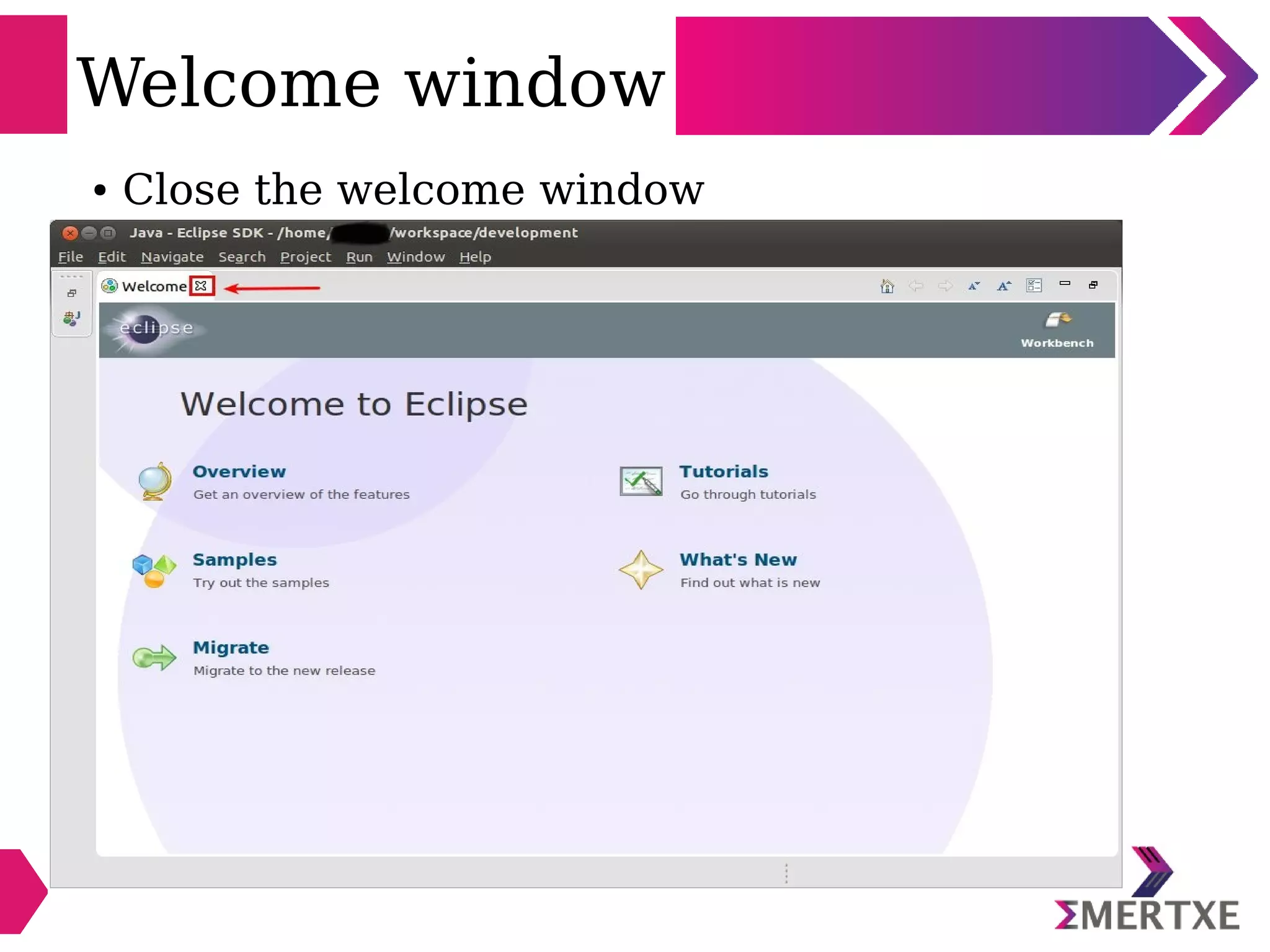
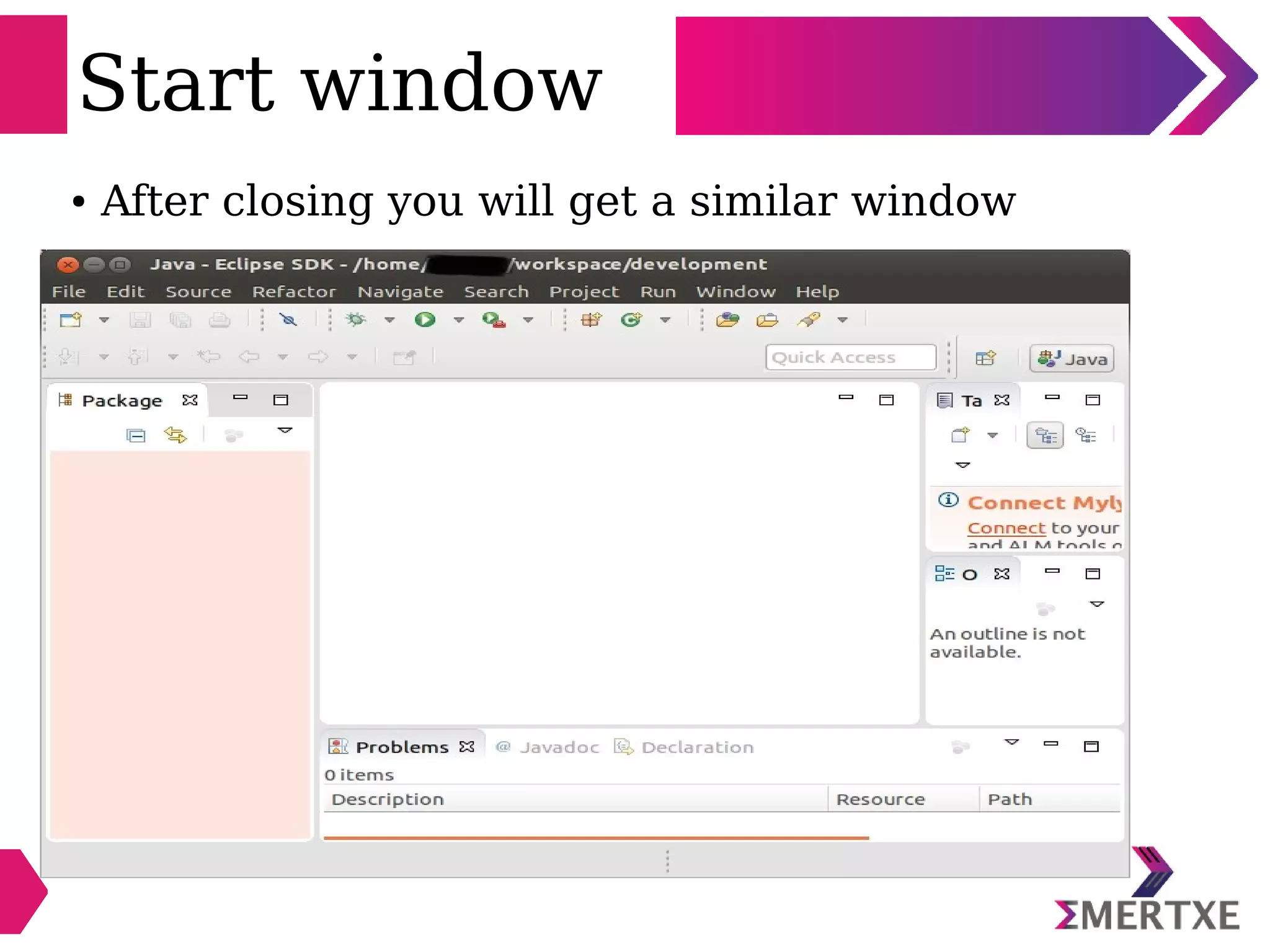
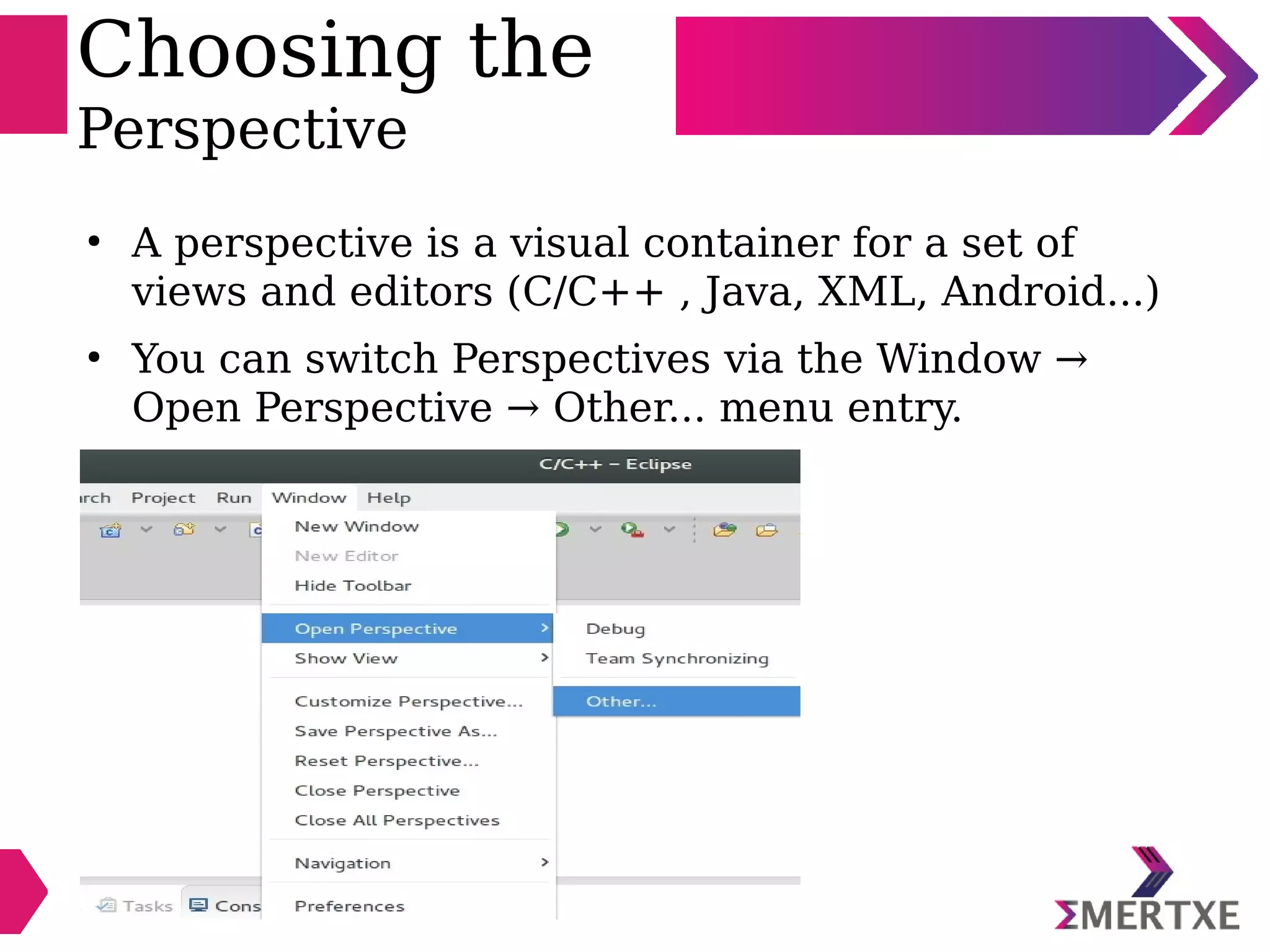
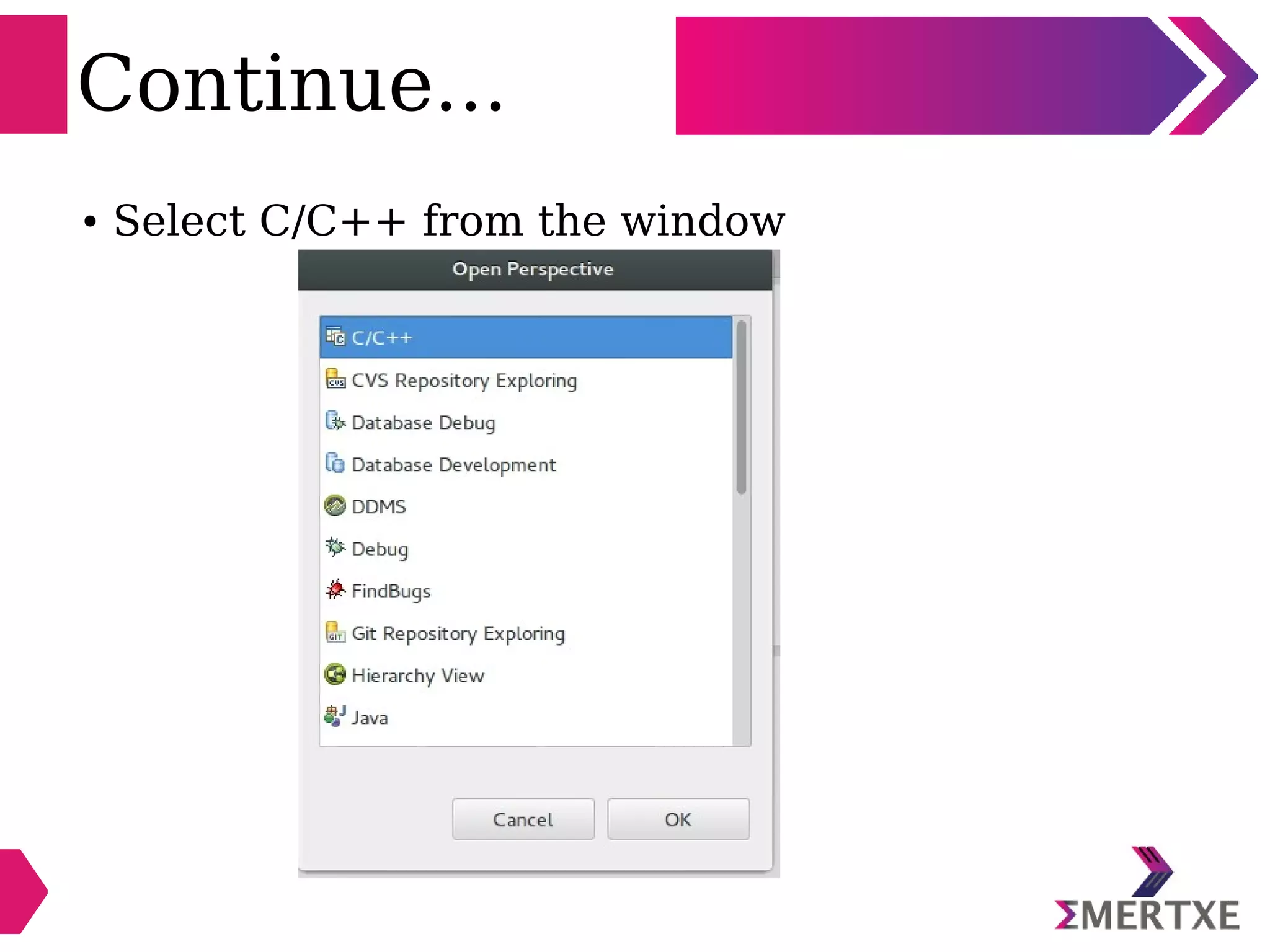
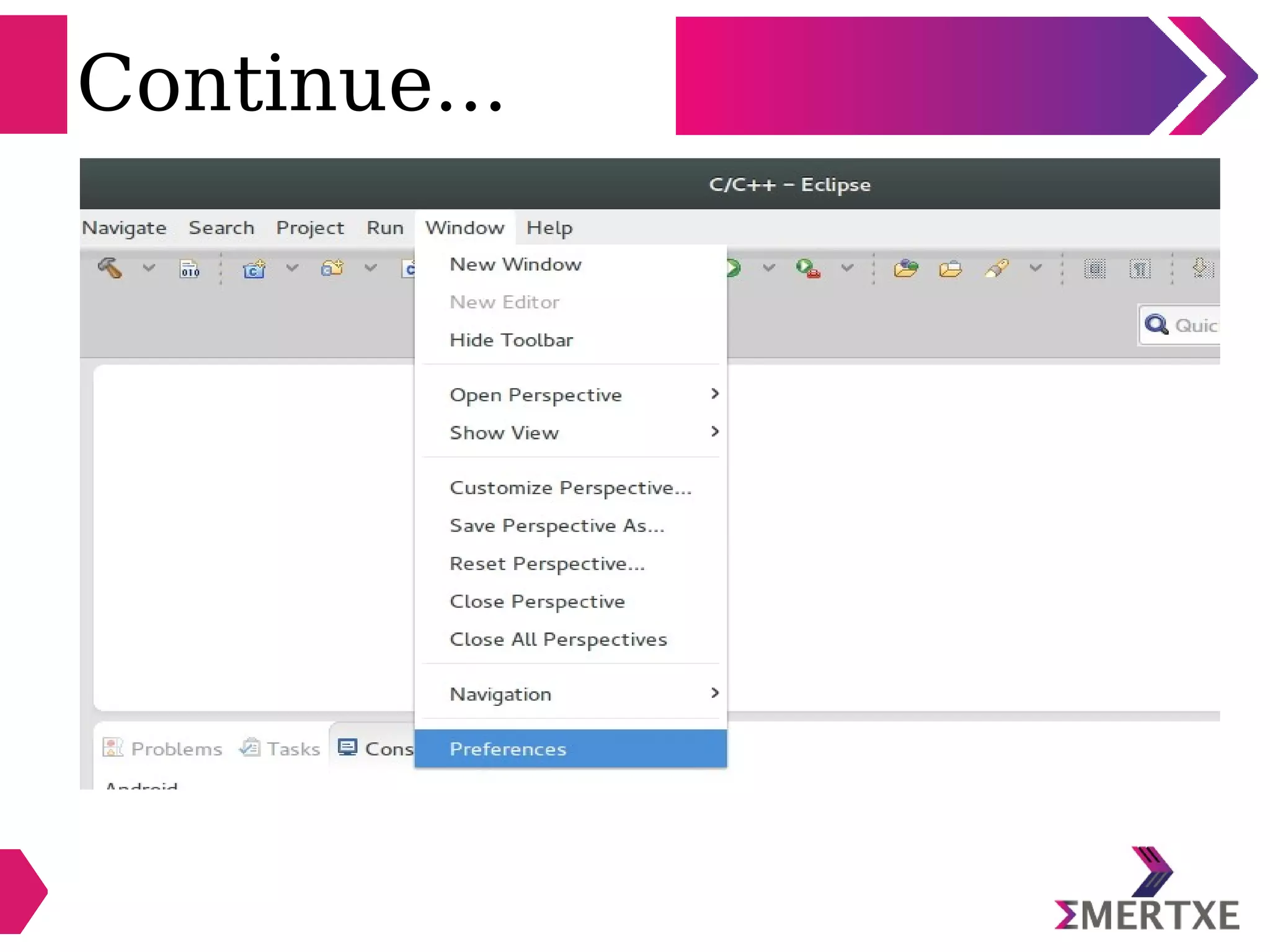
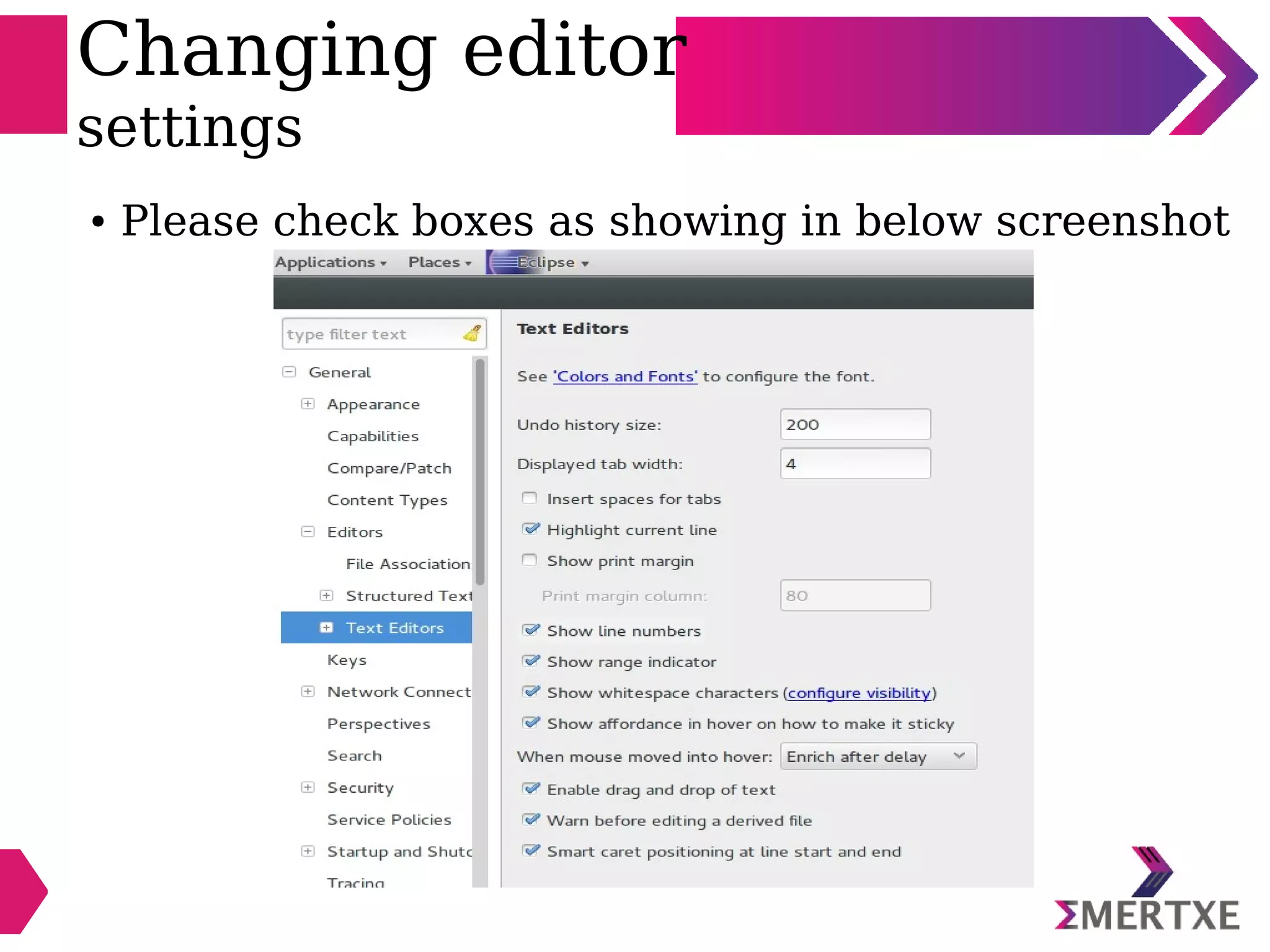
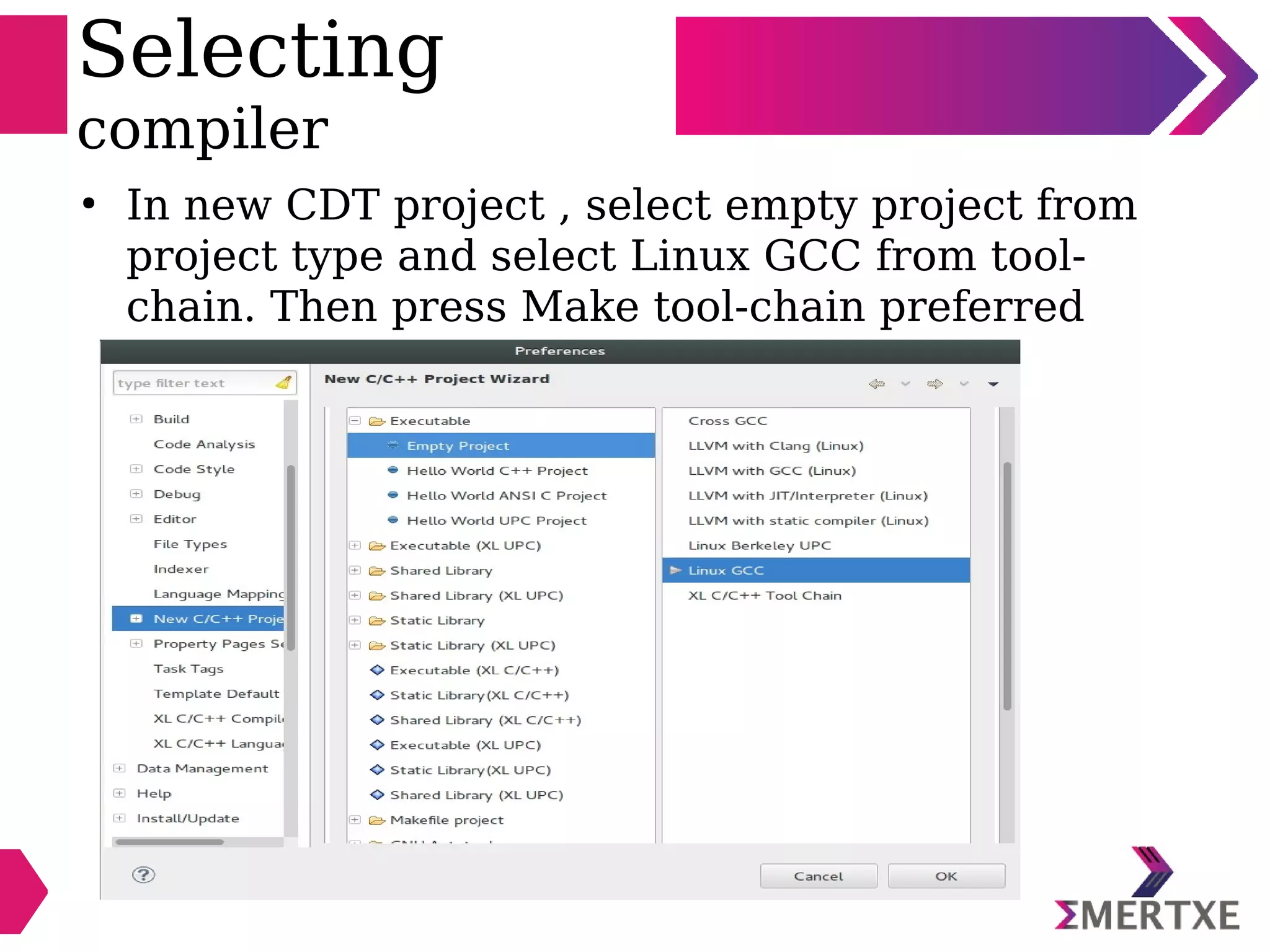
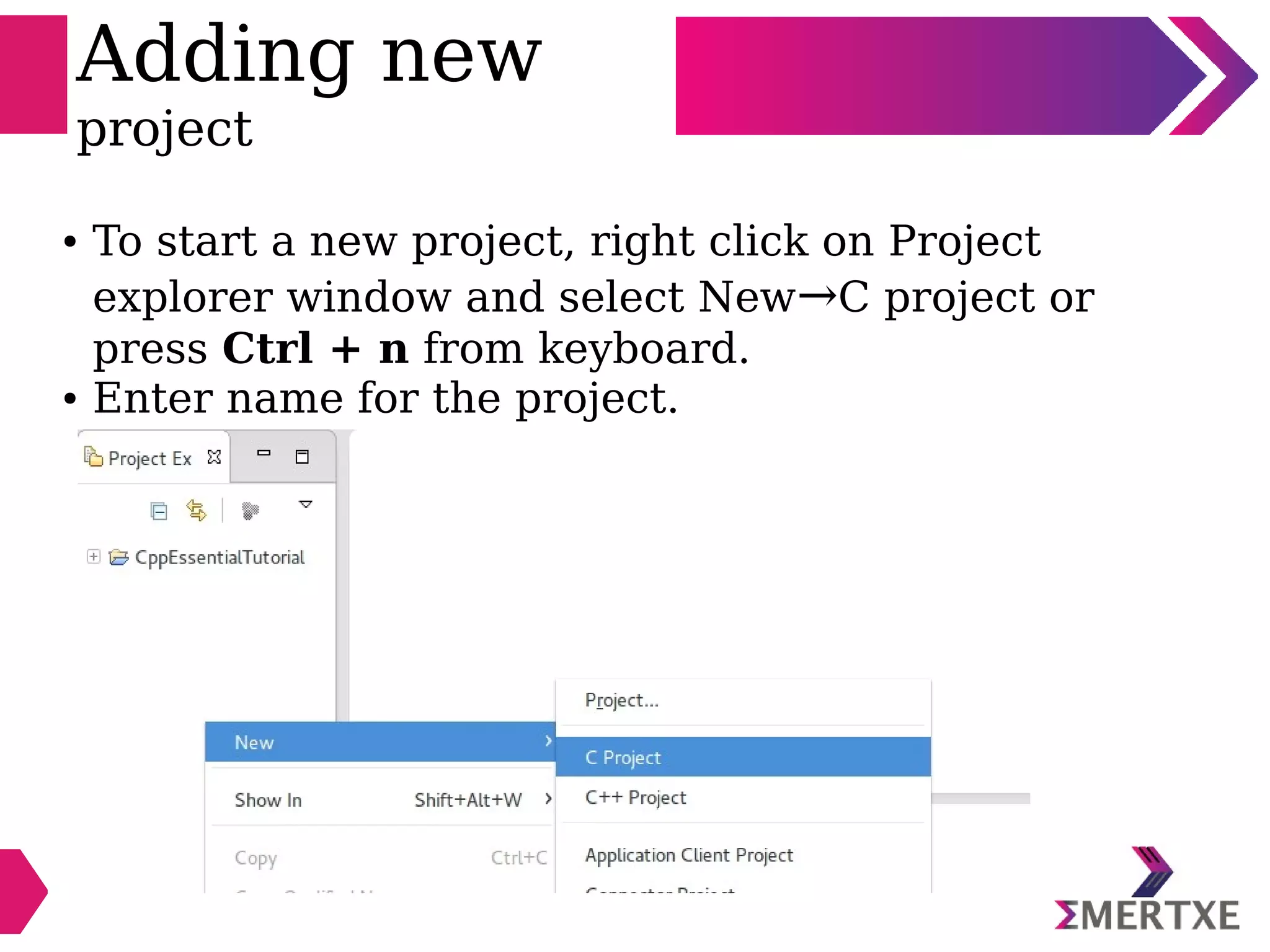
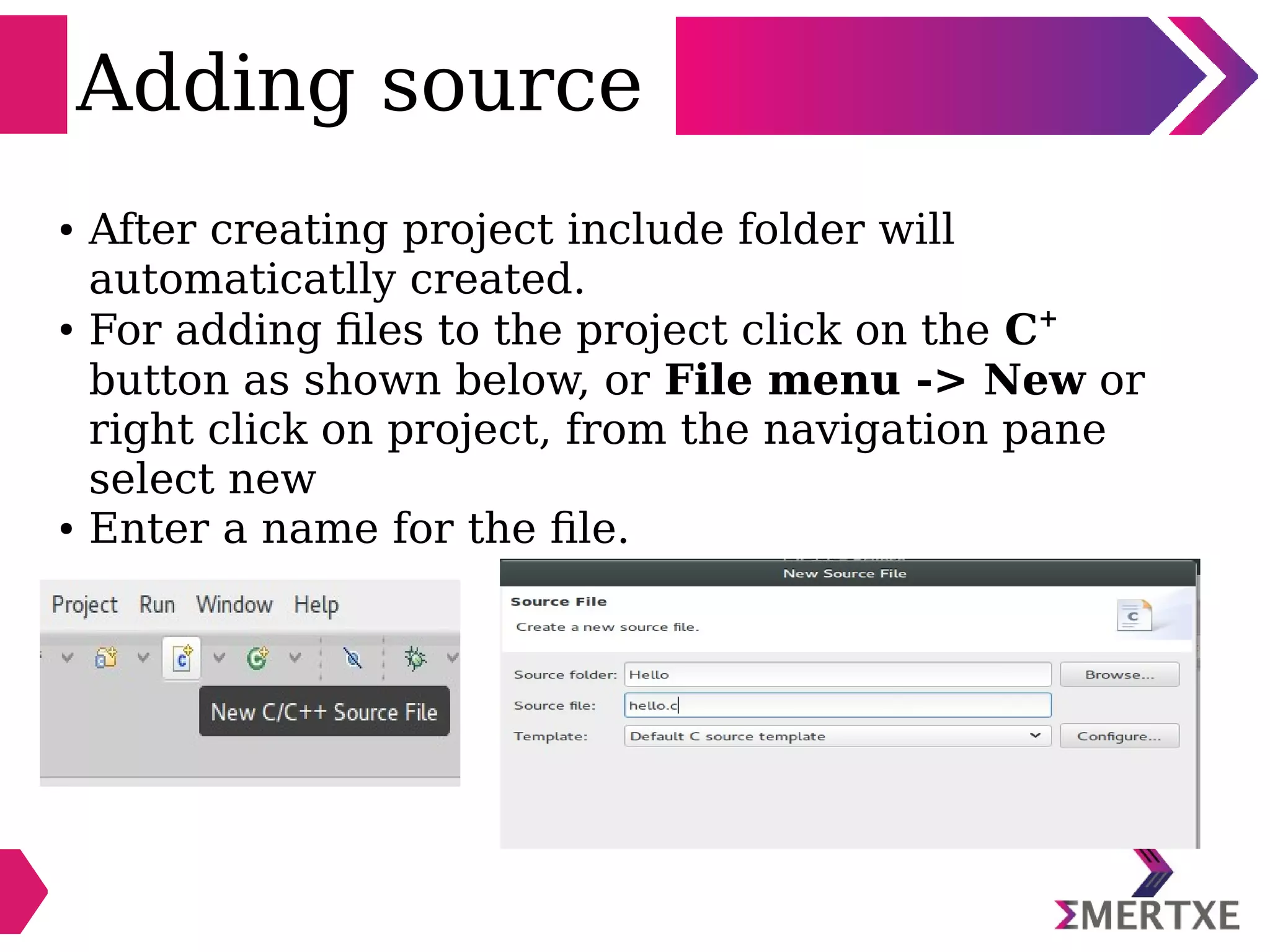
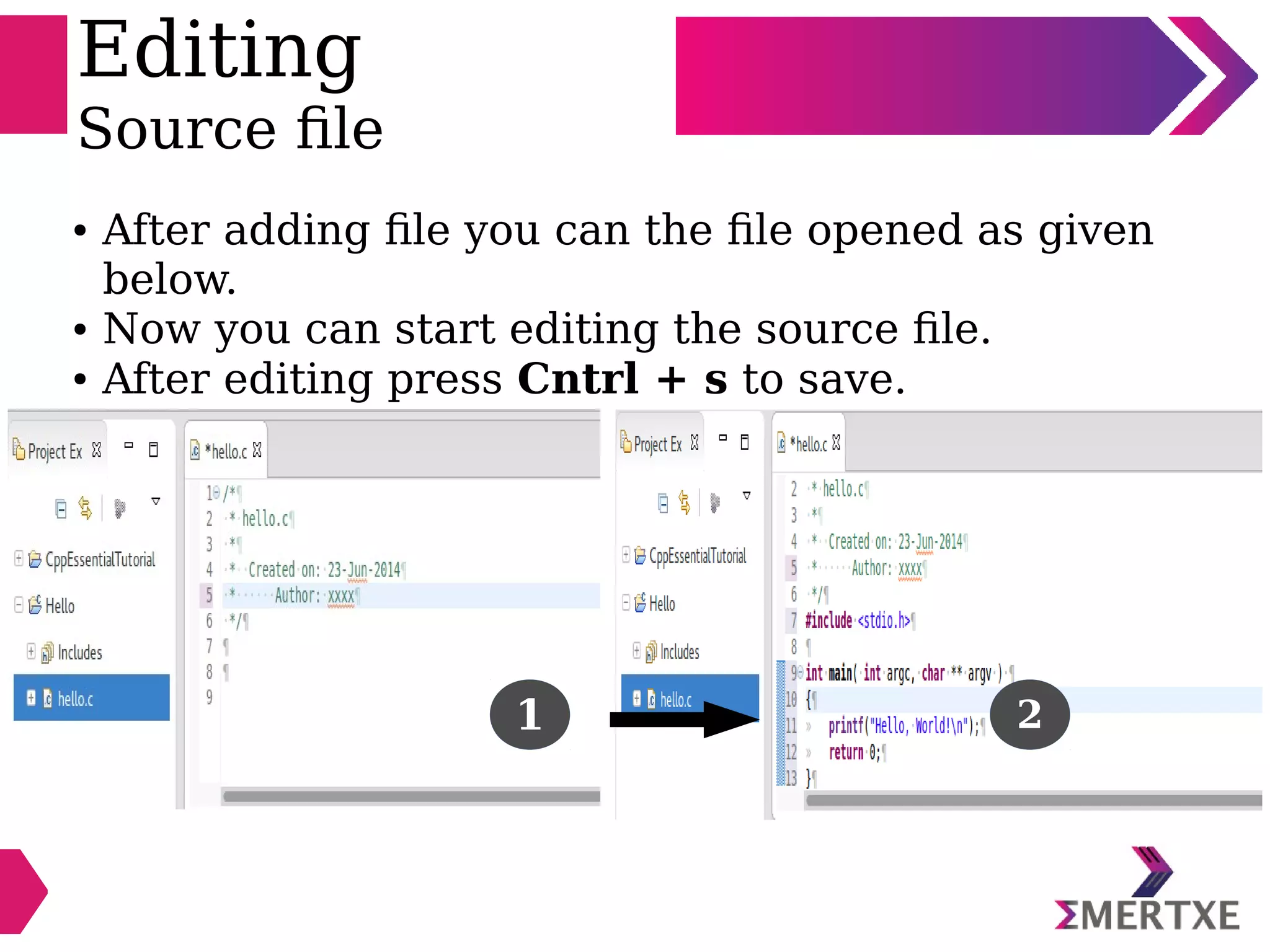
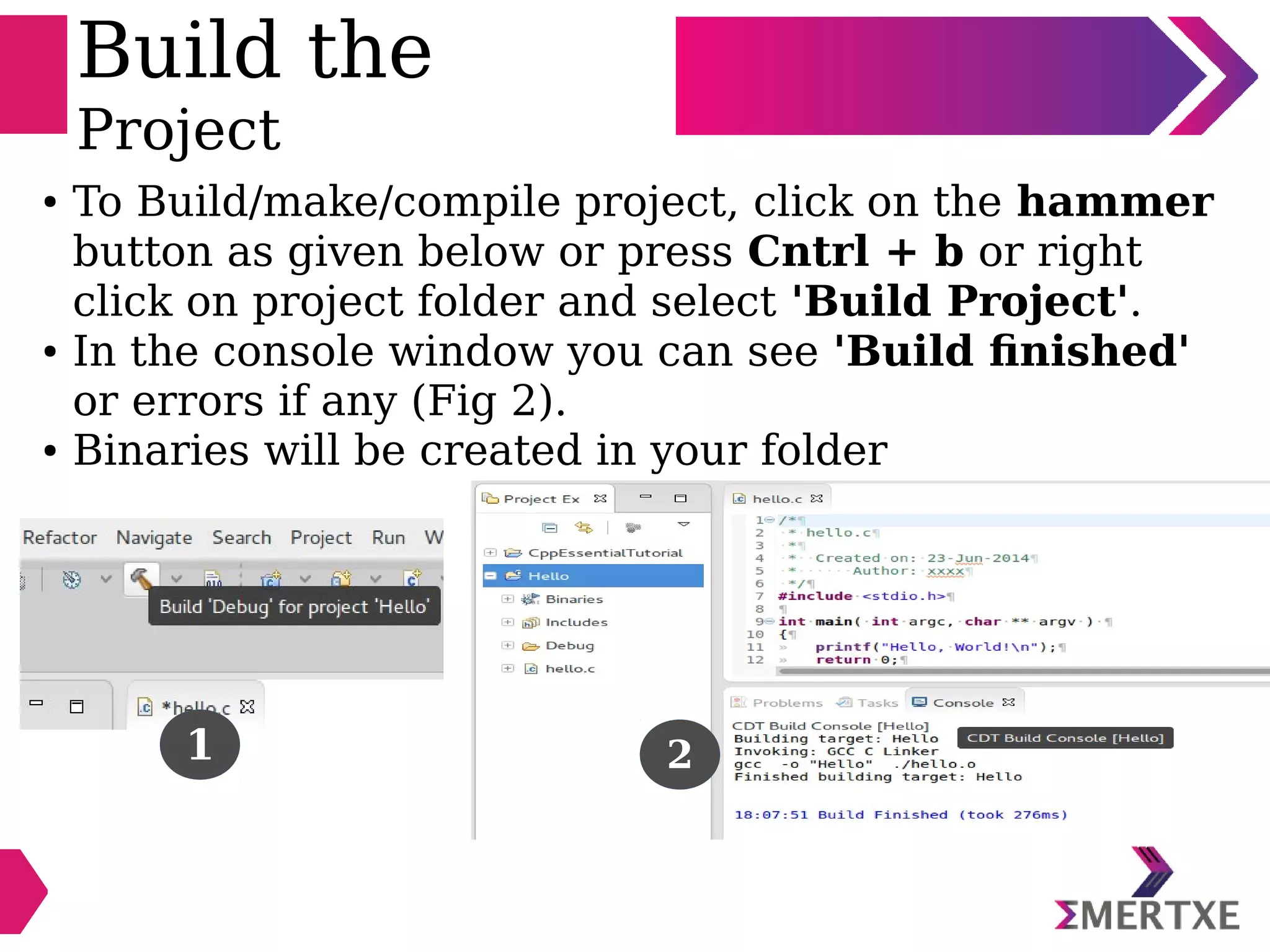
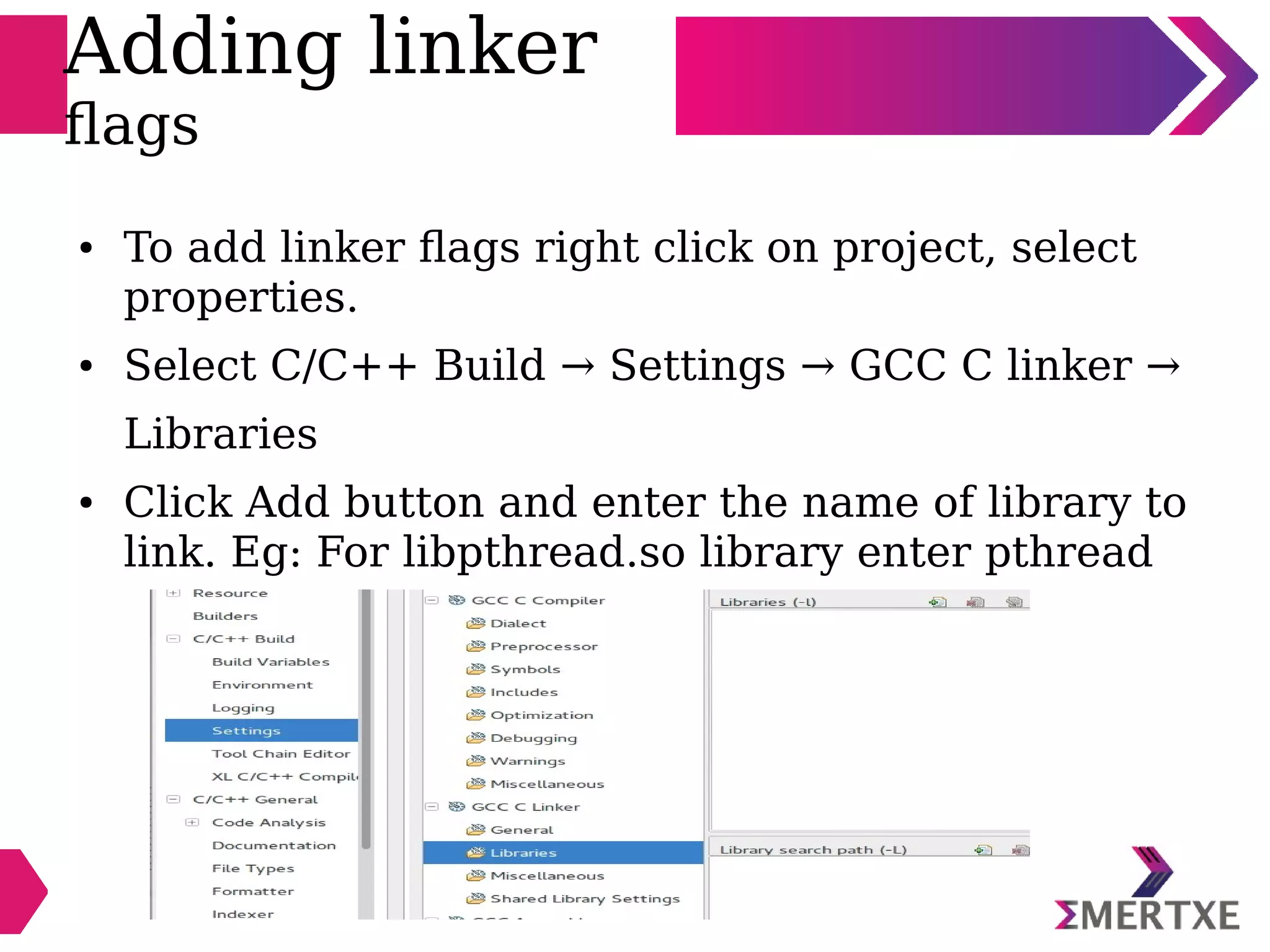
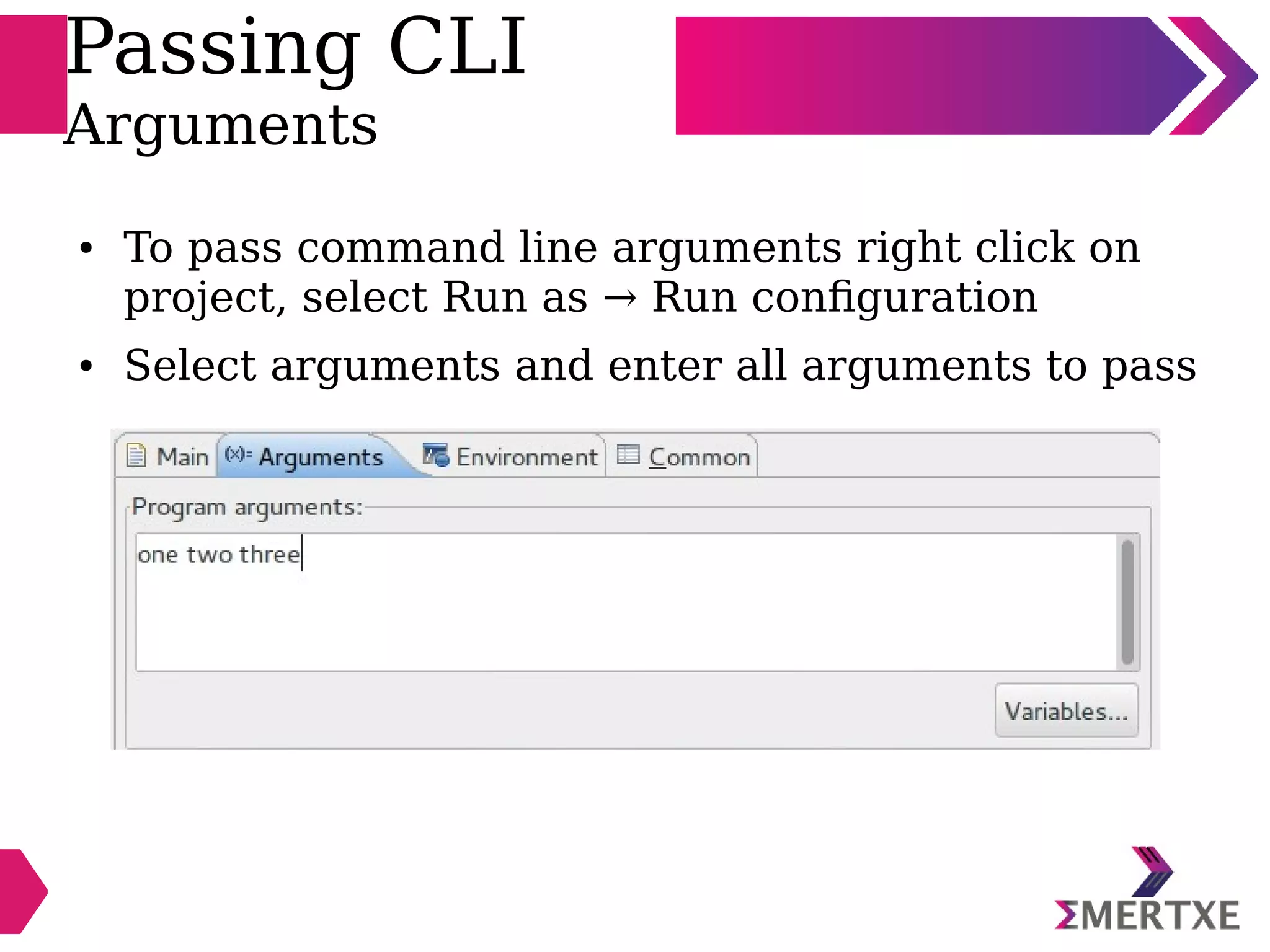
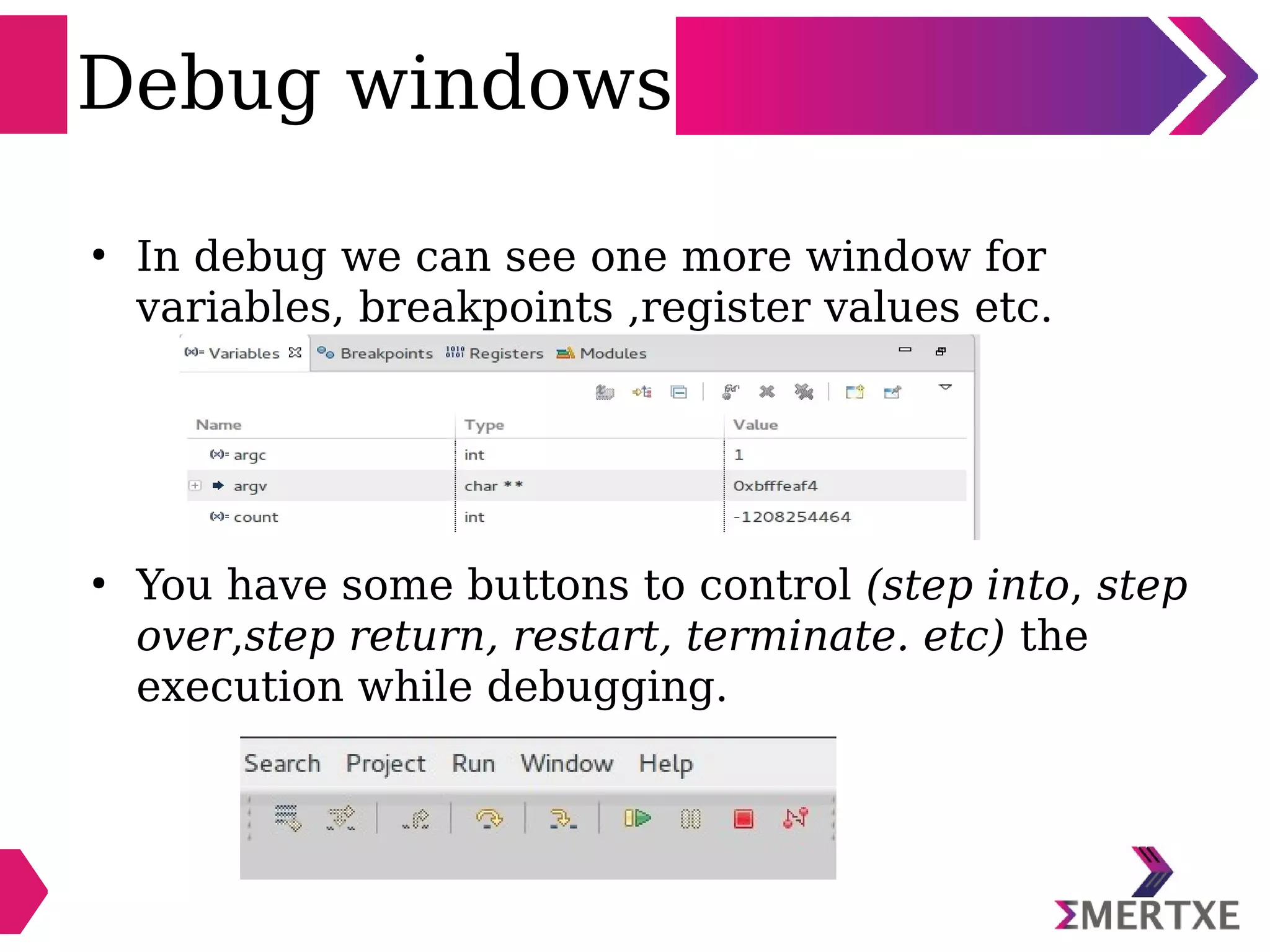
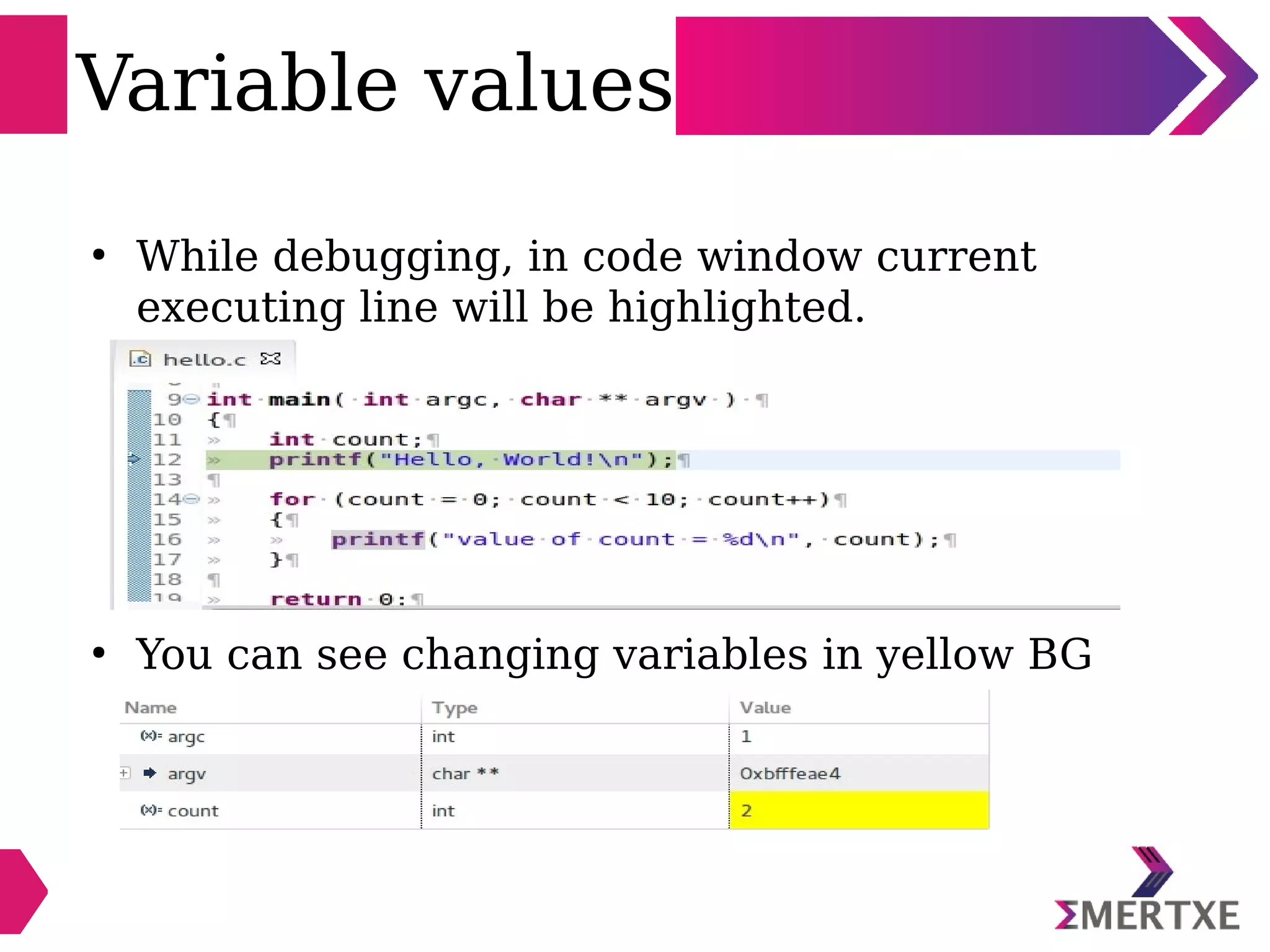
Eclipse is an integrated development environment that can be used for C programming. It requires the installation of a Java runtime environment. The document outlines the steps to install Eclipse, set it up for C programming by choosing the C/C++ perspective and compiler, create a C project, add and build source files, run and debug the project, and pass command line arguments. Debugging in Eclipse allows setting breakpoints and viewing variable values as the code executes line by line.