Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,850 times





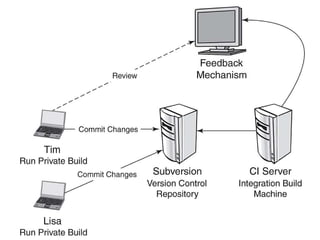


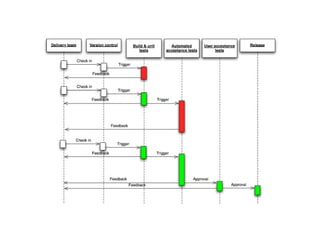
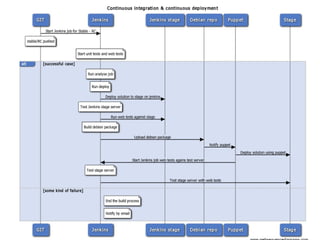
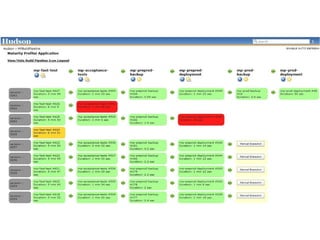

Continuous integration involves developers committing code changes daily which are then automatically built and tested. Continuous delivery takes this further by automatically deploying code changes that pass testing to production environments. The document outlines how Jenkins can be used to implement continuous integration and continuous delivery through automating builds, testing, and deployments to keep the process fast, repeatable and ensure quality.










