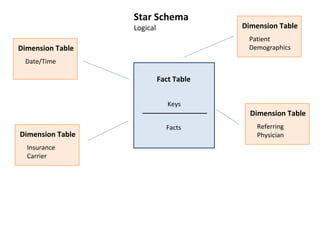
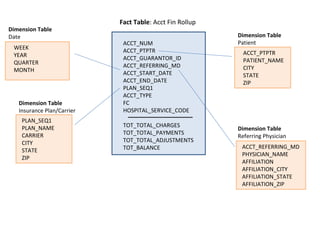
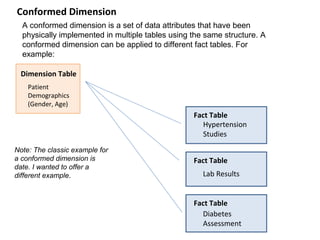
This document defines key concepts in data warehousing including dimensions, facts, star schemas, and snowflake schemas. Dimensions categorize data and provide structure through labeling and tagging. Facts contain measures and aggregates. A star schema consists of dimension tables modeled around a fact table, optimized for querying large datasets. A snowflake schema is similar to a star schema but with normalized dimension tables to separate null data for faster lookups. Conformed dimensions have a common structure that can be applied across multiple fact tables.