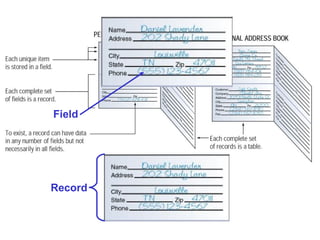
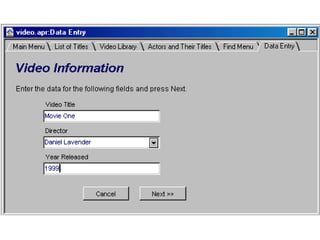
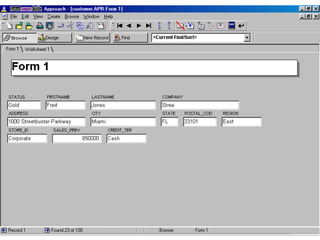
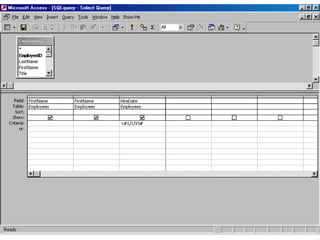
A database is a collection of related data, while a database management system (DBMS) is software that allows users to add, view and manage data in a database. DBMSes enable users to perform tasks like entering, sorting and querying data, and common database structures include flat-file databases with one table and relational databases with multiple related tables. Key aspects of working with databases involve creating tables to organize fields and records, using filters and forms to view and enter data, and querying the database using languages like SQL to search for specific records.