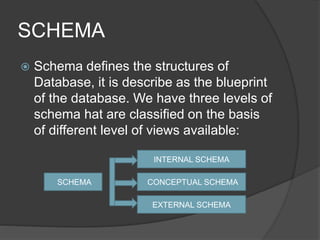
The document defines key terms related to database management systems (DBMS). It states that a DBMS is a collection of programs that allows users to store, retrieve, modify, and update data stored in a database. A DBMS also allows users to create or drop databases. Popular DBMS platforms include Oracle, Sybase, MySQL, and Microsoft SQL Server. The document also defines data, information, databases, database administrators, schemas, primary keys, and foreign keys as important concepts relating to DBMS.