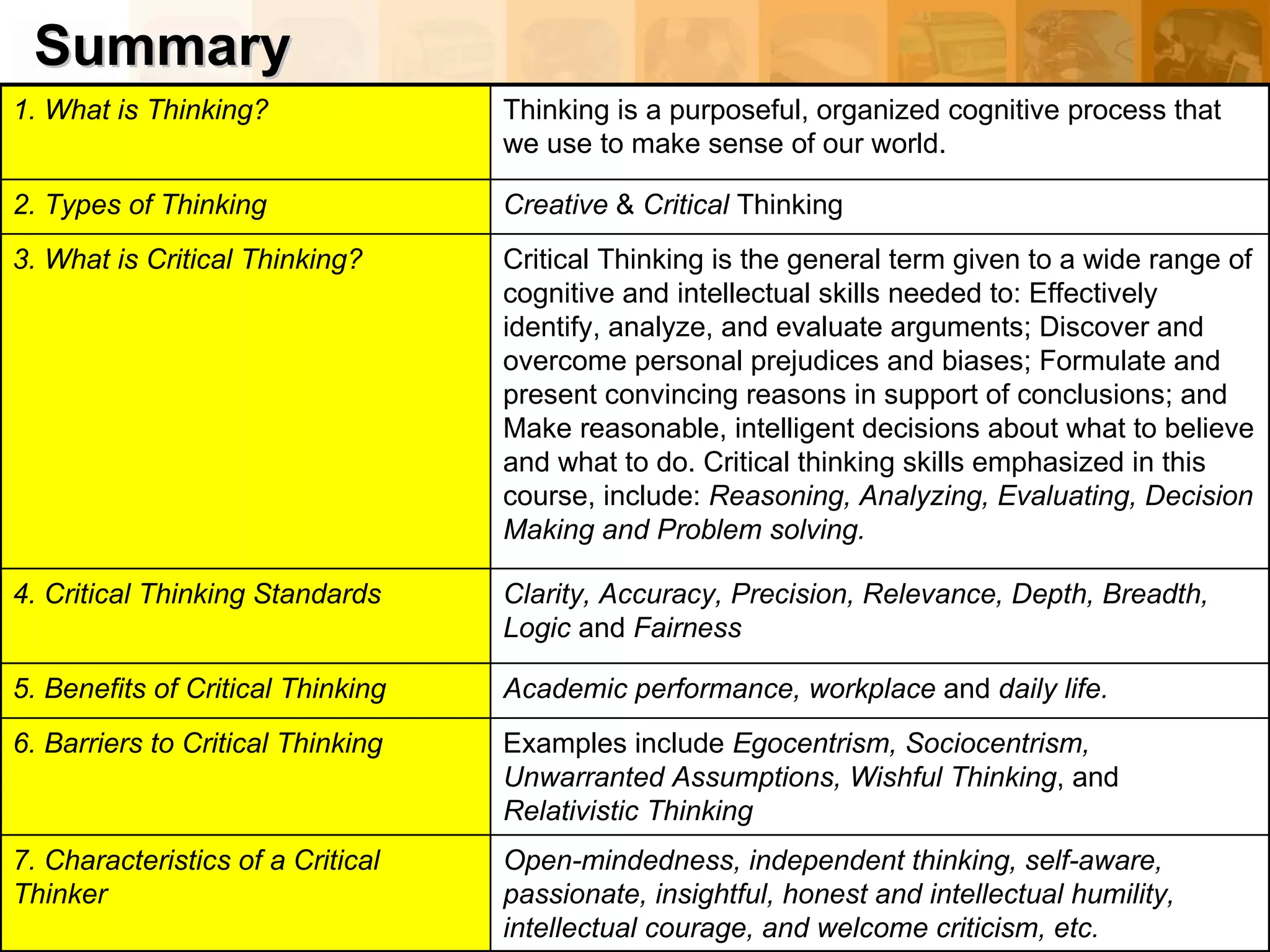
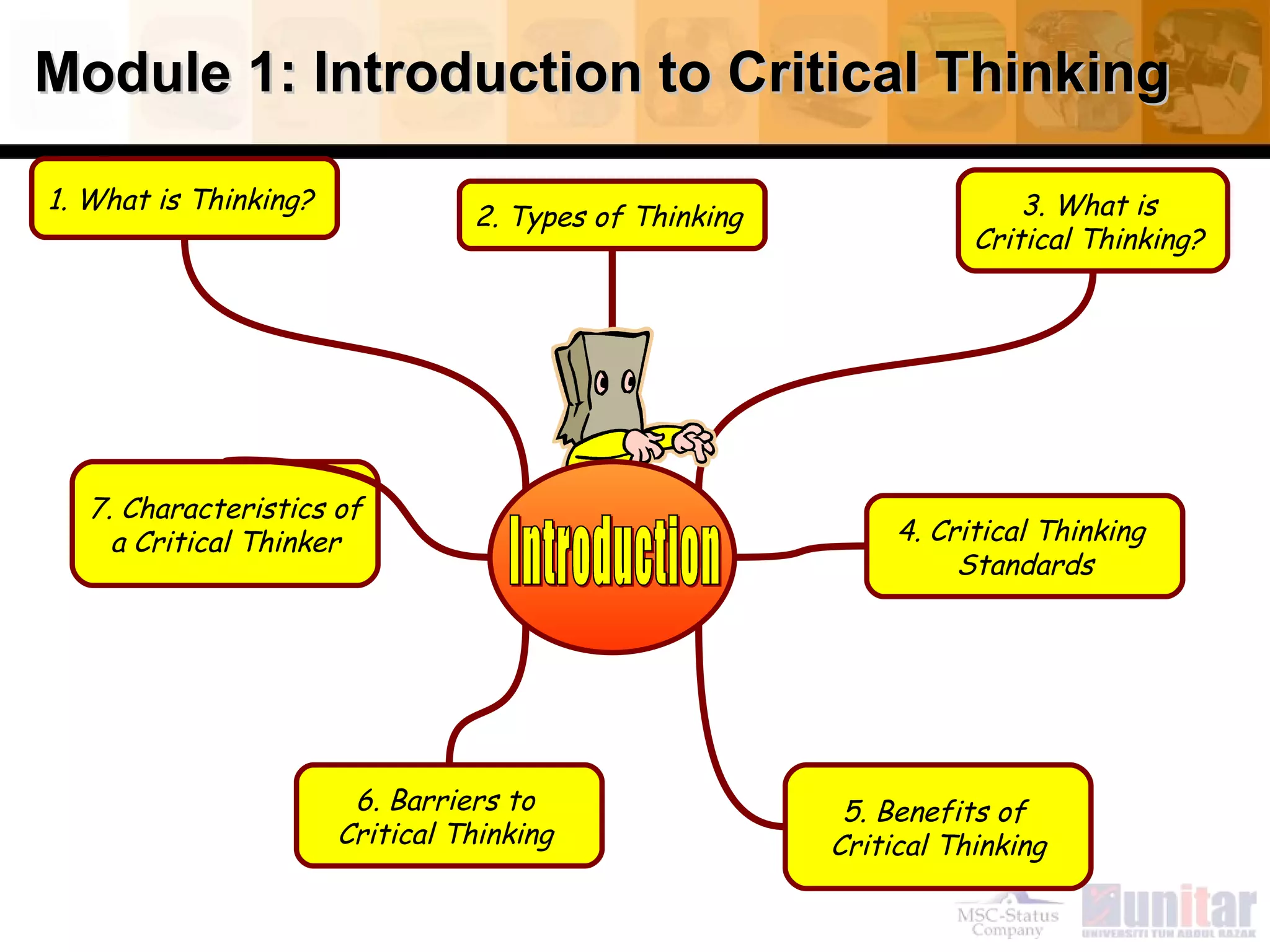
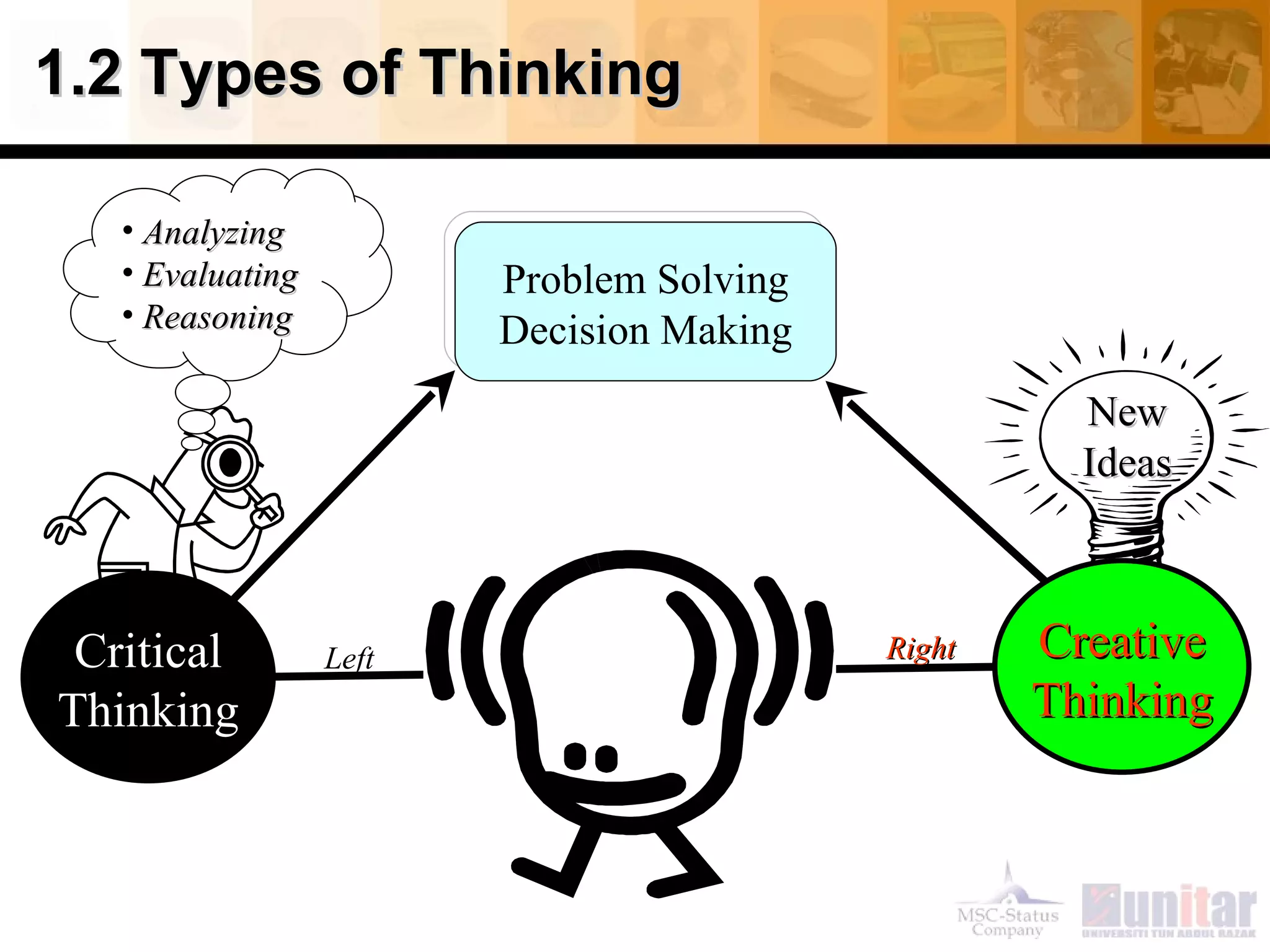
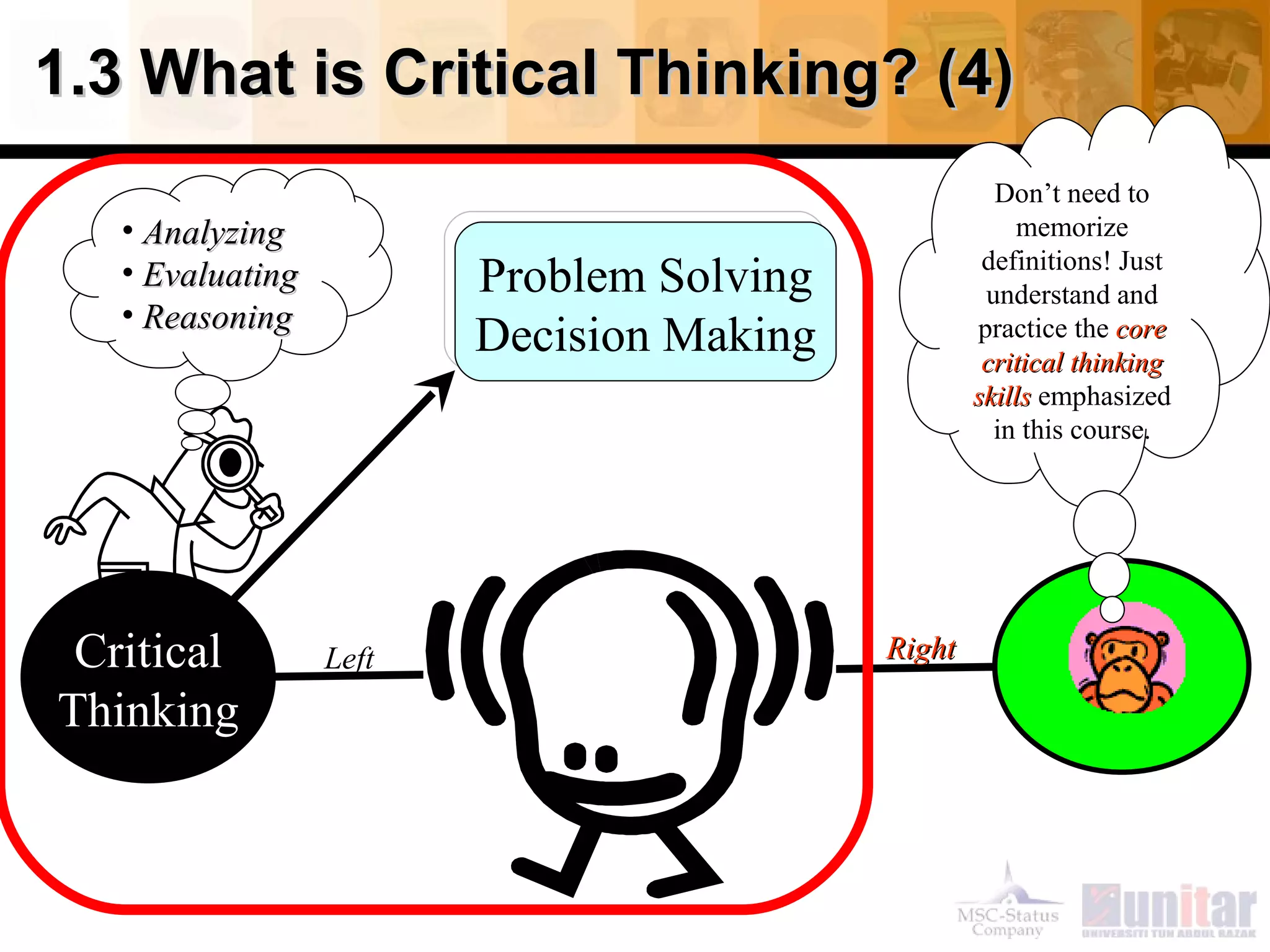
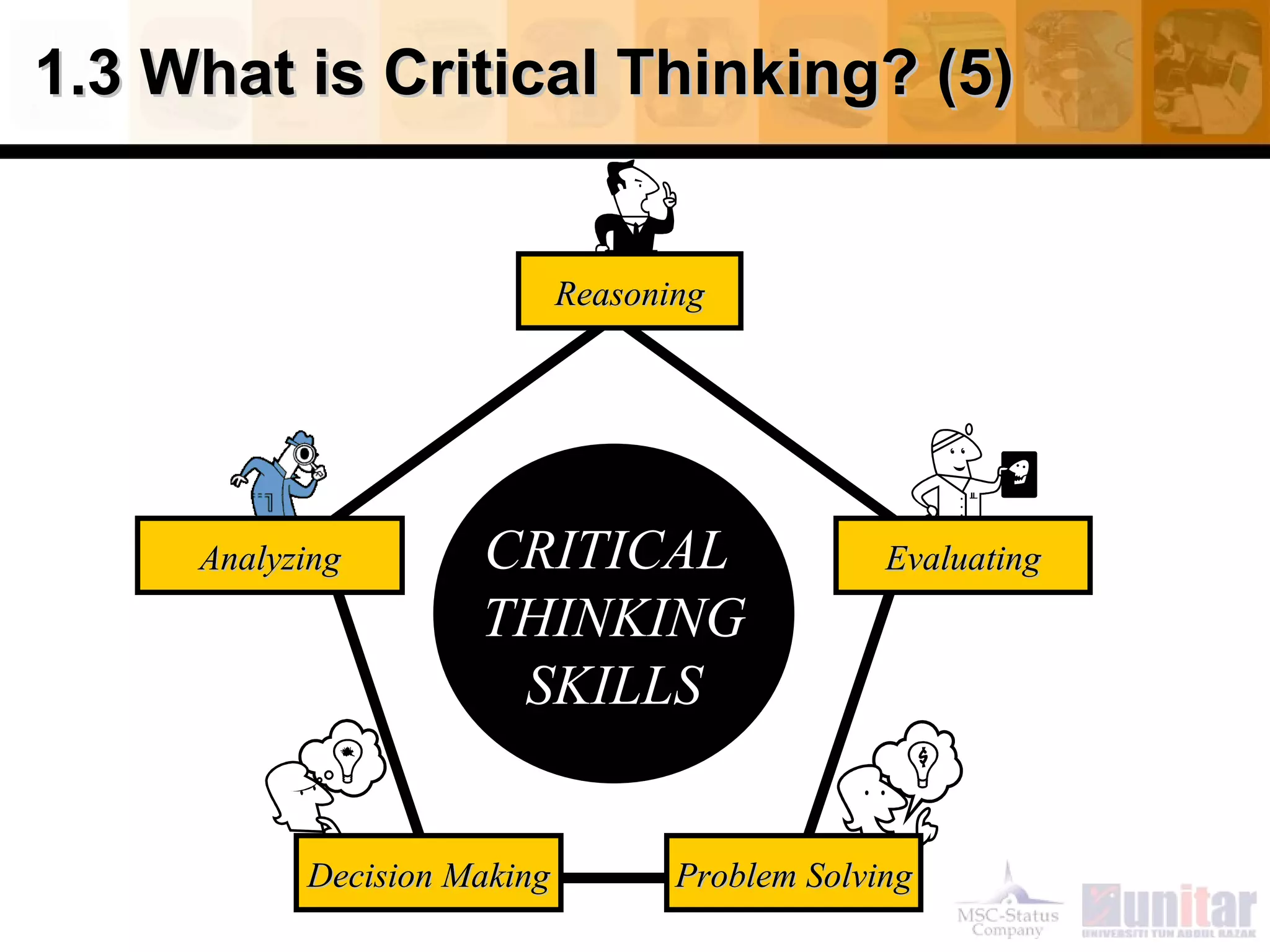
This document provides an overview of critical thinking concepts covered in Module 1 of the course. It defines thinking and different types of thinking. Critical thinking is defined as purposefully analyzing, evaluating, and reasoning about information to form judgments. The document outlines several critical thinking standards including clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, and logic. It provides examples to illustrate each standard and how a statement could potentially lack one or more of the standards. The overall purpose of the module and course is to help students improve their thinking and critical thinking skills.


























![1.6 Mini Quiz – Question 2
Muhammad Ali [speaking in Zaire, Africa]: "There's no country
as great as the smallest city in America. I mean [here in Zaire]
you can't watch television. The water won't even run right.
The toilets won't flush. The roads, the cars- there's nothing as
great as America."
Which critical thinking barrier does Ali display in this
passage?
A) Self-interested thinking
B) Group bias
C) Self-serving bias
D) Conformism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introduction-to-critical-thinking-120518075545-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Critical-Thinking-36-2048.jpg)