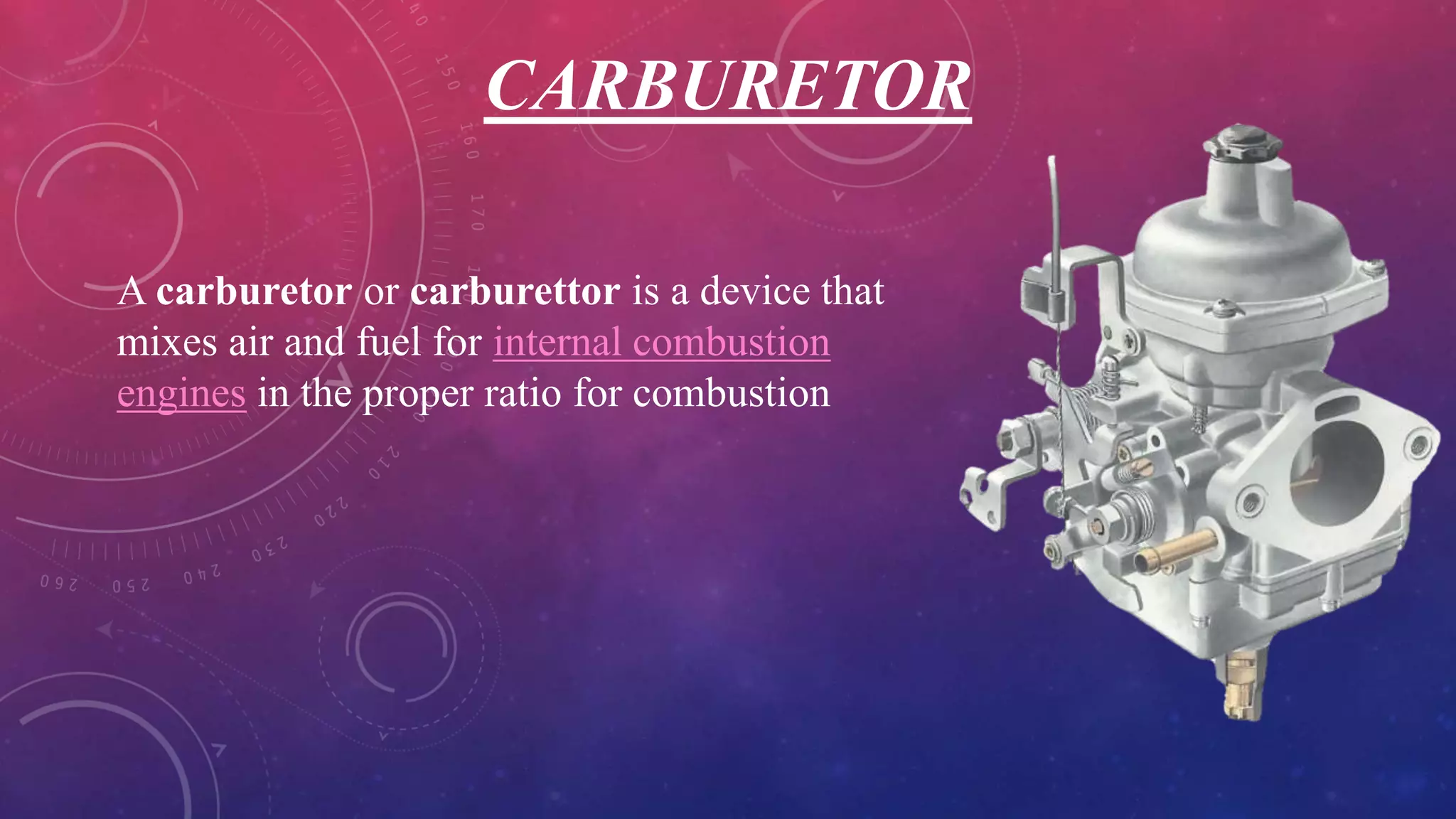
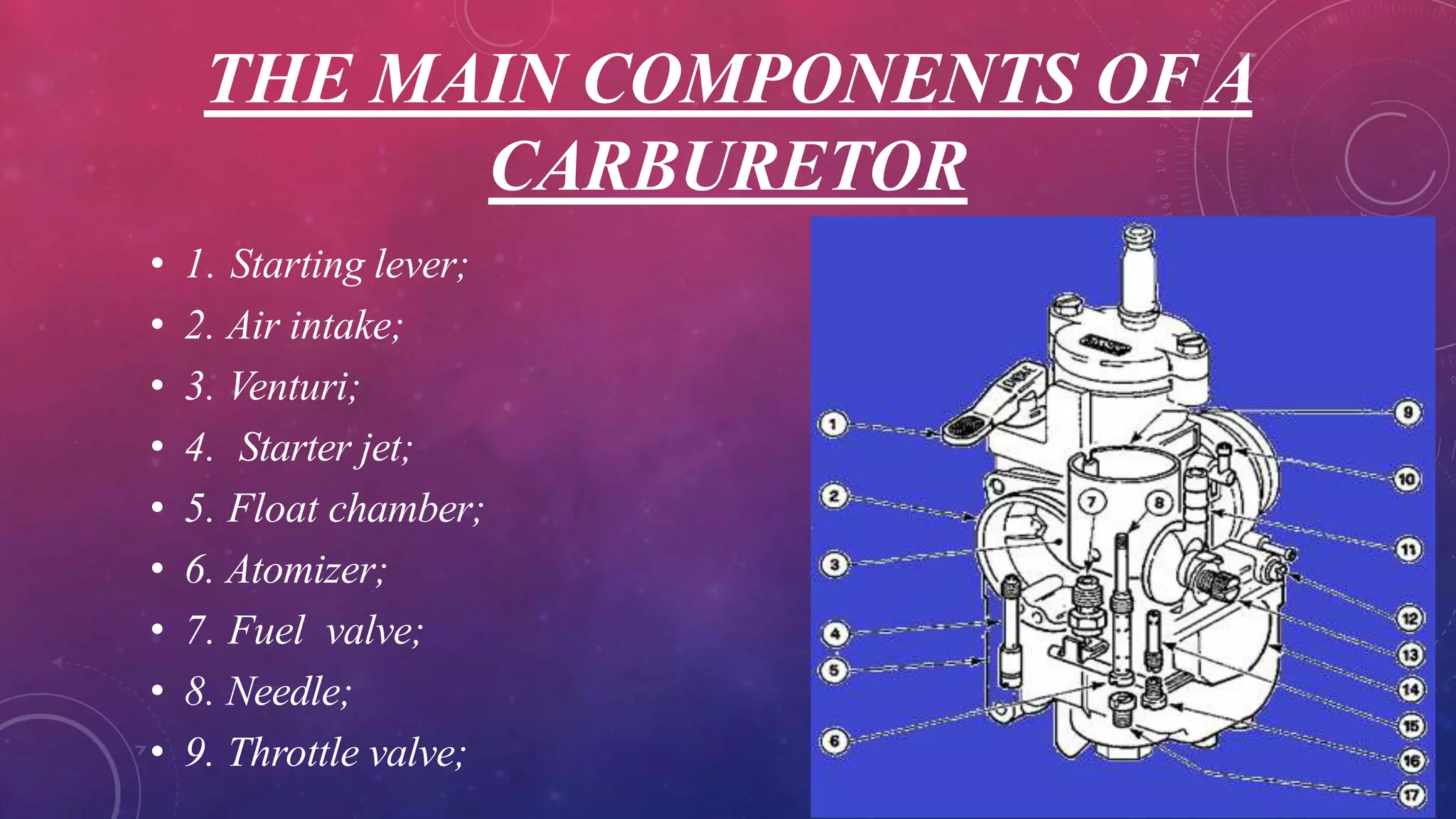
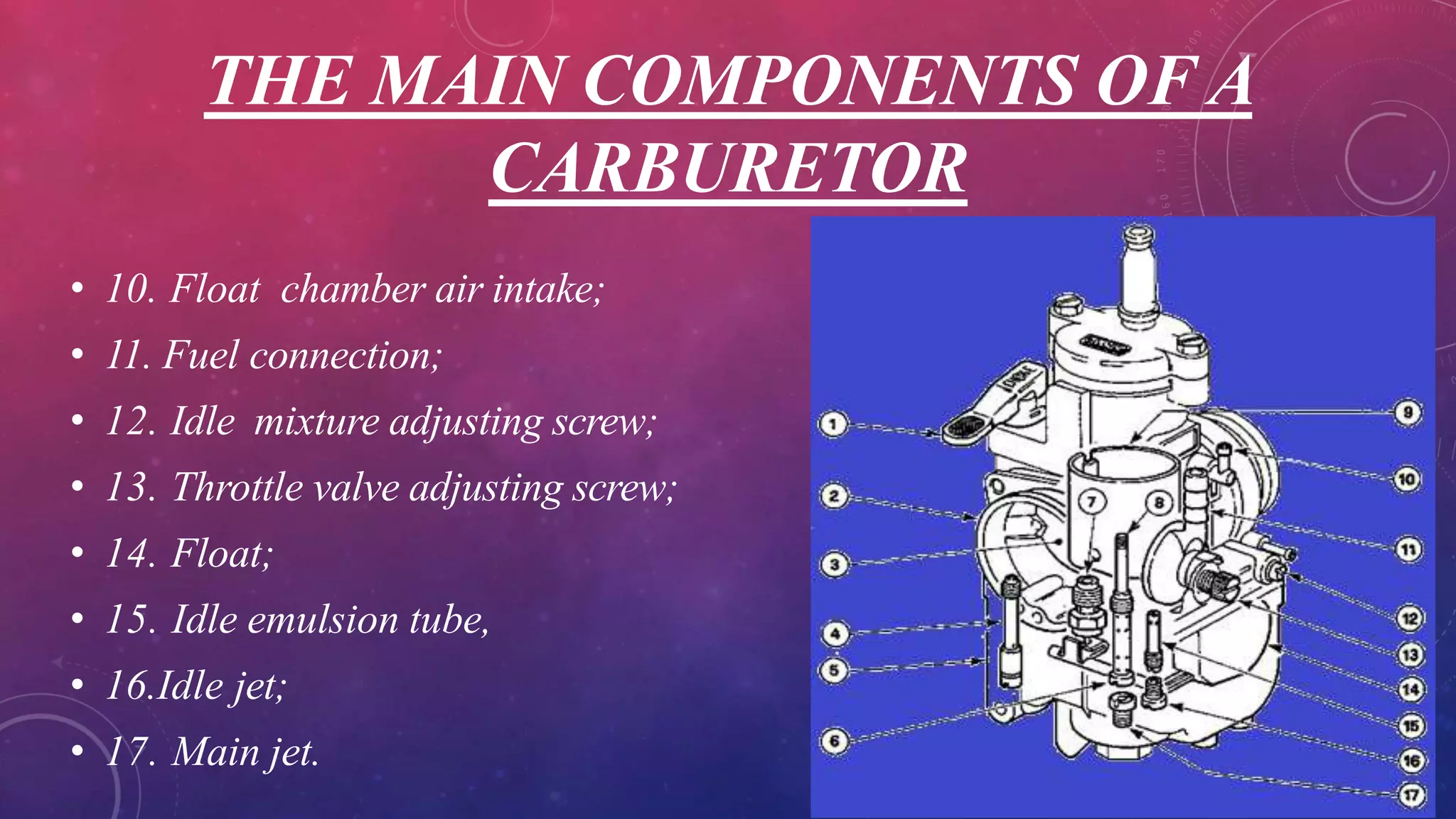
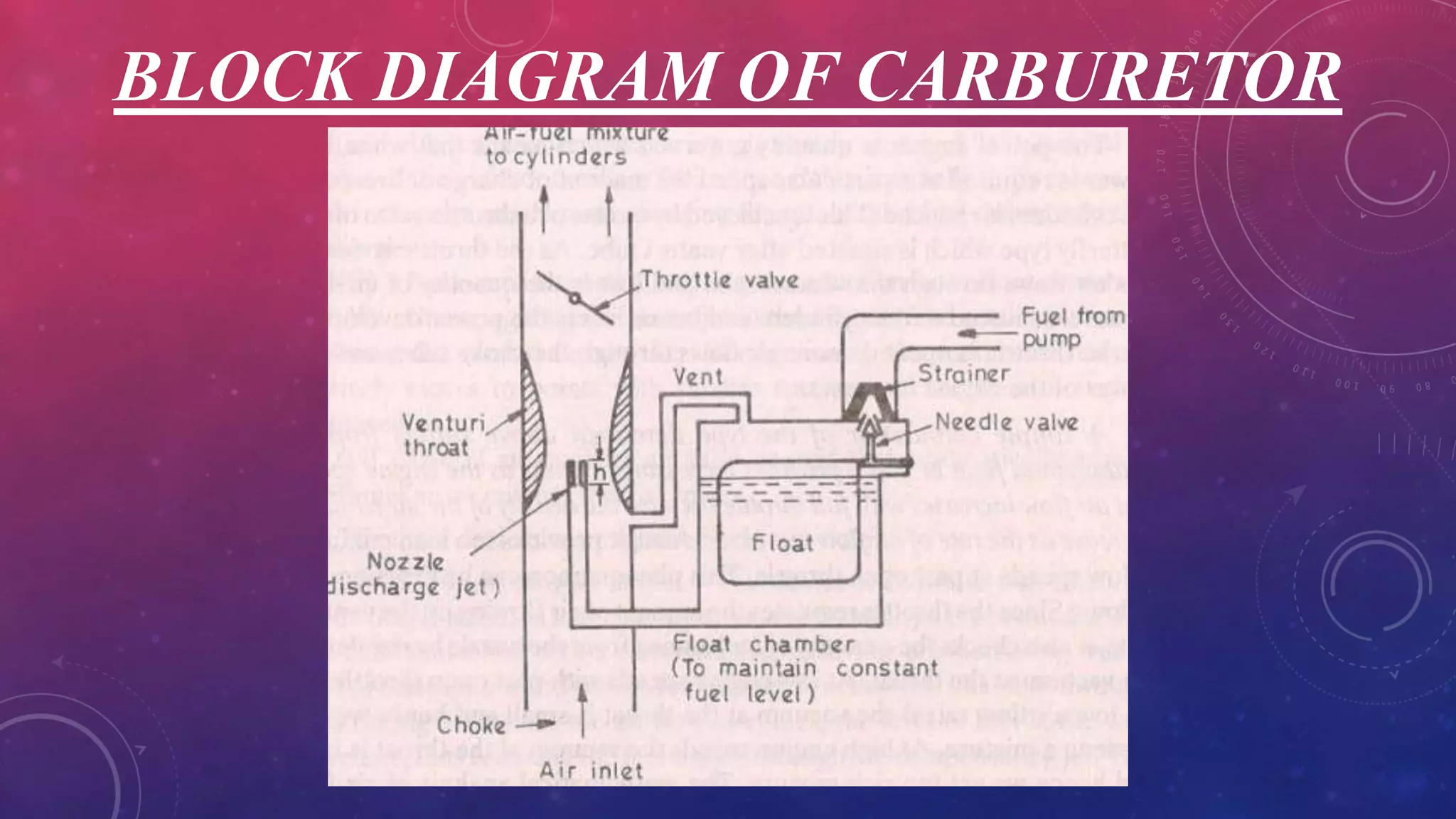
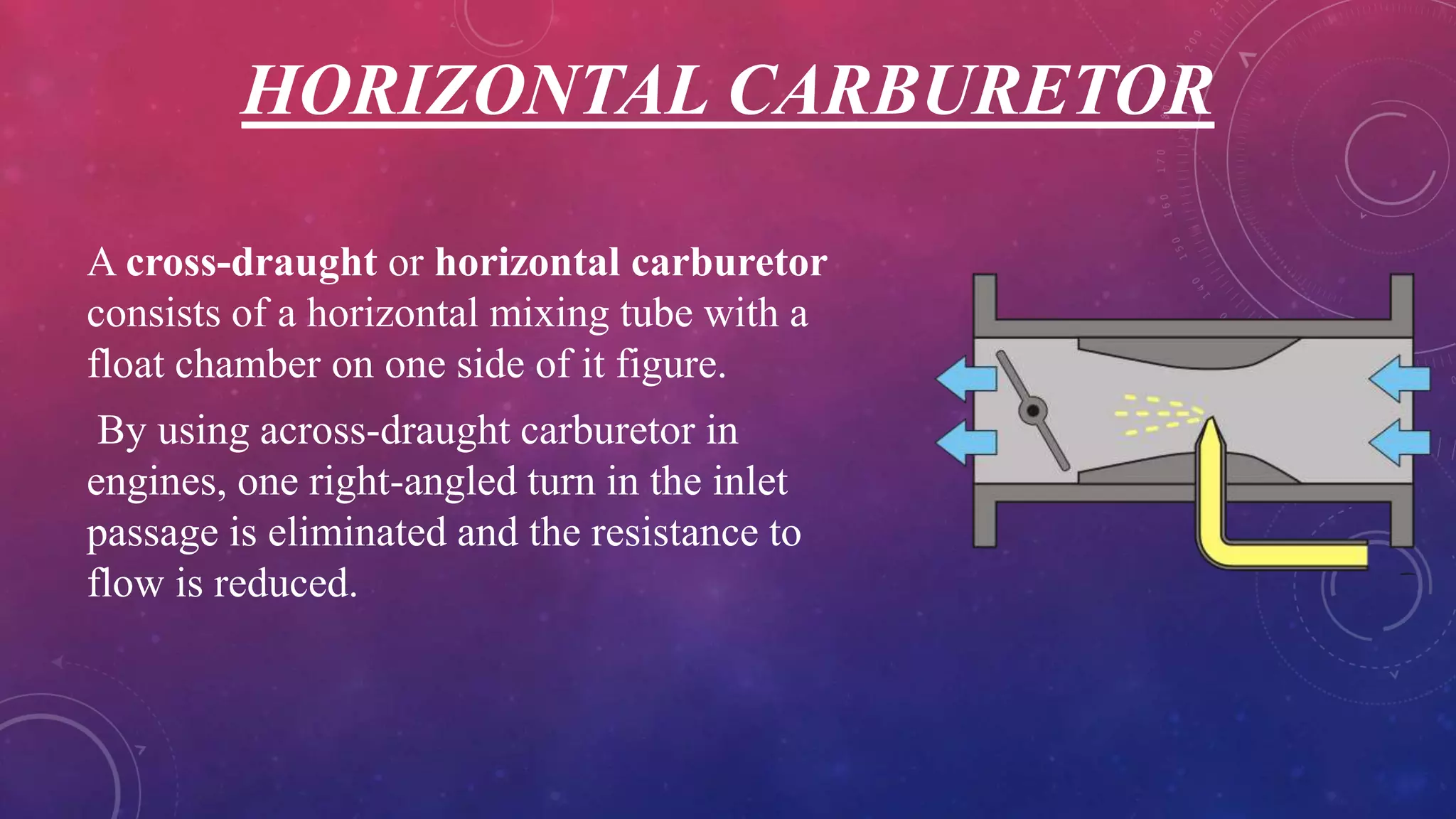
A carburetor mixes air and fuel for combustion in internal combustion engines. It has several main components including venturis, jets, floats, valves and levers that work together to provide the optimal air-fuel ratio for different engine speeds and loads. There are several types of carburetors including updraft, downdraft and horizontal, as well as constant vacuum, multiple venturi and multi-jet varieties. Common modern carburetor brands discussed include Zenith, Solex and Carter.