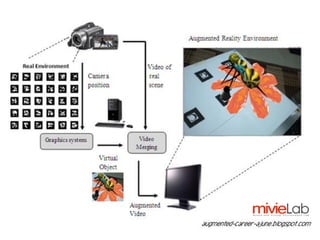
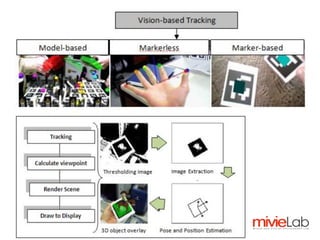
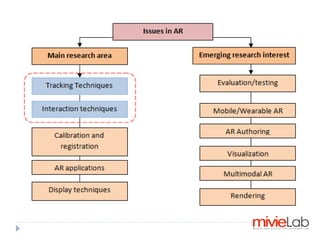
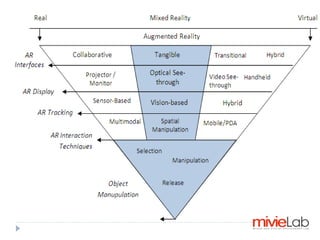
Augmented Reality (AR) merges real-world environments with computer-generated data and is utilized in various applications such as advertising, education, tourism, and gaming. Key challenges include tracking accuracy, occlusion, and natural interaction via gesture or speech recognition. Future trends involve improving interfaces and reducing system delays for enhanced user experiences.