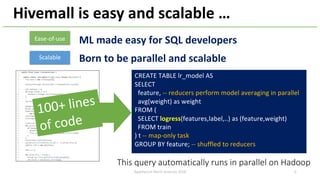
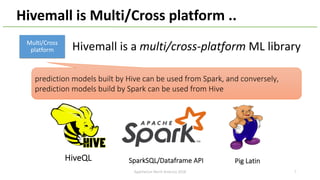
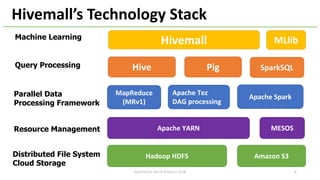
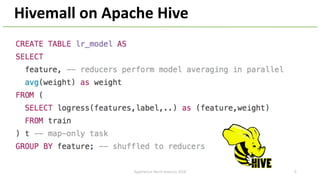
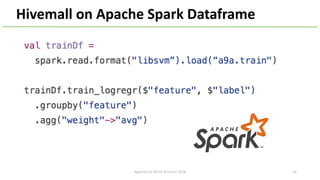
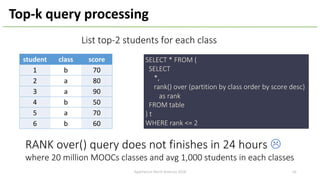
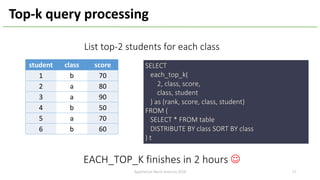
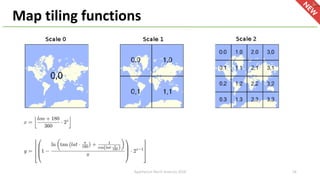
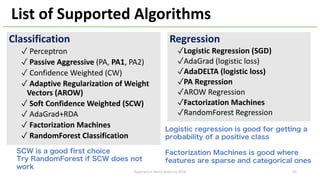
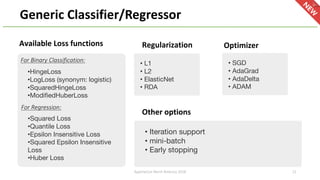
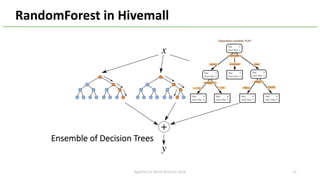
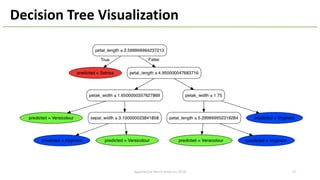
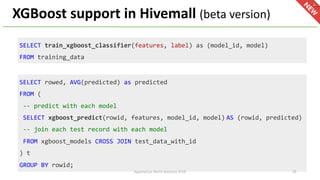
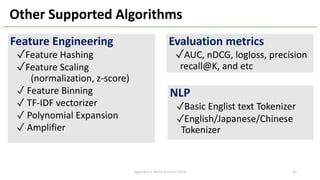
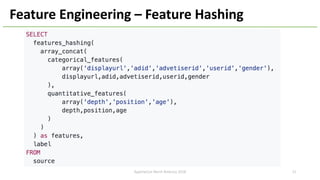
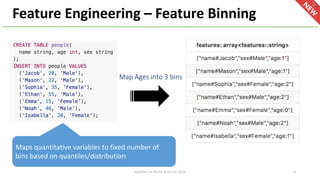
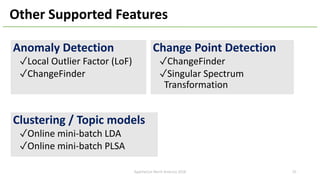
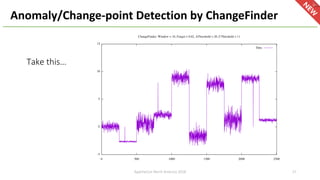
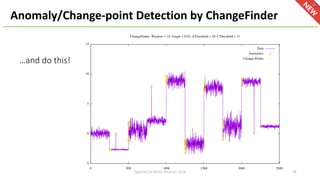
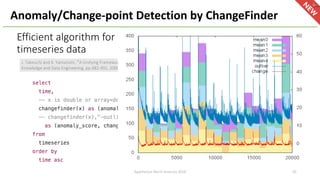
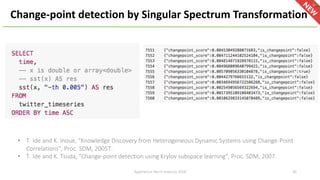
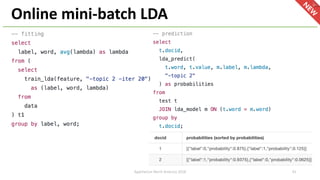
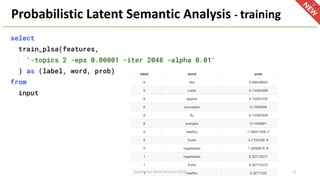
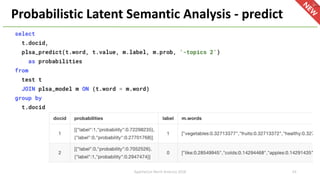
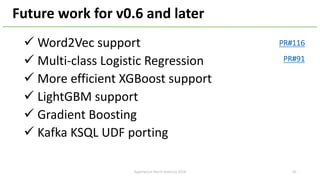
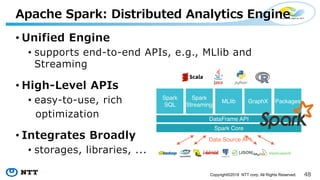
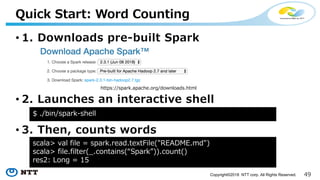
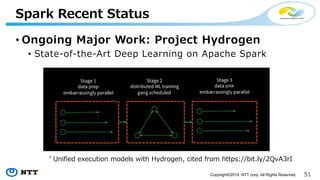
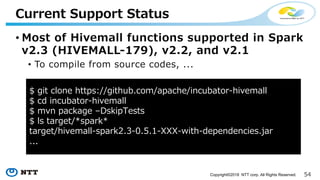
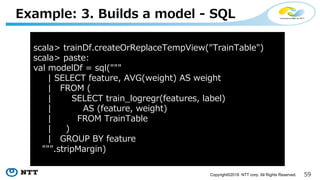
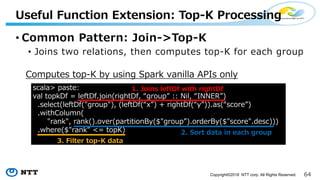
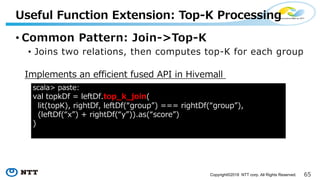
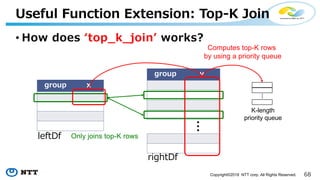
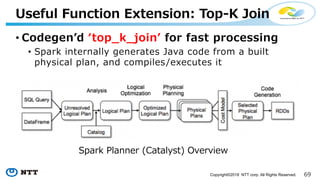
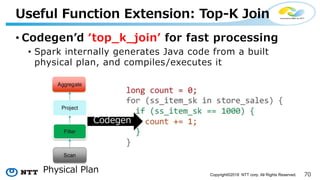
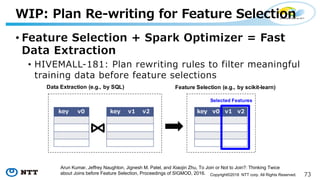
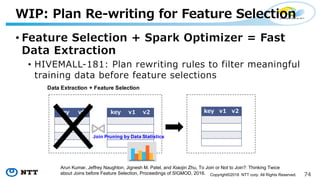
The document introduces Apache Hivemall v0.5.0, a scalable machine learning library for Hadoop and Spark, highlighting its features, such as anomaly detection, topic modeling, and support for various algorithms and utilities. It details the multi-platform capabilities that allow models created in Hive to be used in Spark and vice versa. Upcoming enhancements in future releases include support for Spark 2.3 and advanced algorithms like field-aware factorization machines and XGBoost.