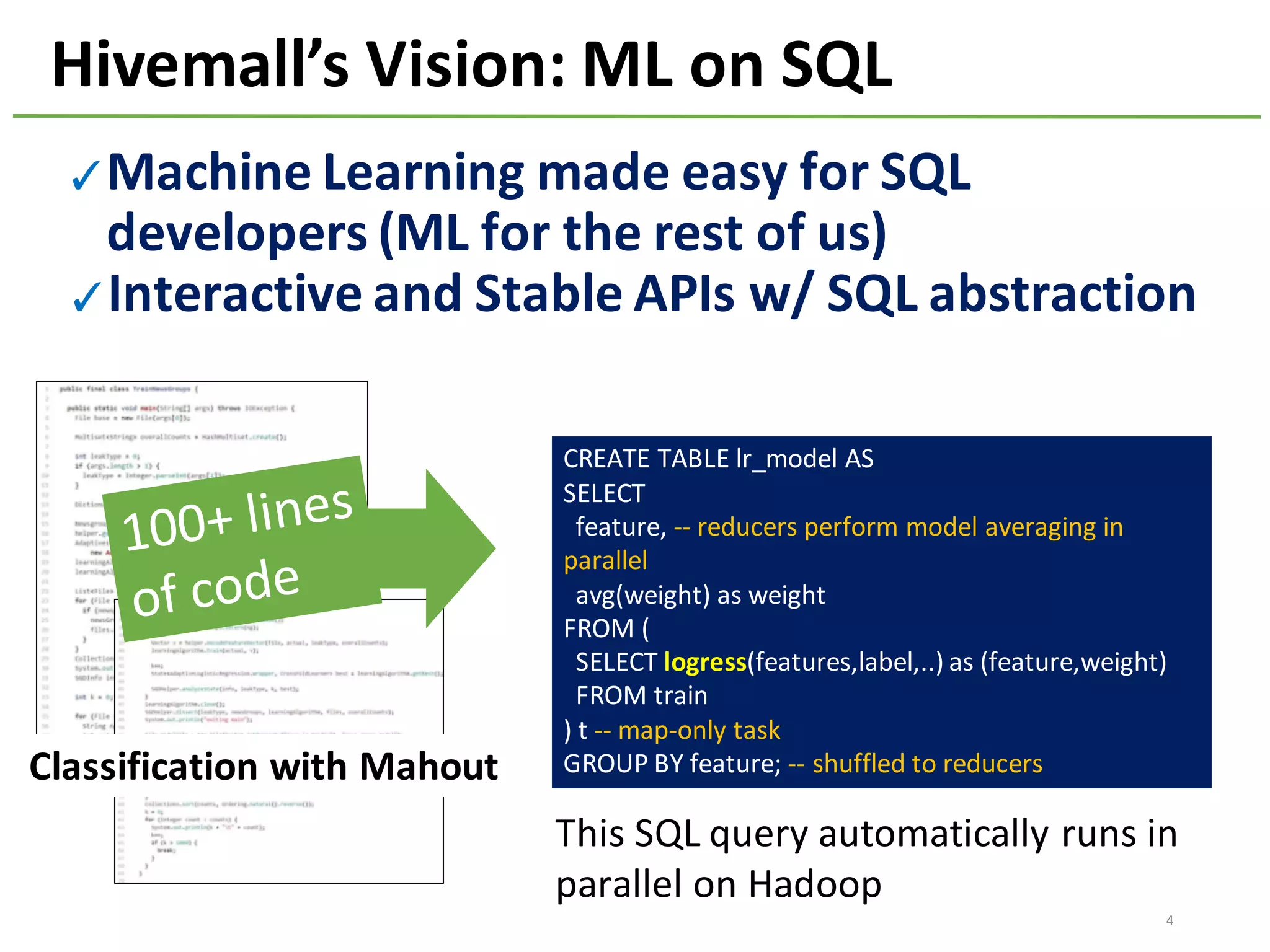
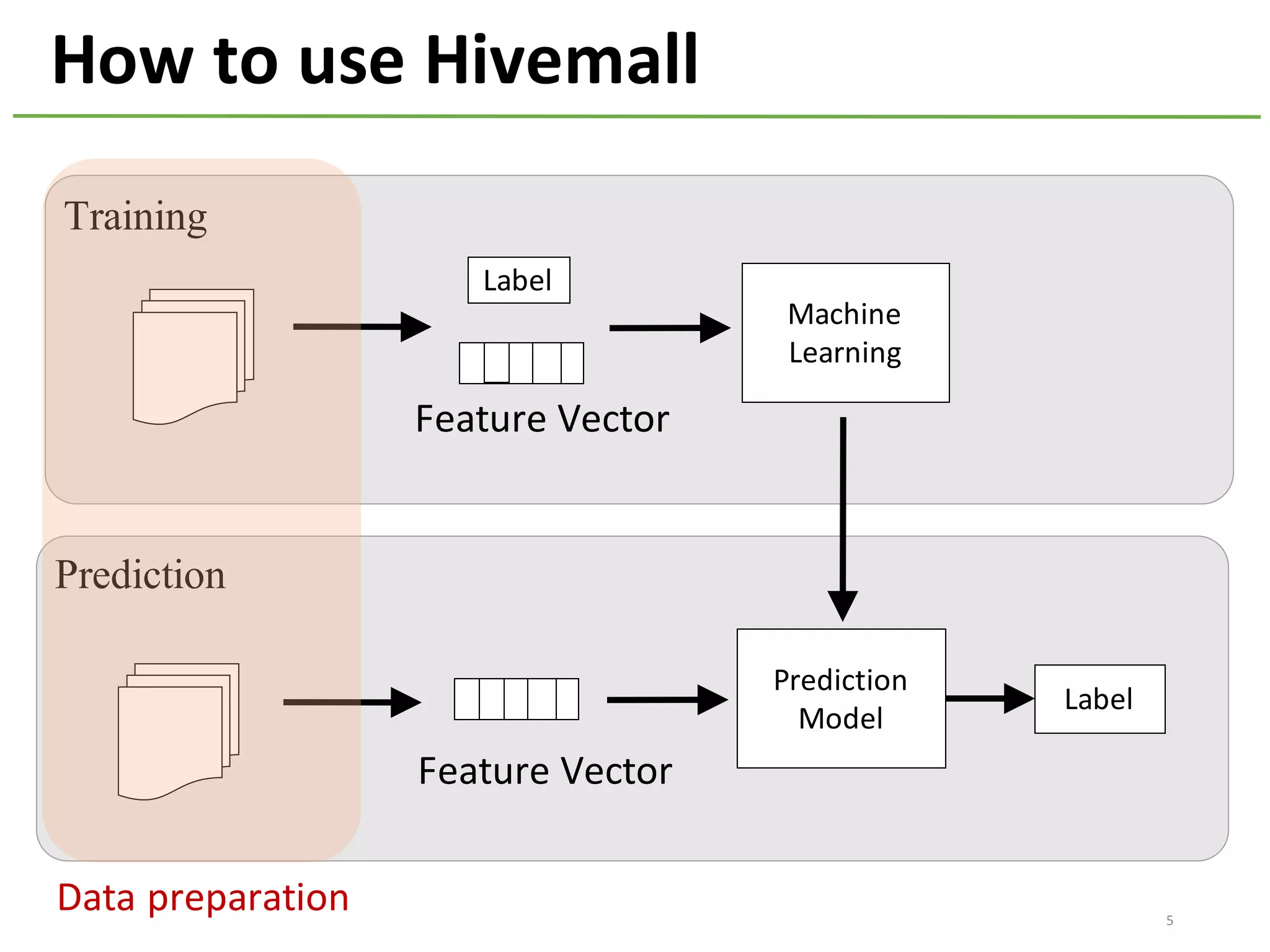
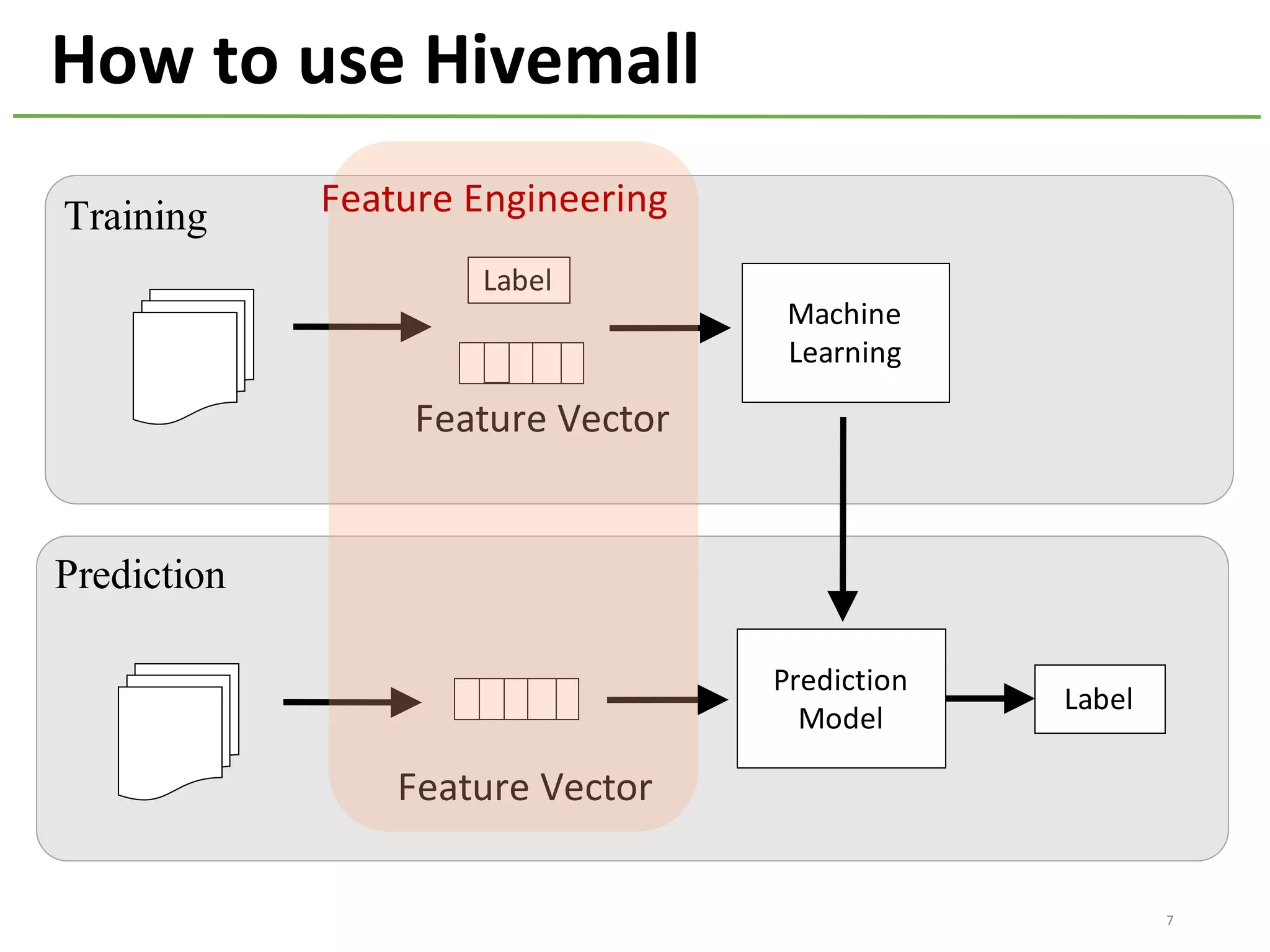
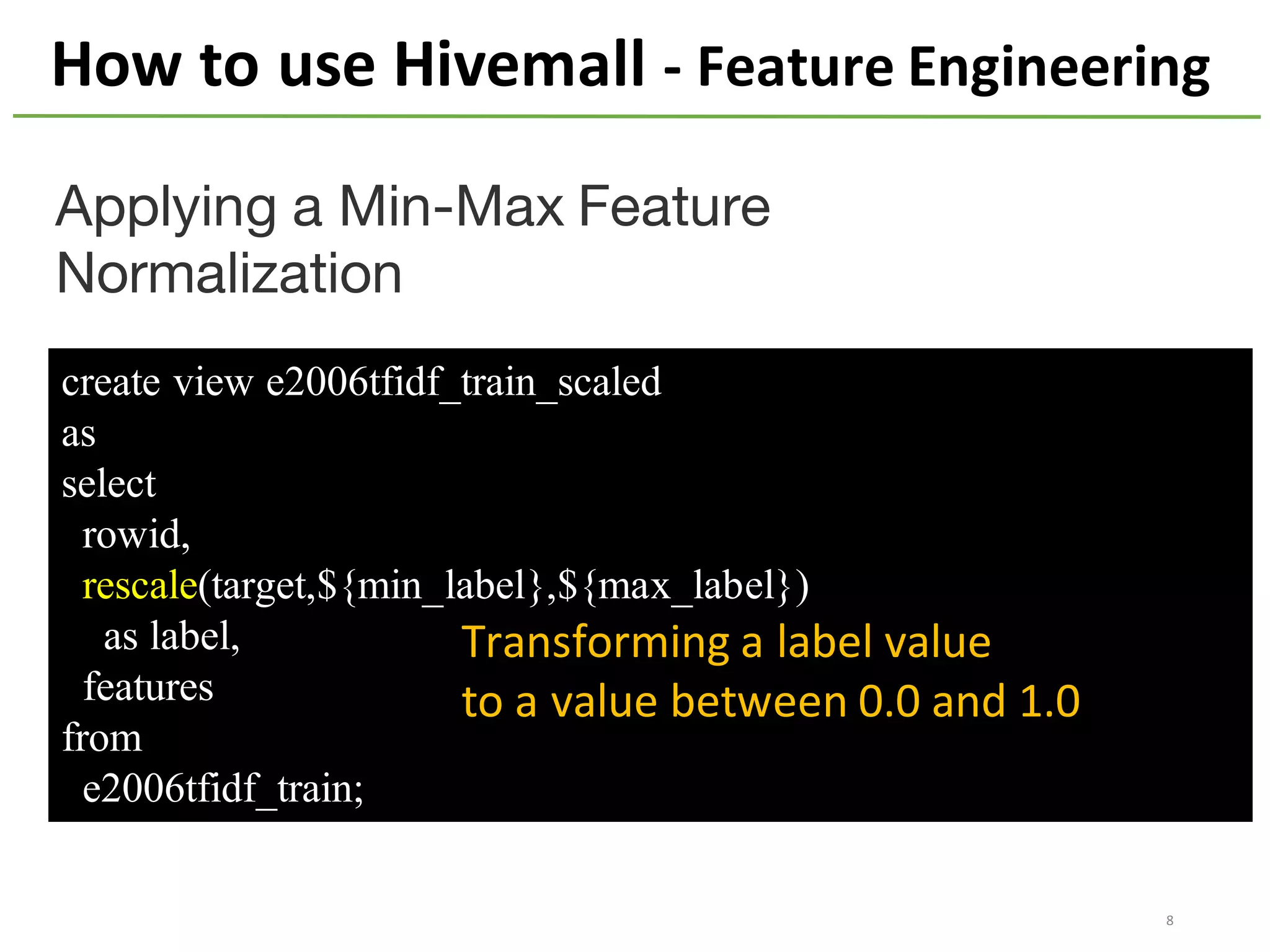
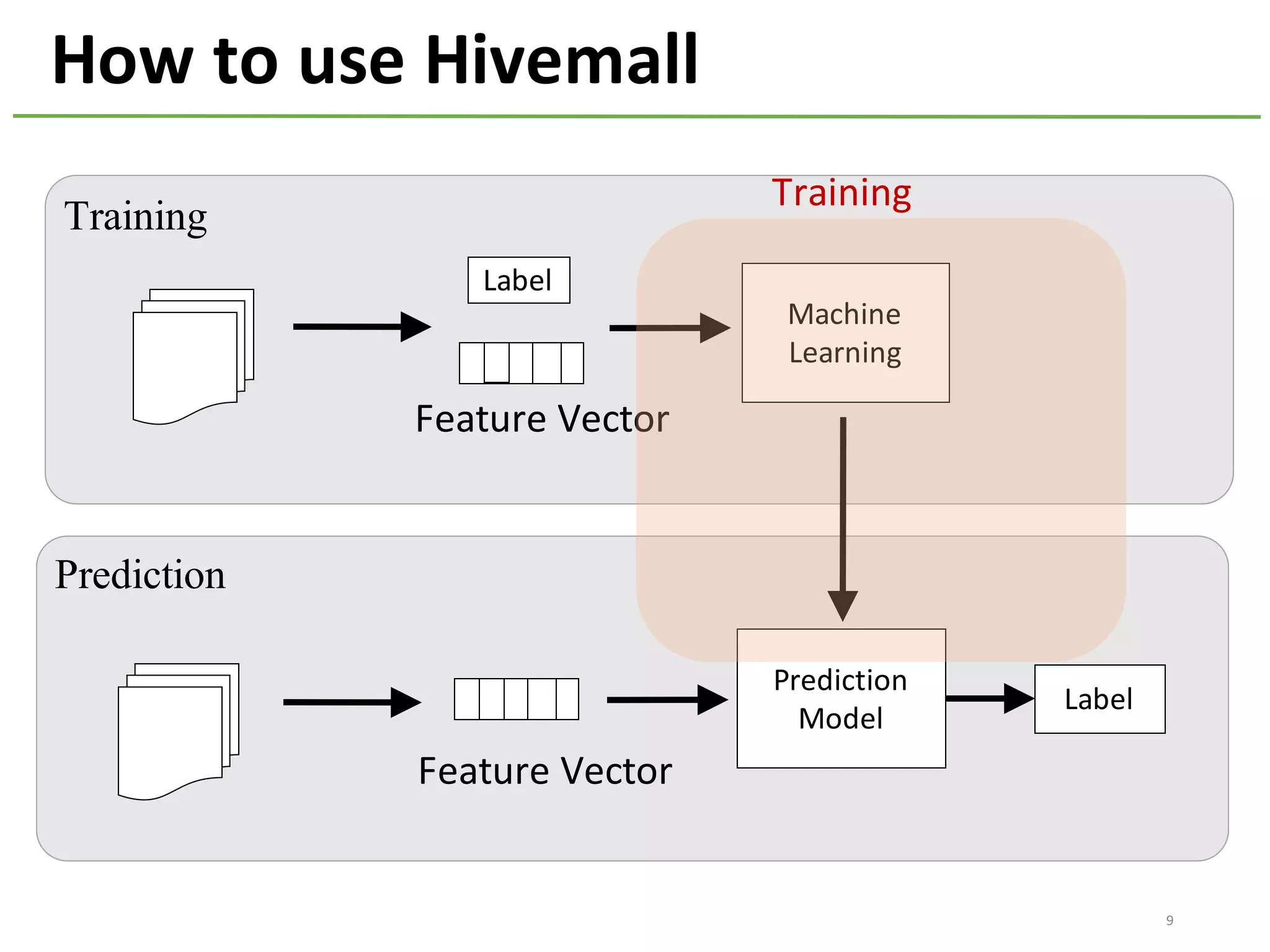
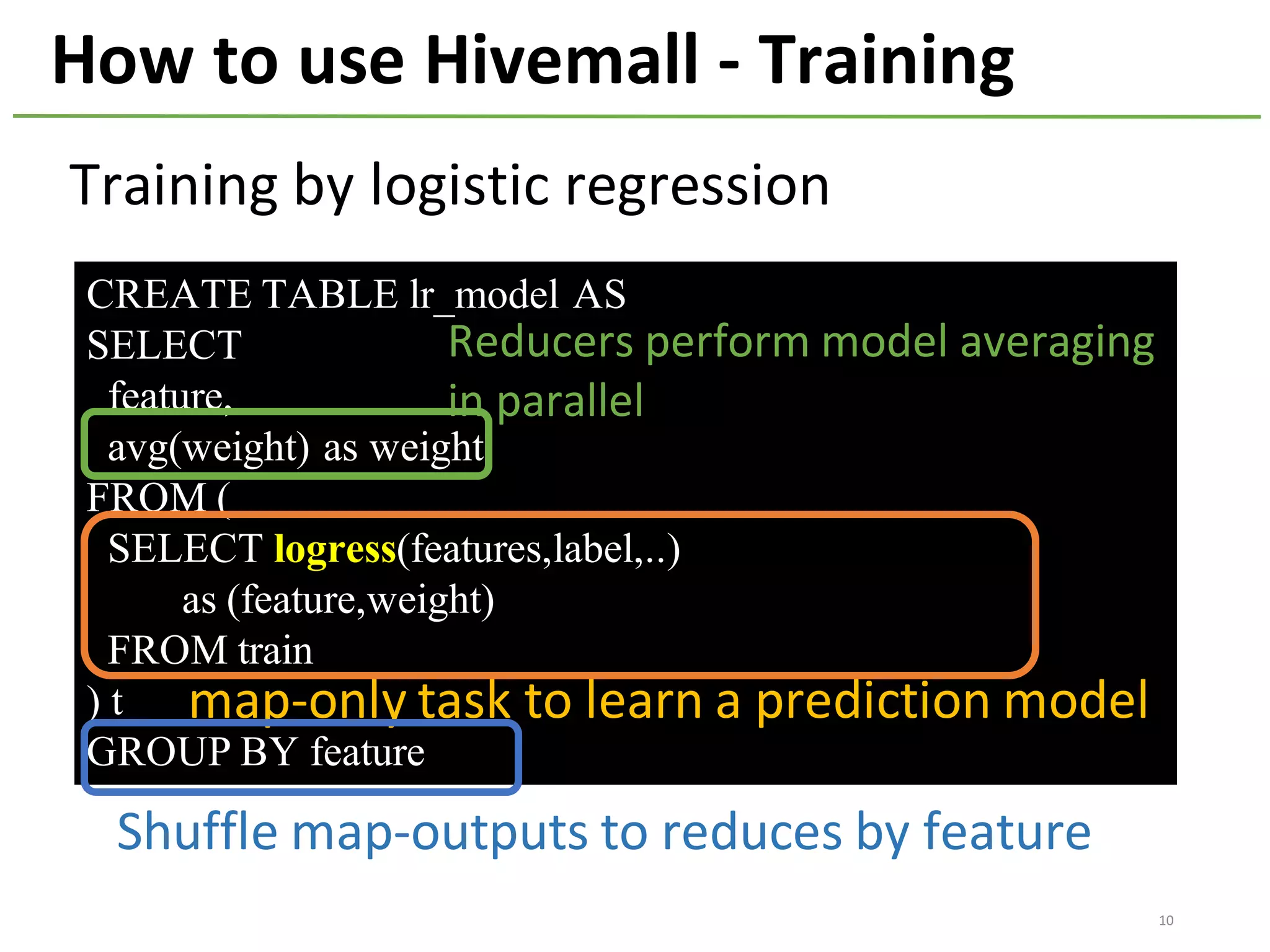
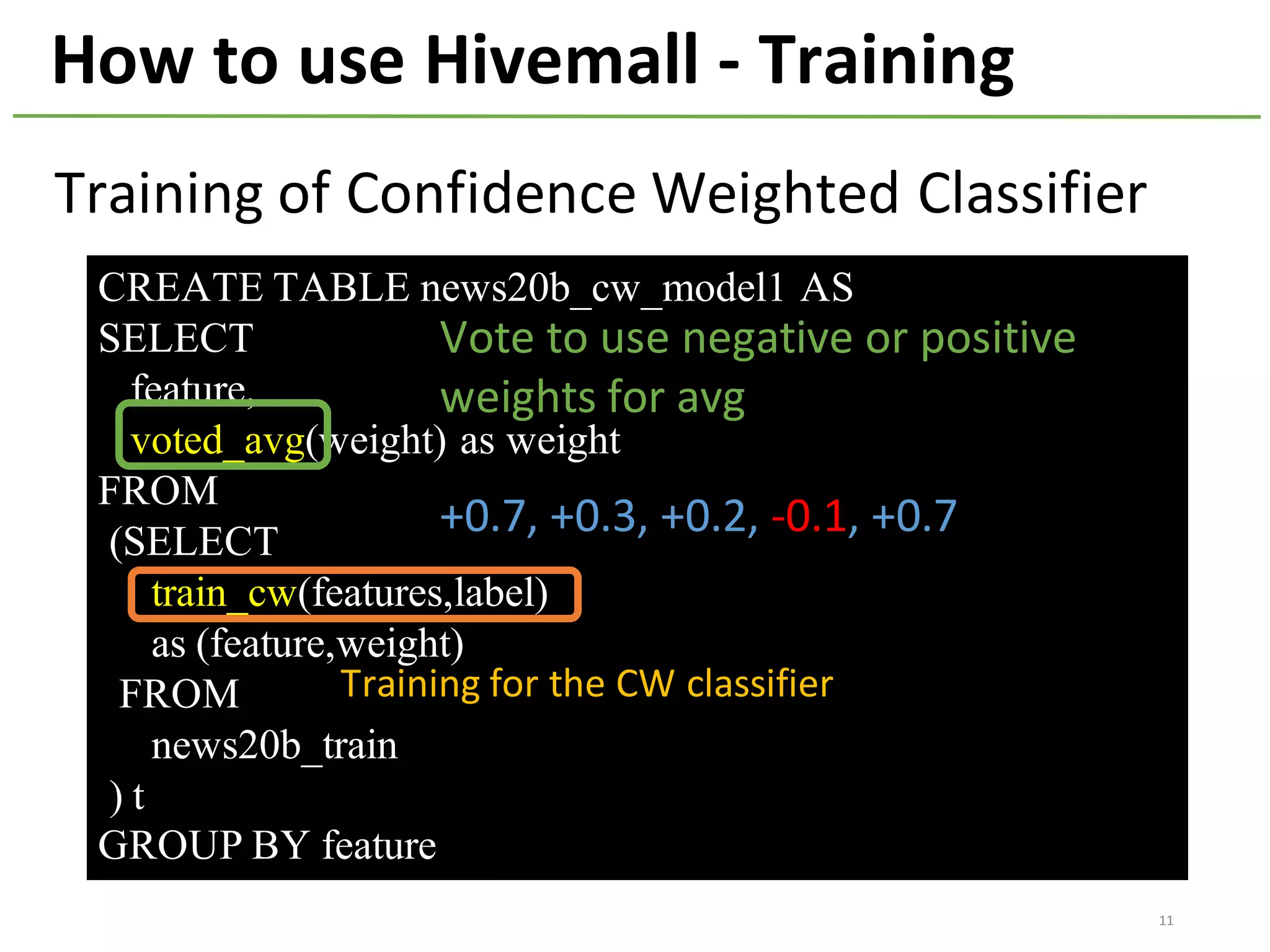
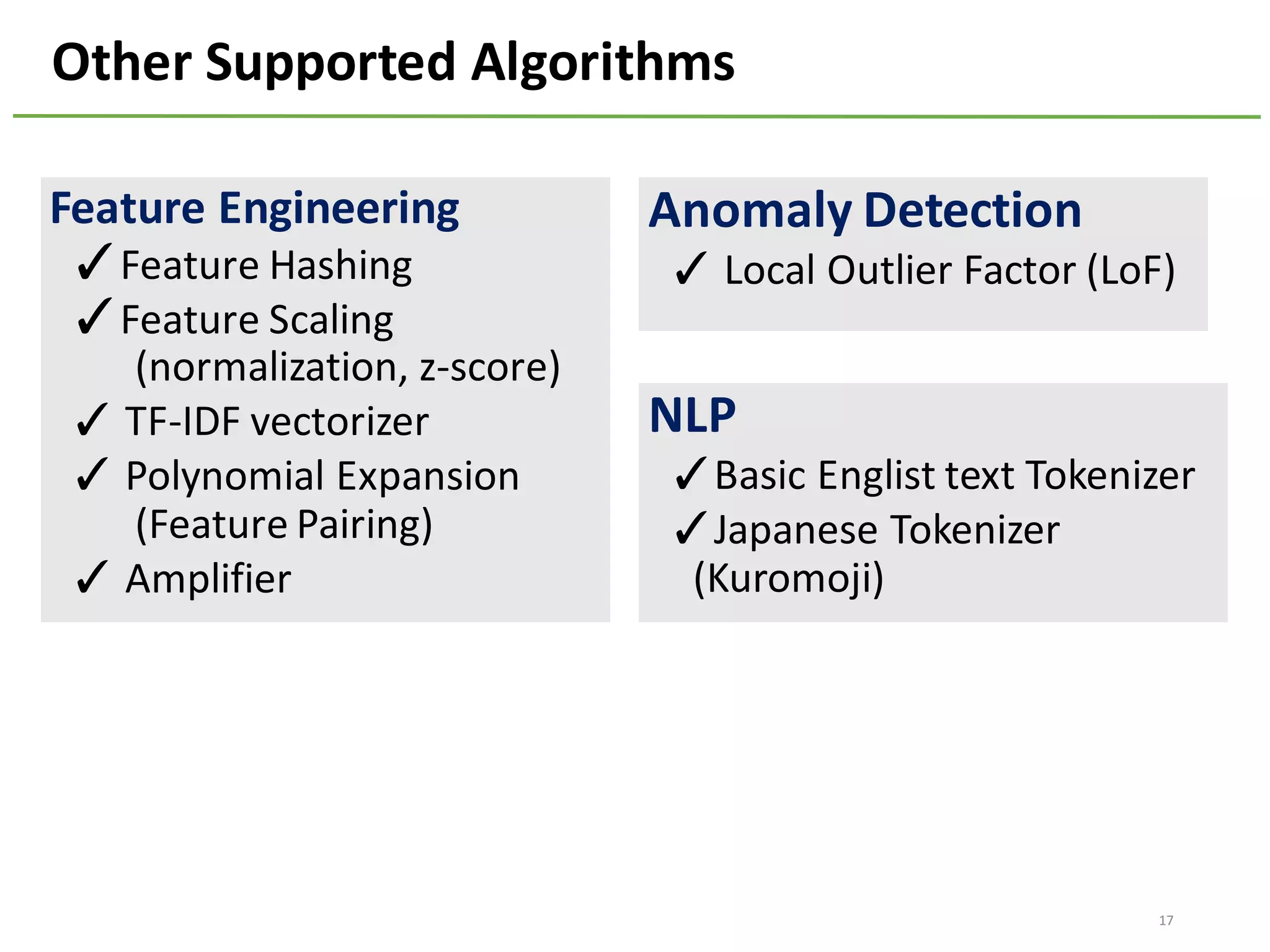
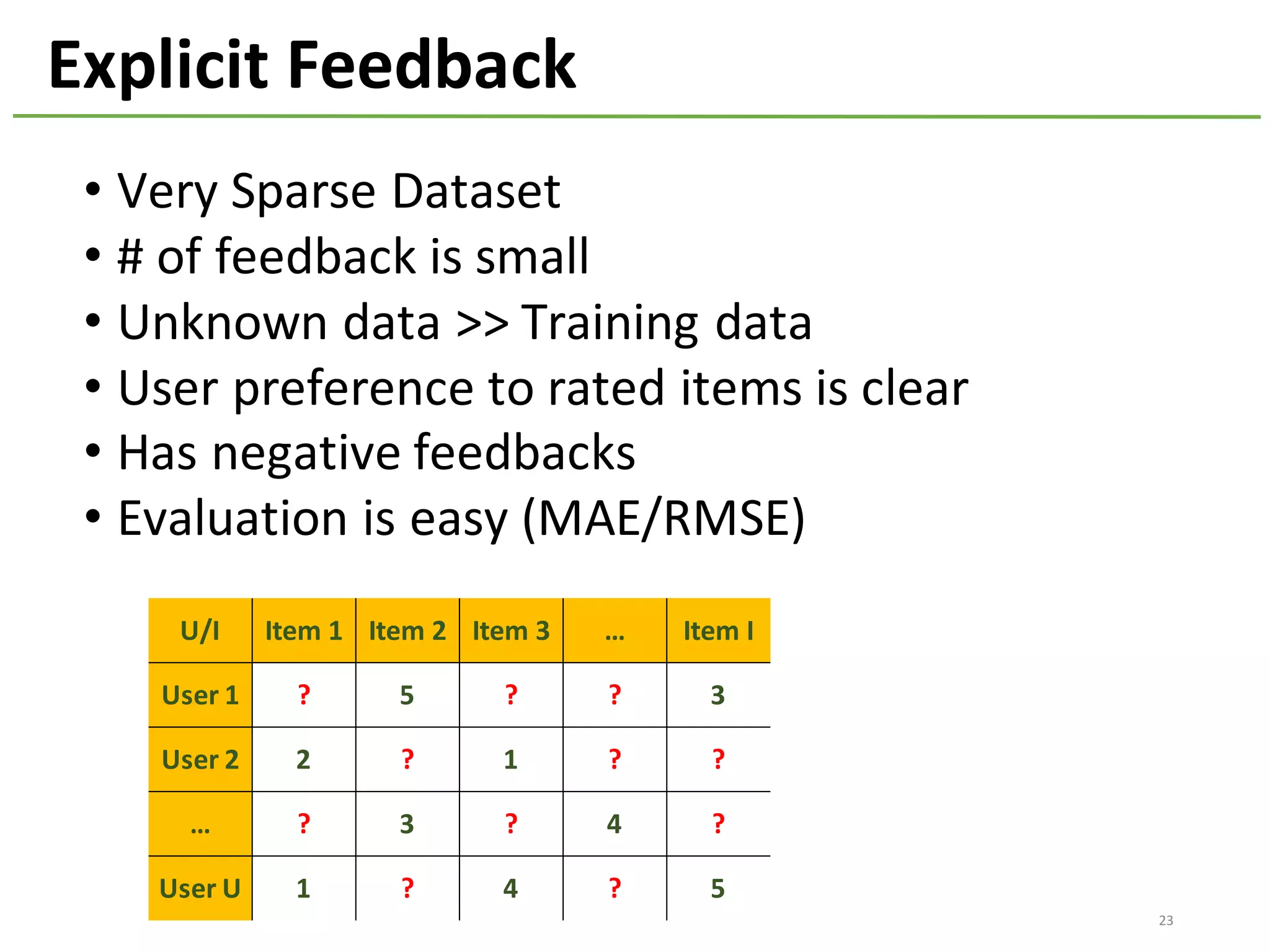
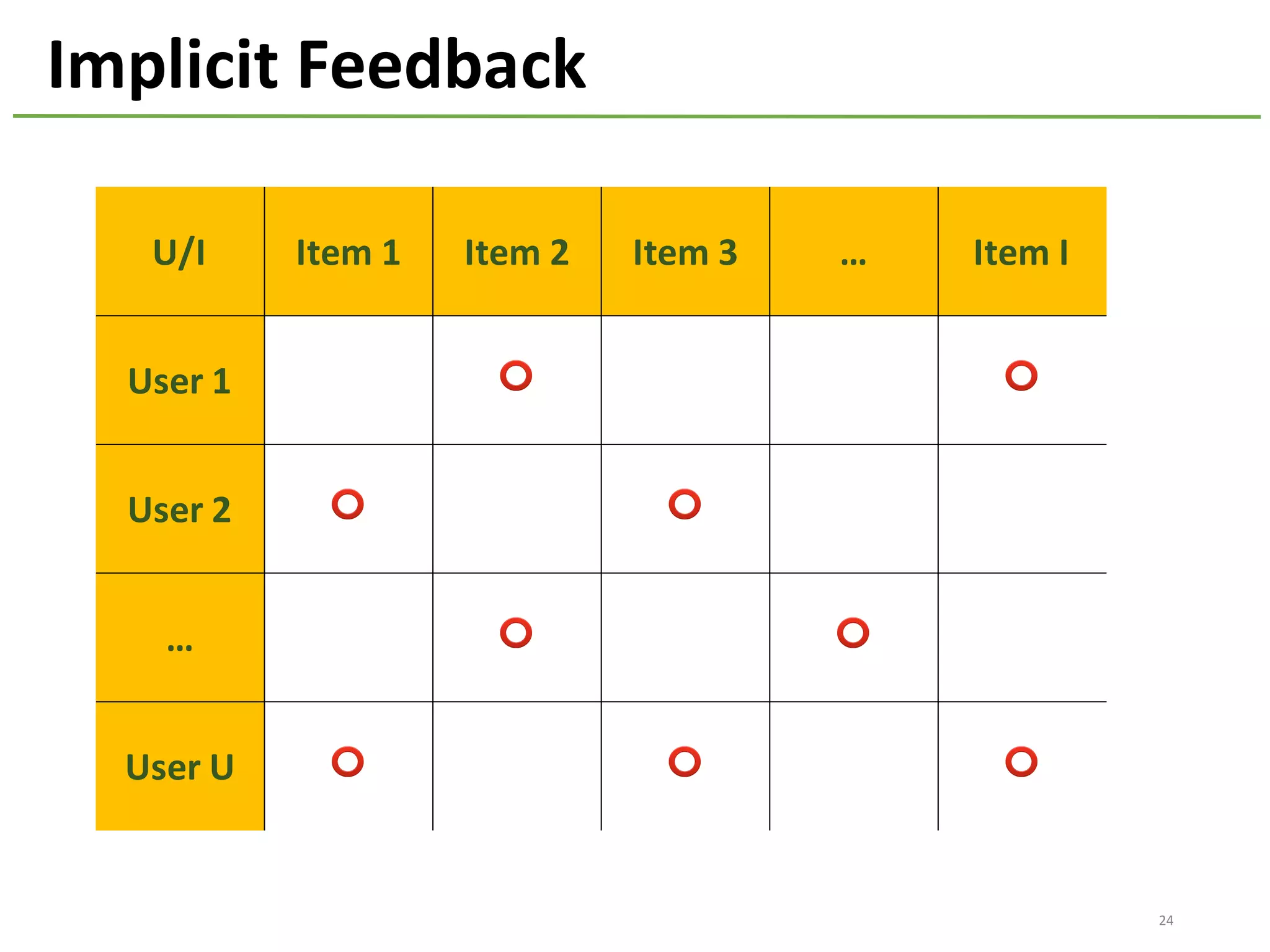
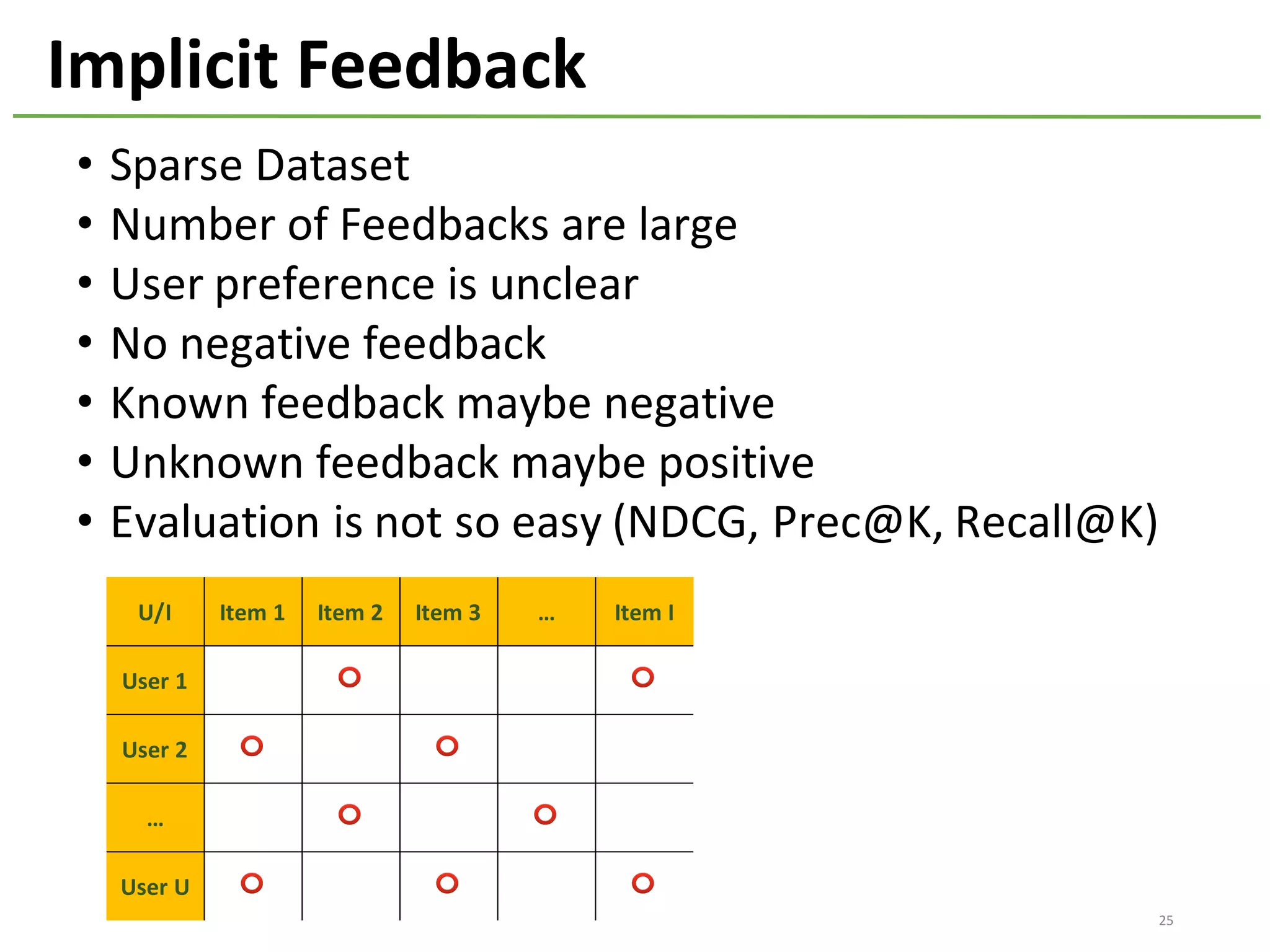
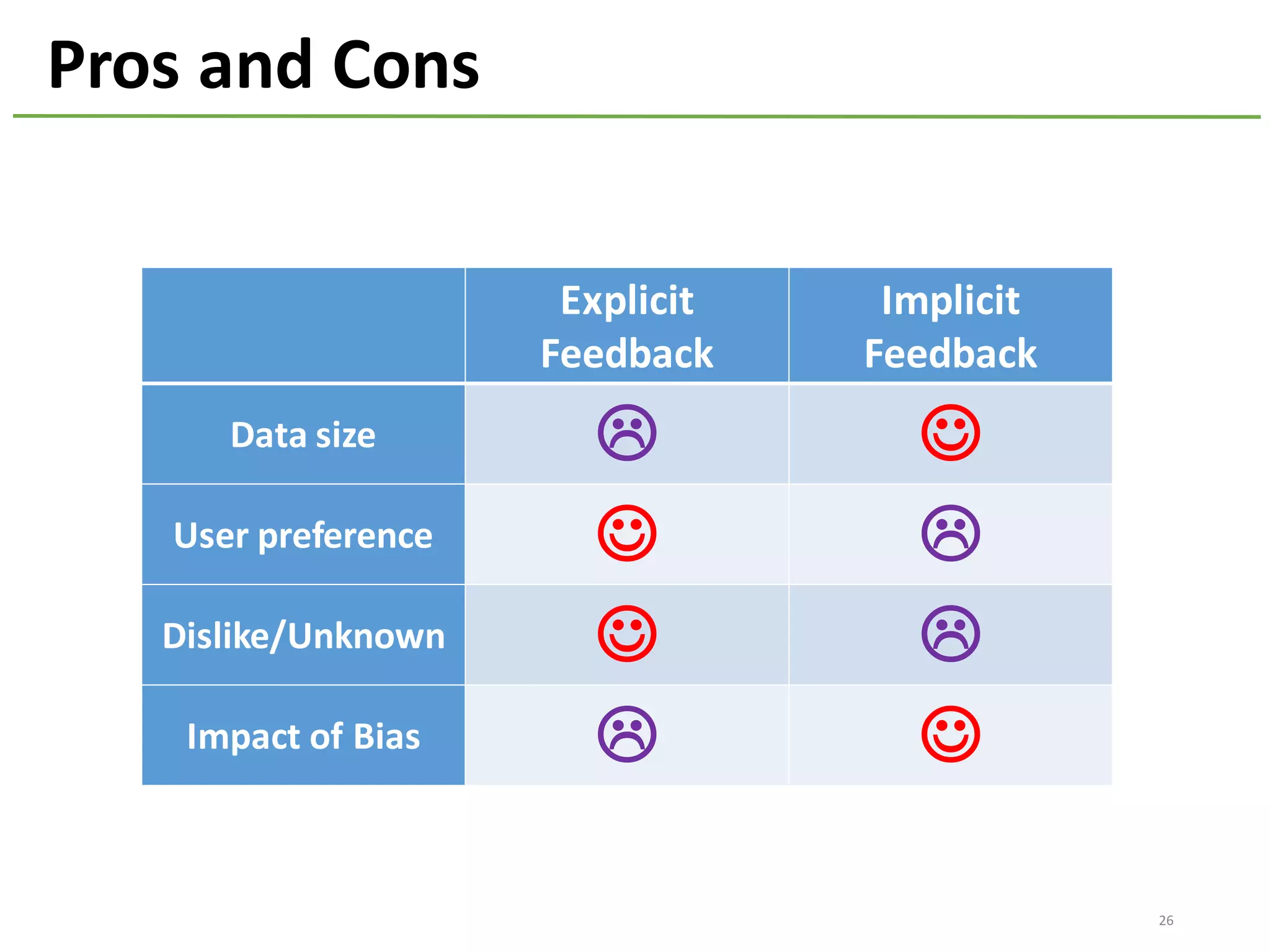
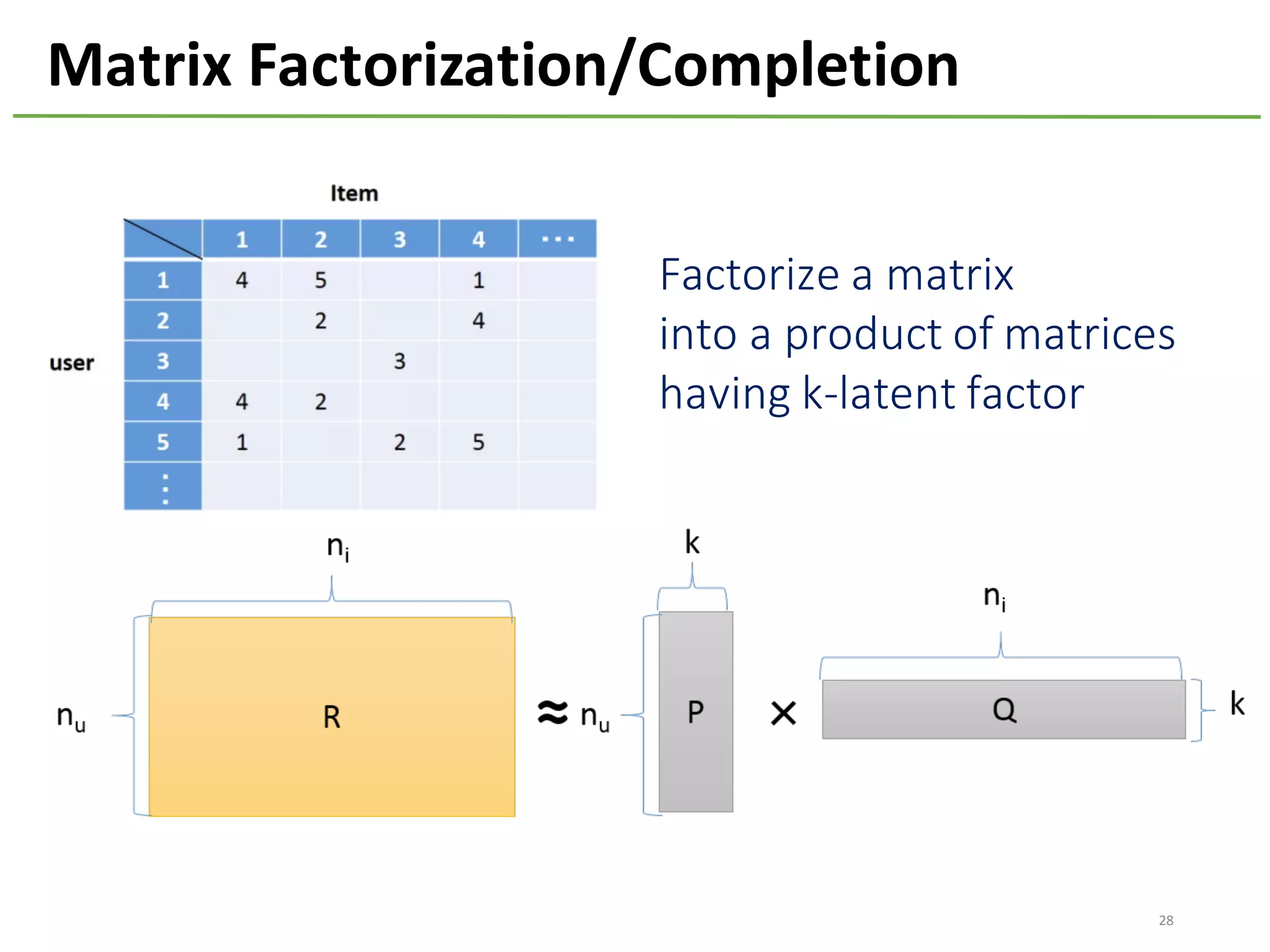
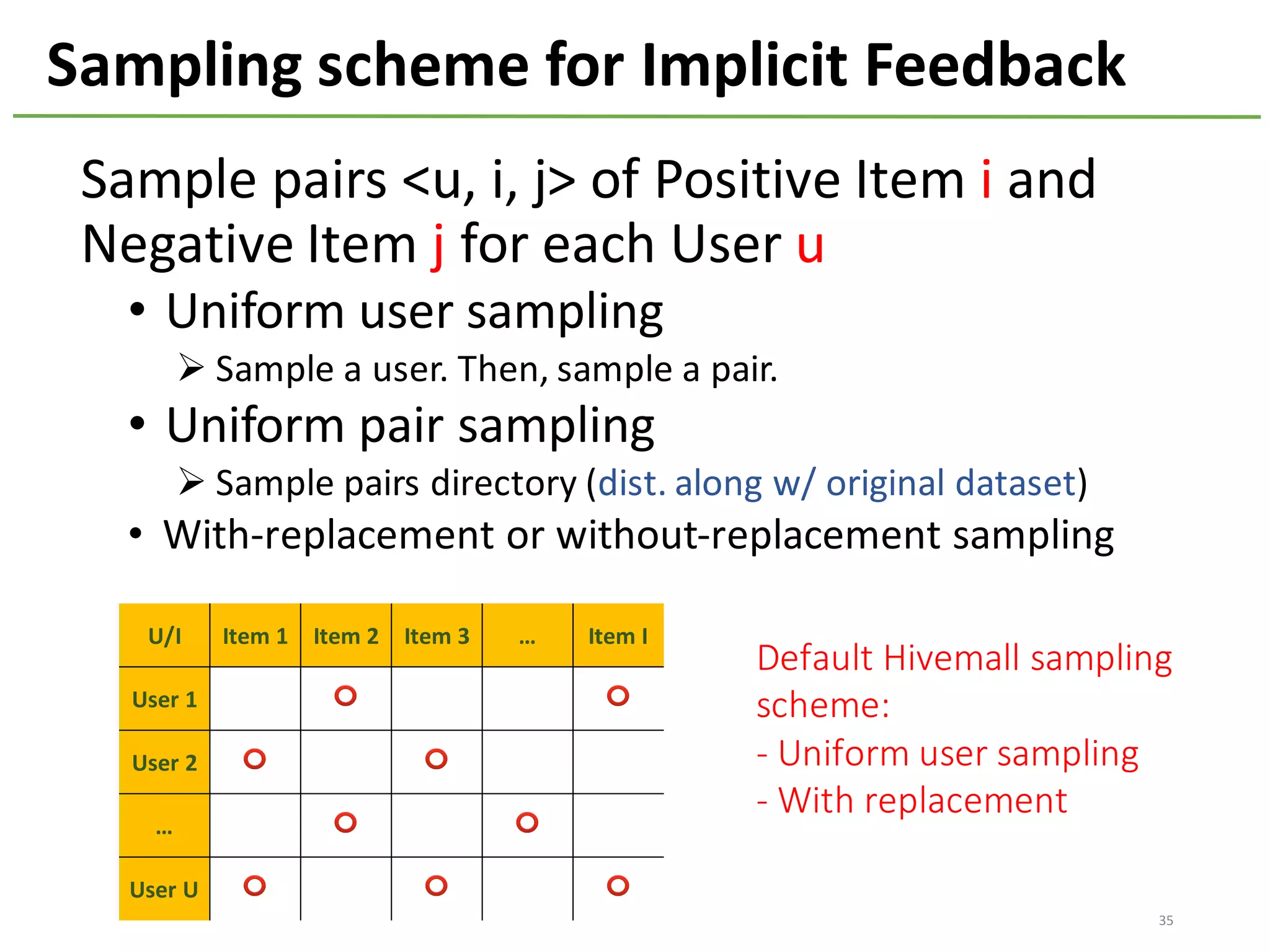
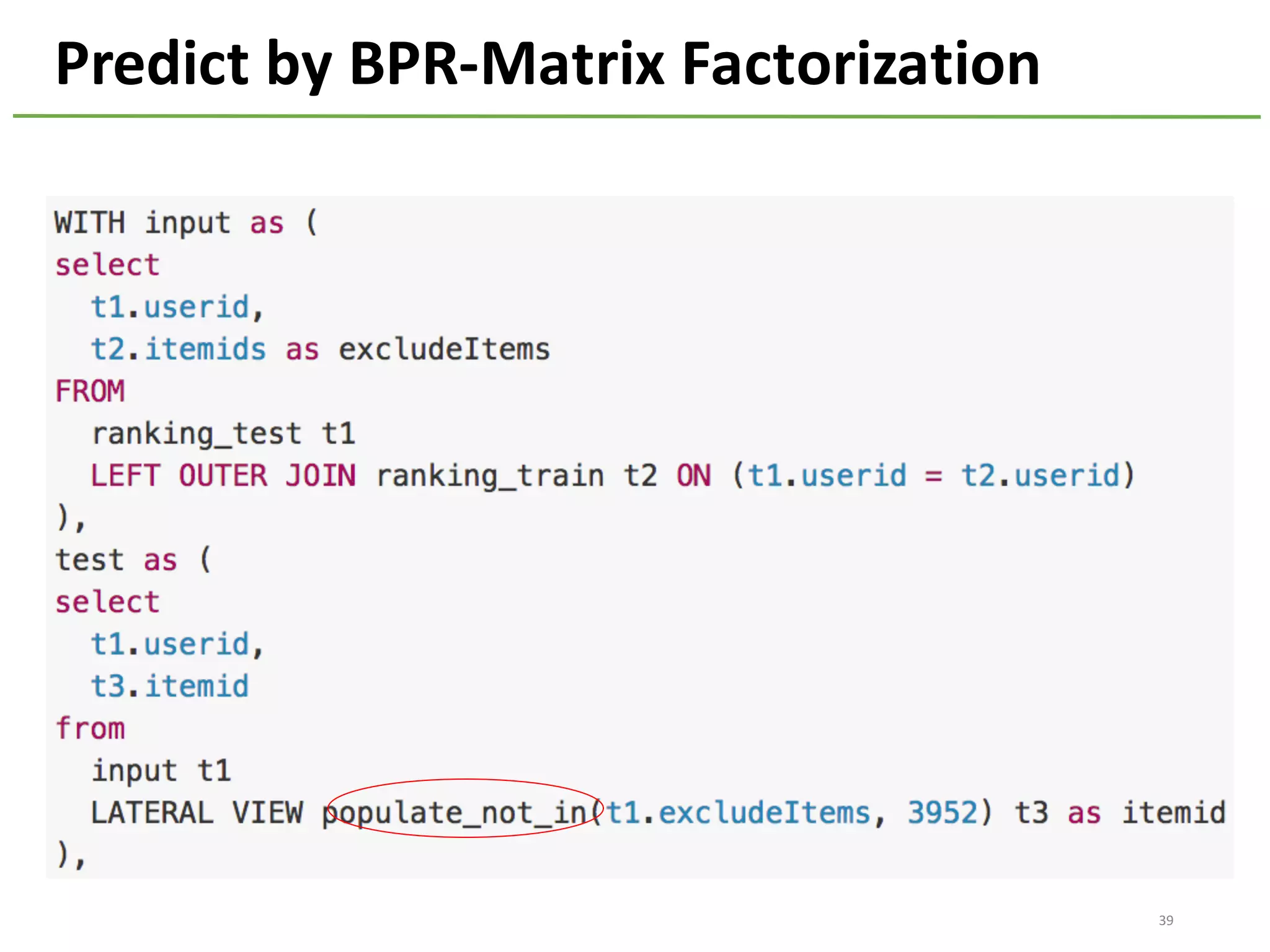
The document provides an overview of using Hivemall, an open source machine learning library built for Hive, for recommendation tasks. It begins with an introduction to Hivemall and its vision of enabling machine learning on SQL. It then covers recommendation 101, discussing explicit versus implicit feedback. Matrix factorization and Bayesian probabilistic ranking algorithms for recommendations from implicit feedback are described. Key aspects covered include data preparation in Hive, model training, and prediction. The document concludes with considerations for building recommendations on large, implicit feedback datasets in Hivemall.