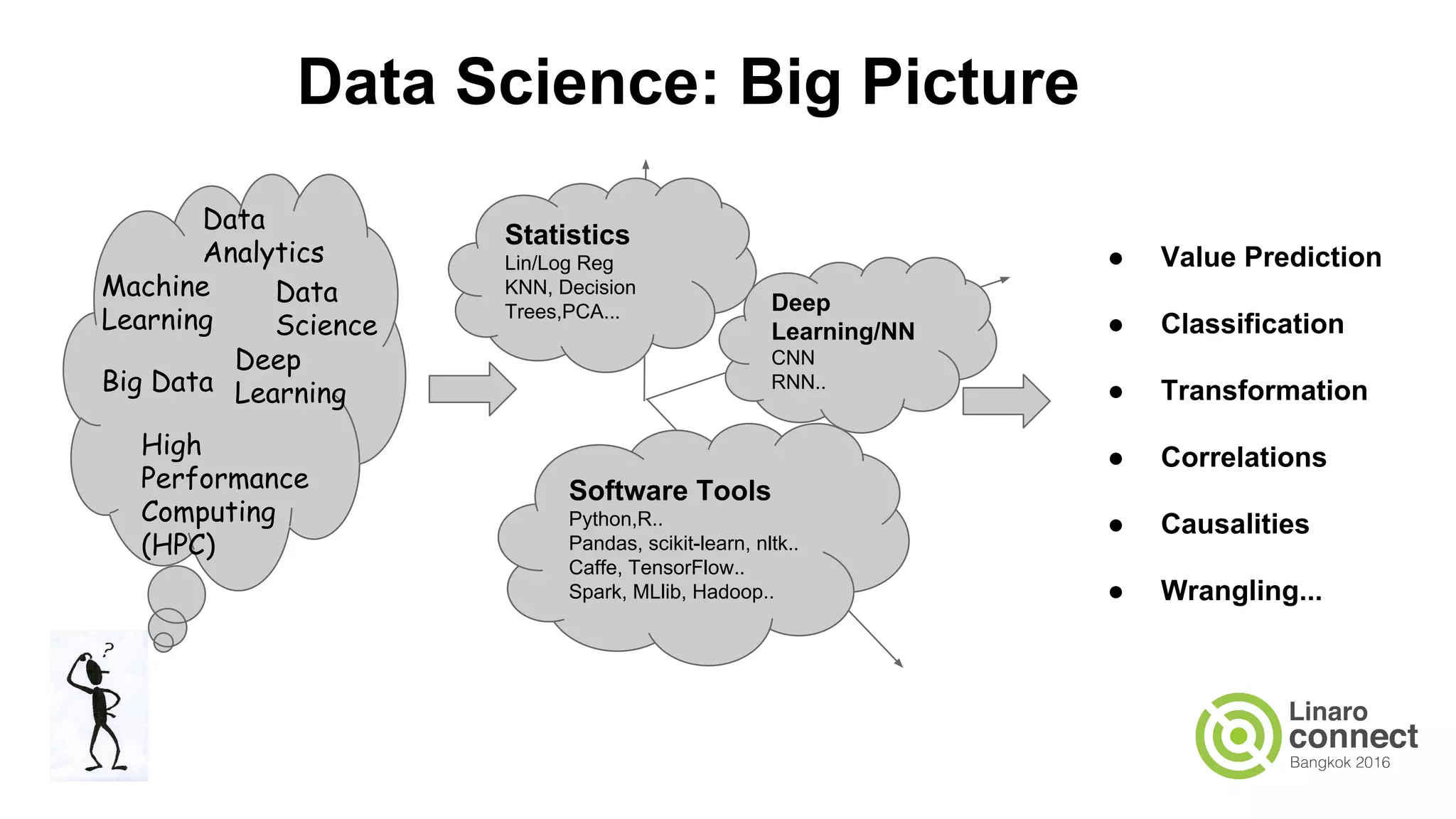
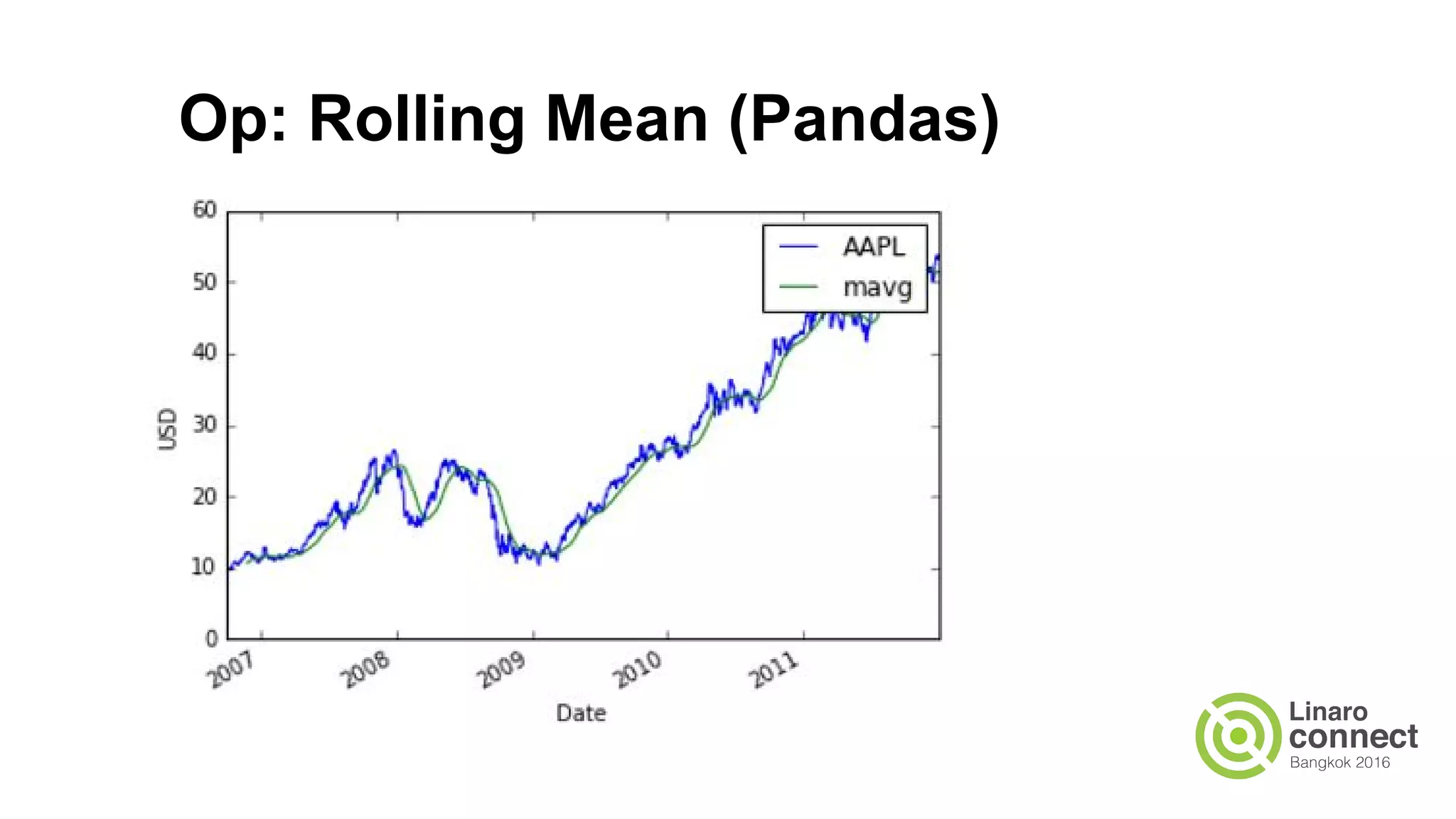
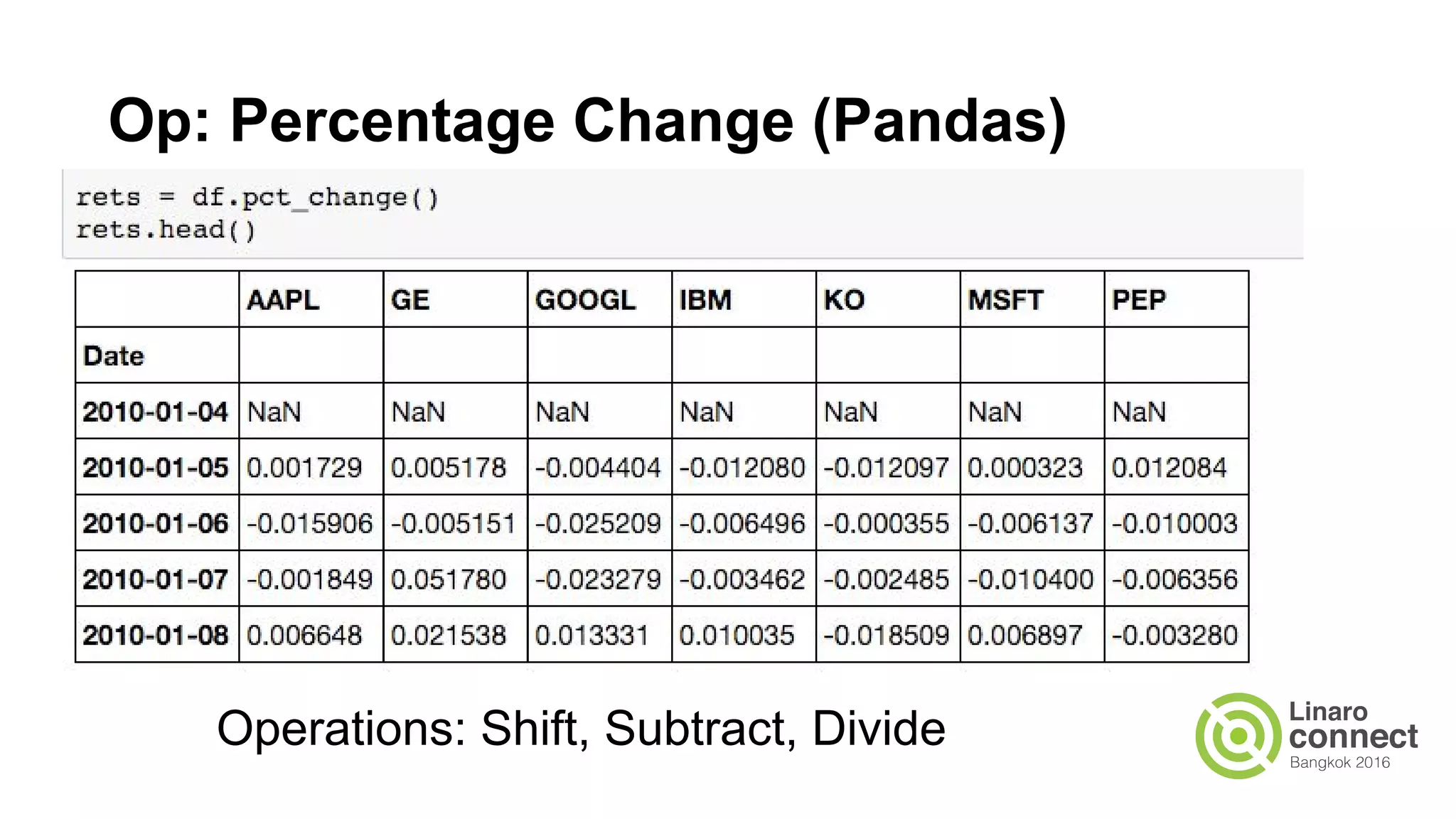
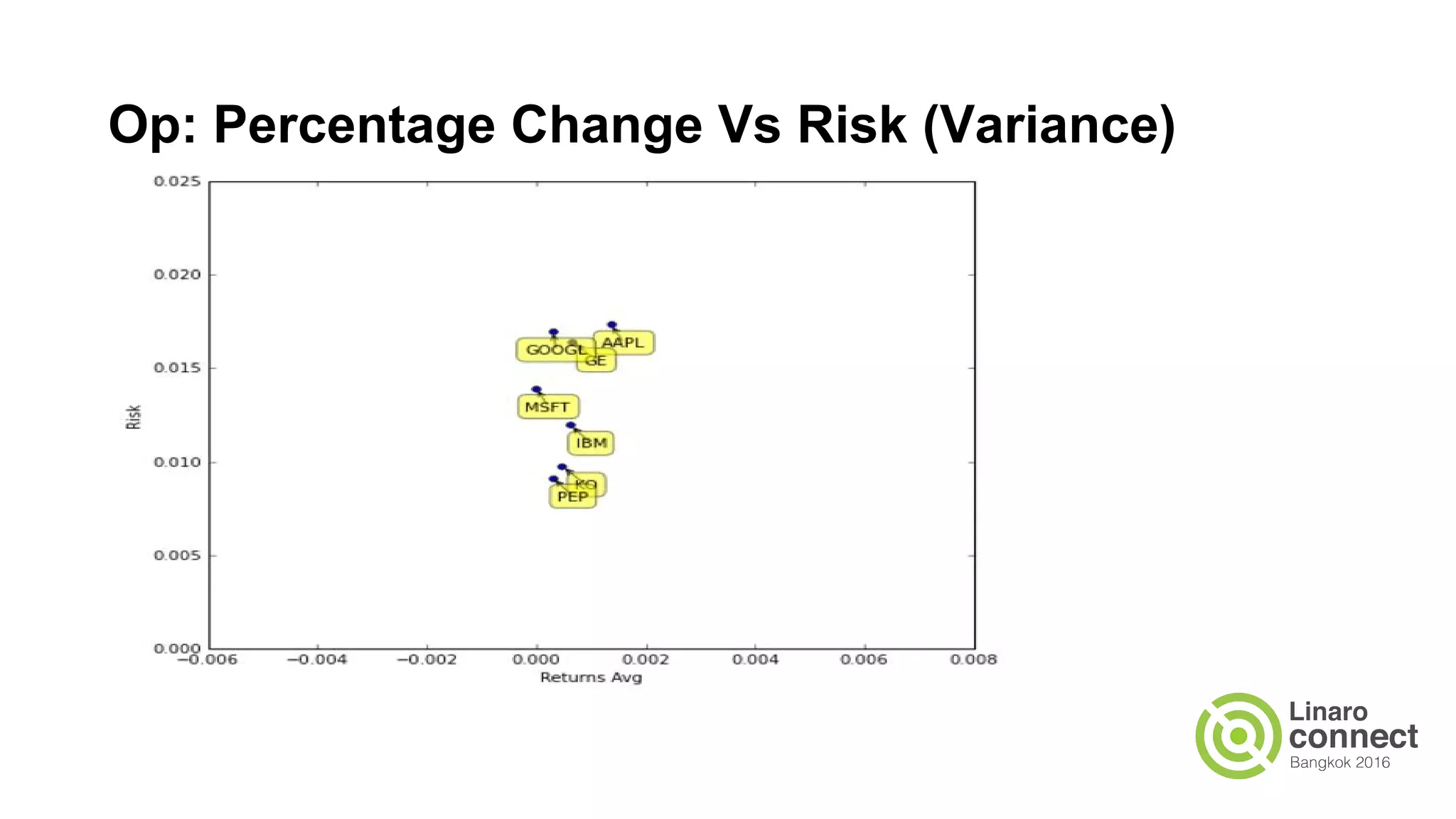
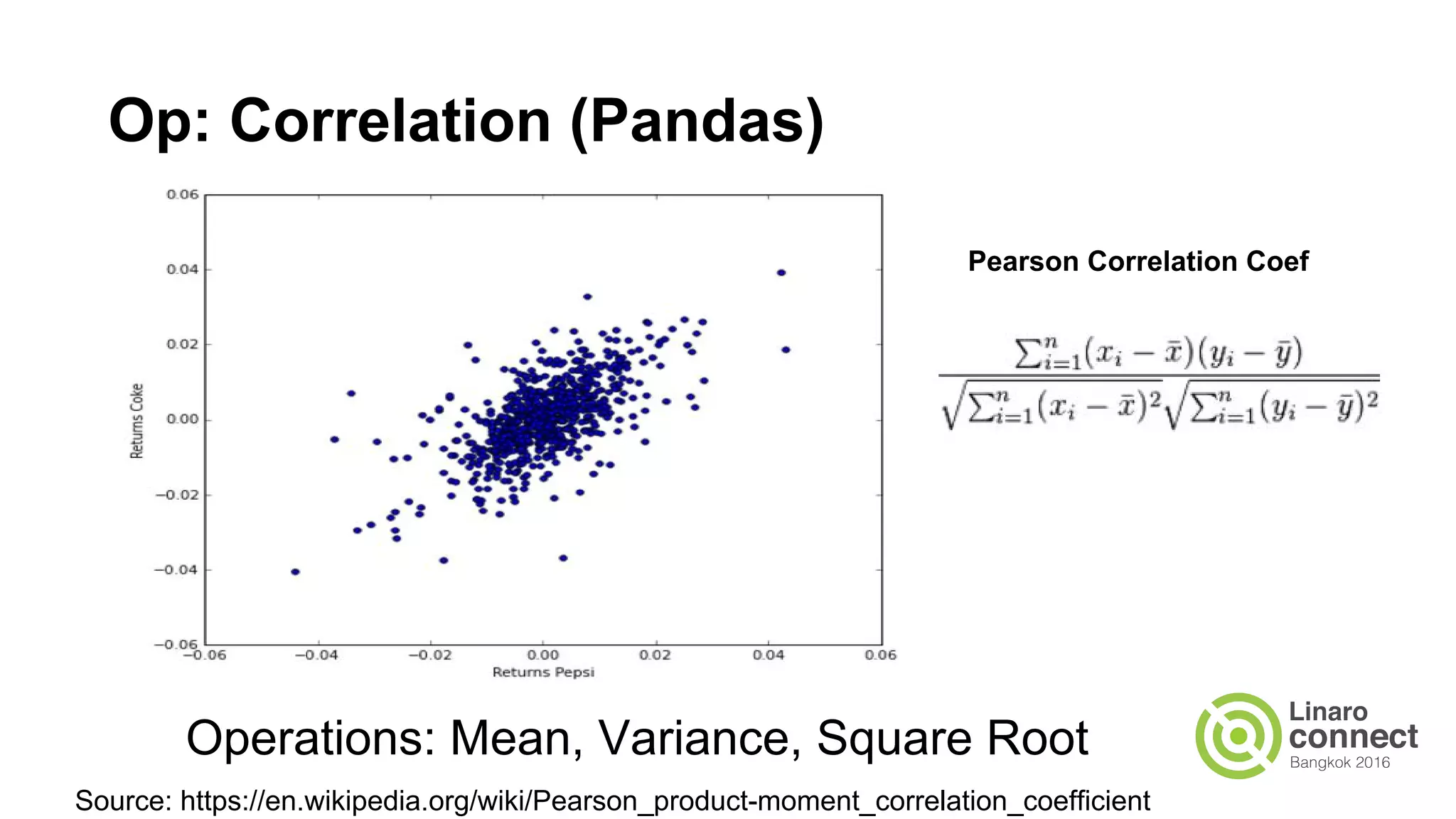
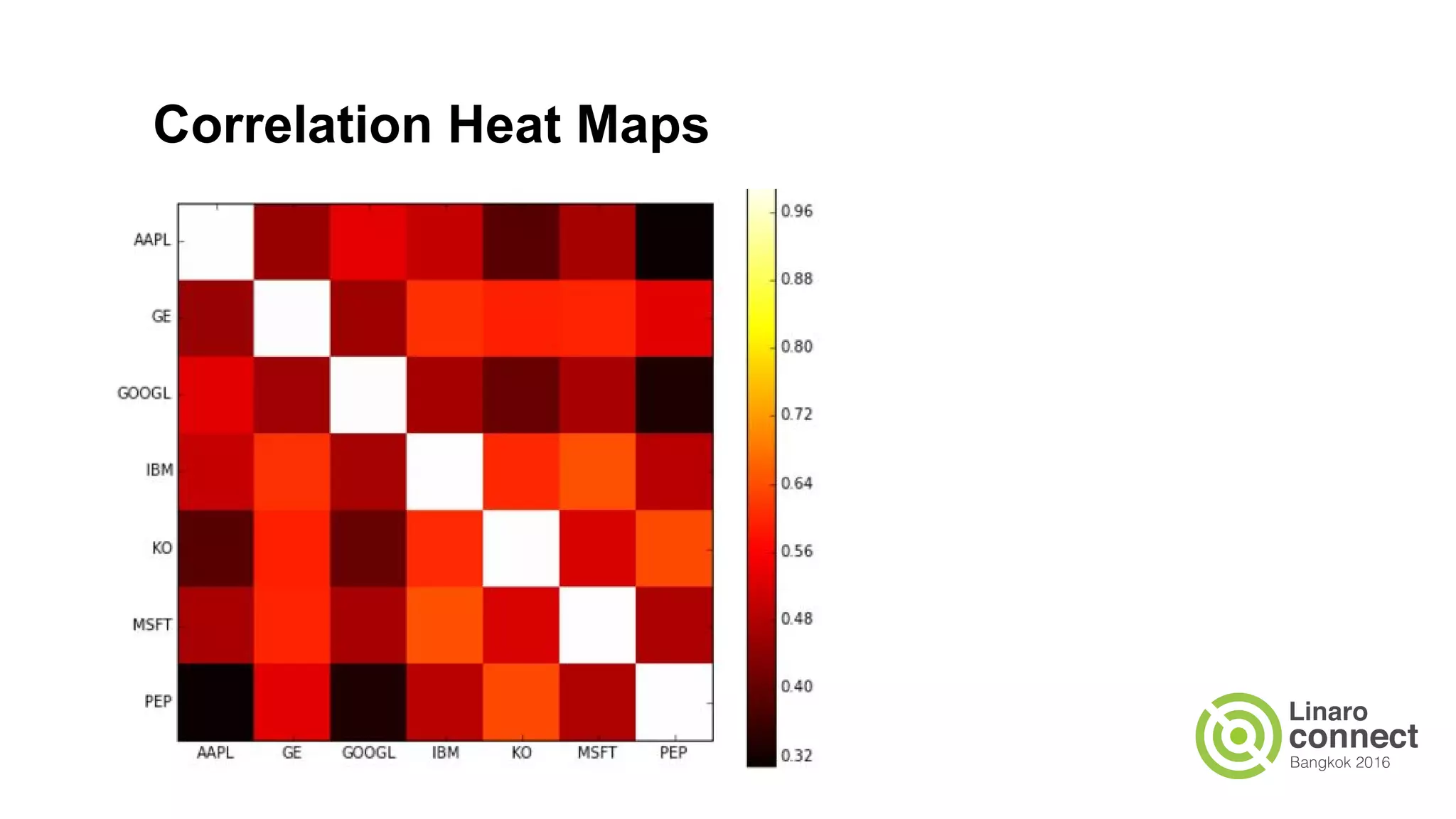
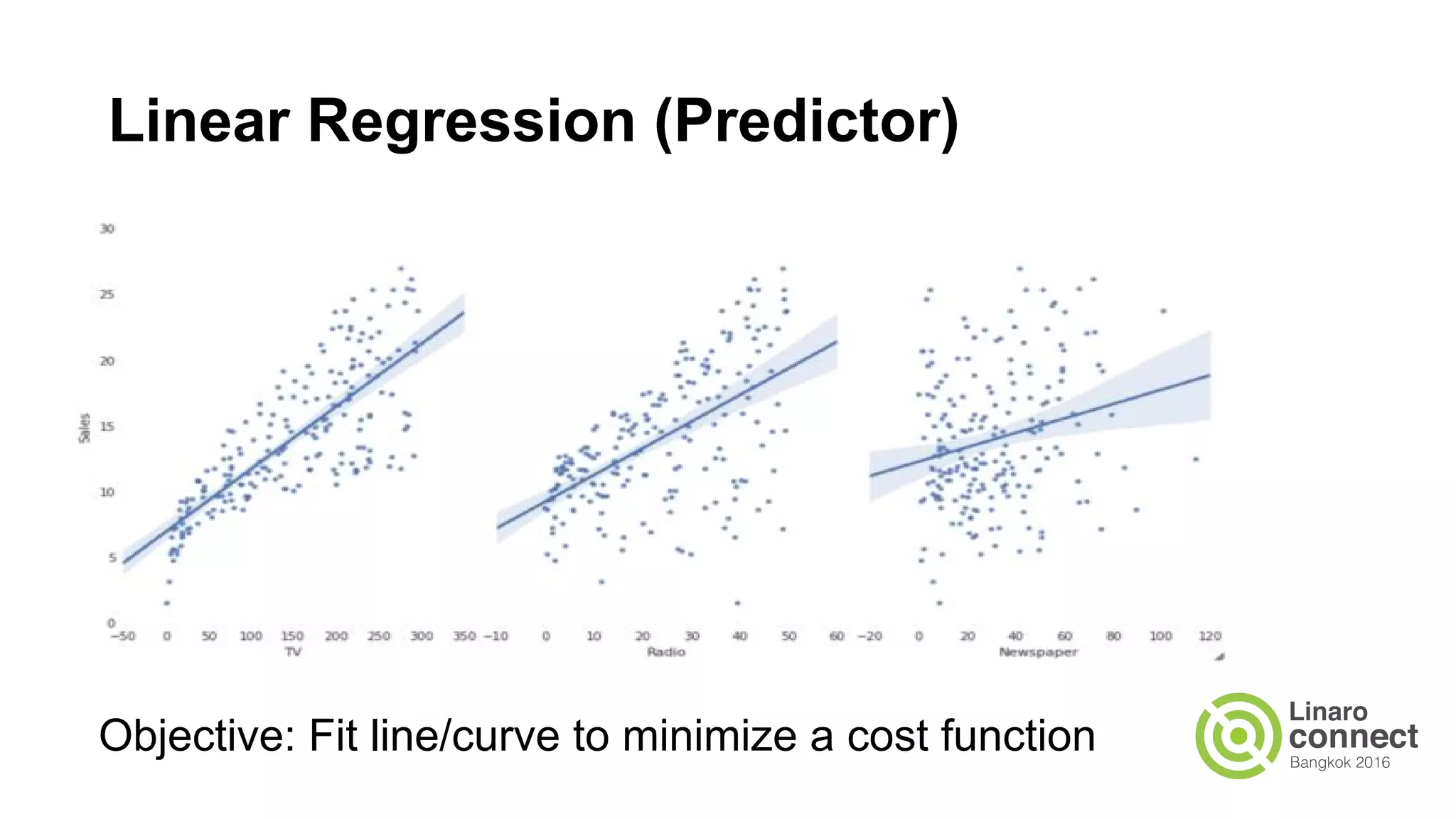
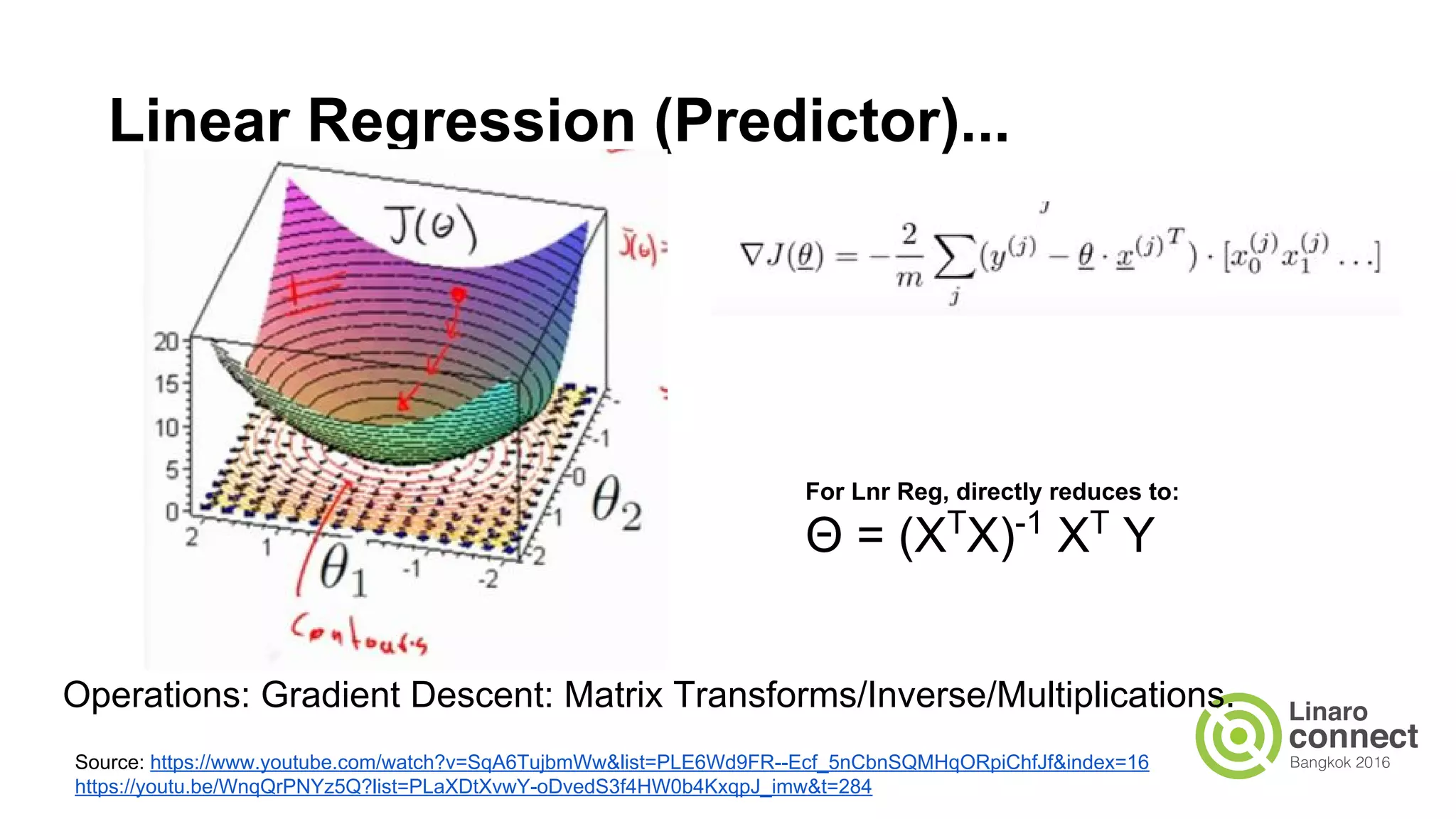
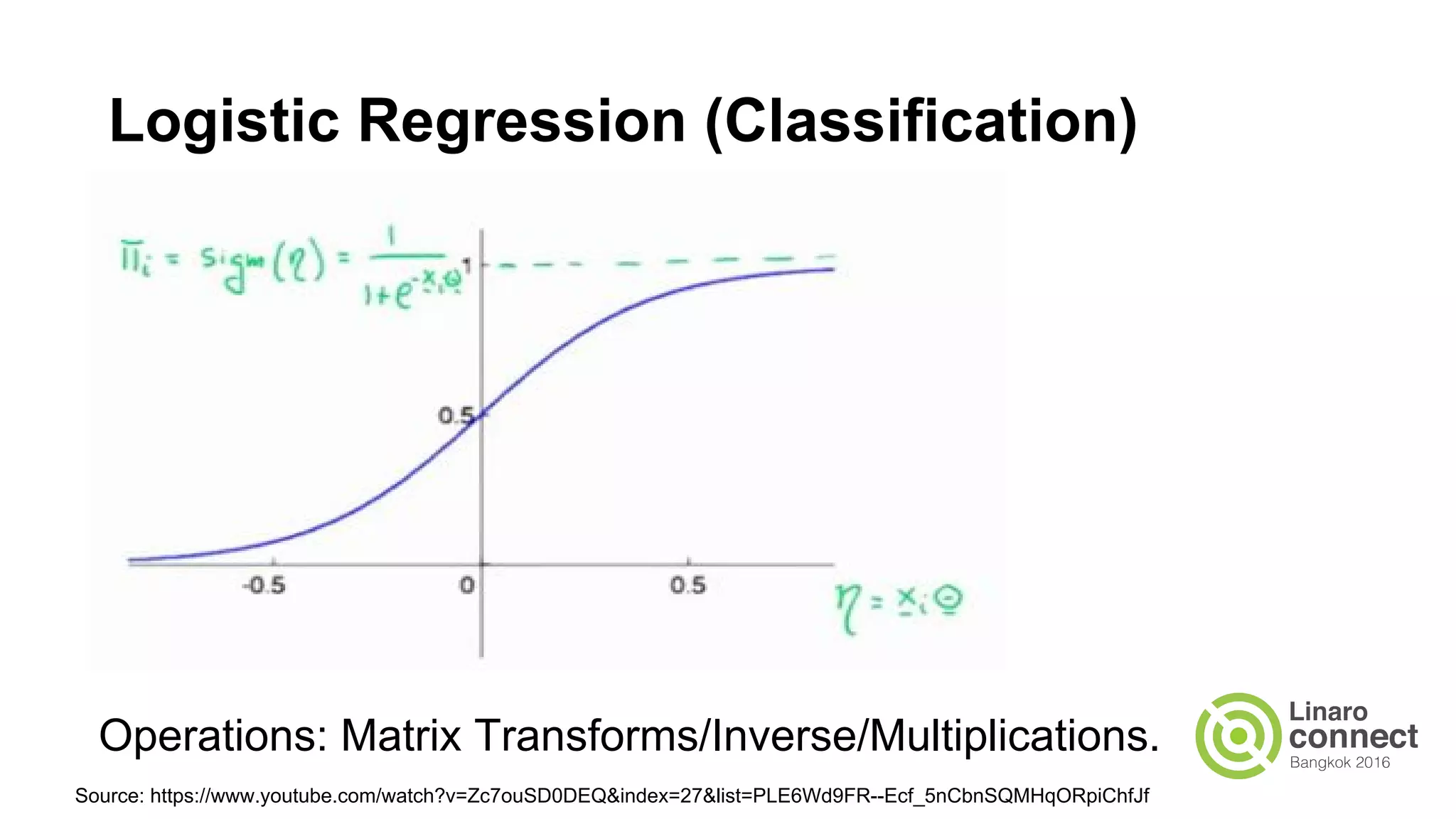
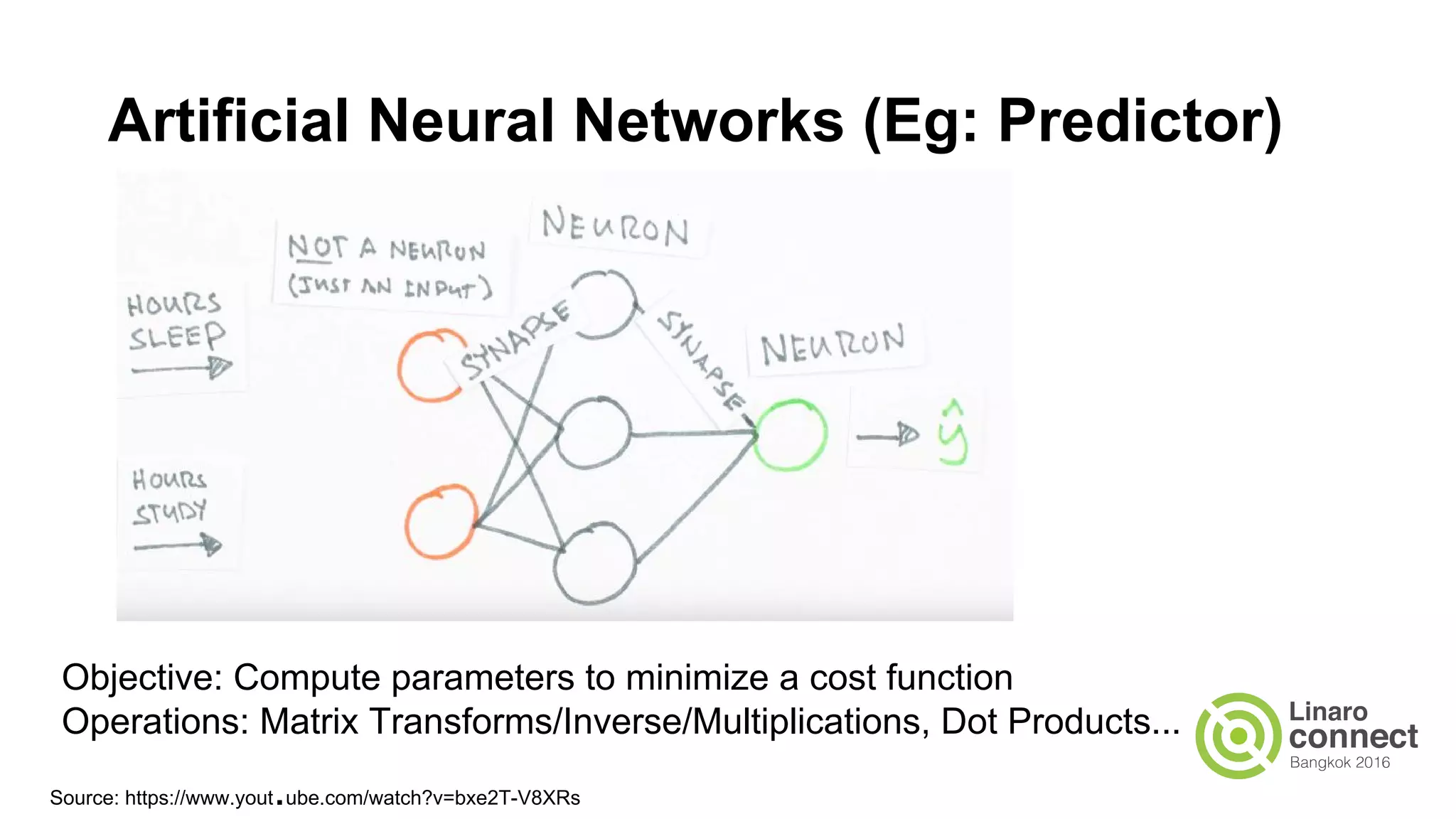
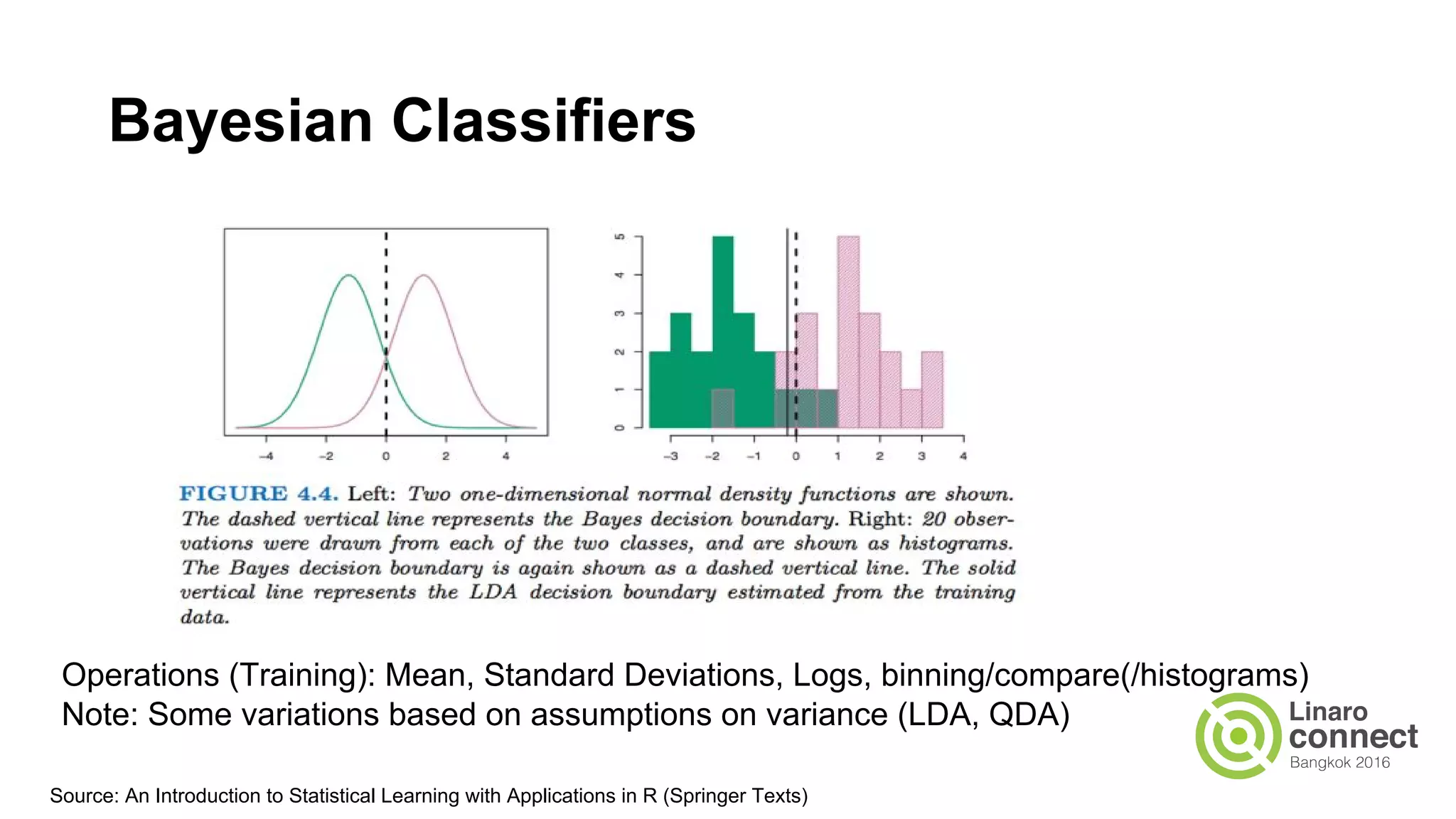
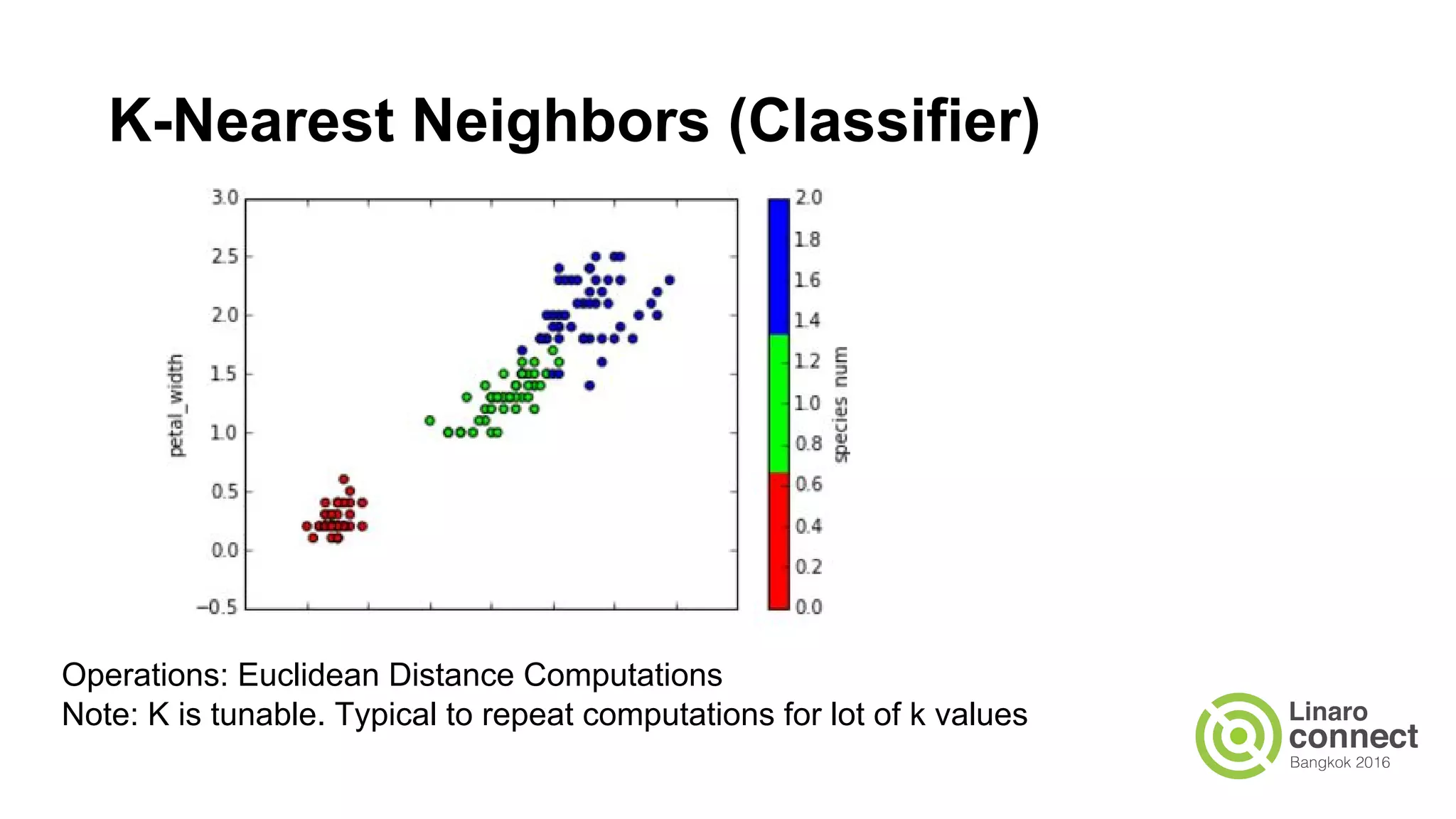
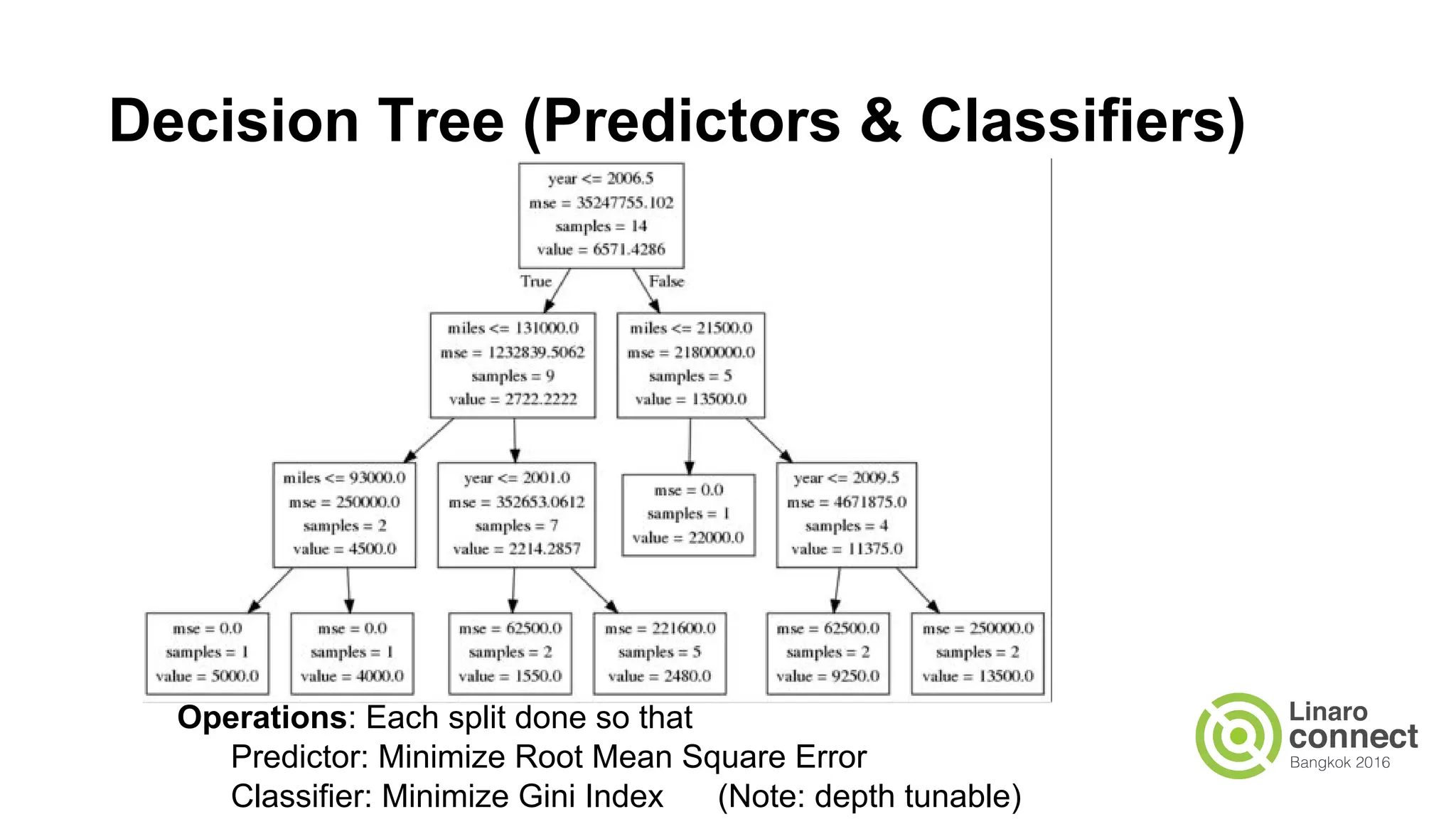
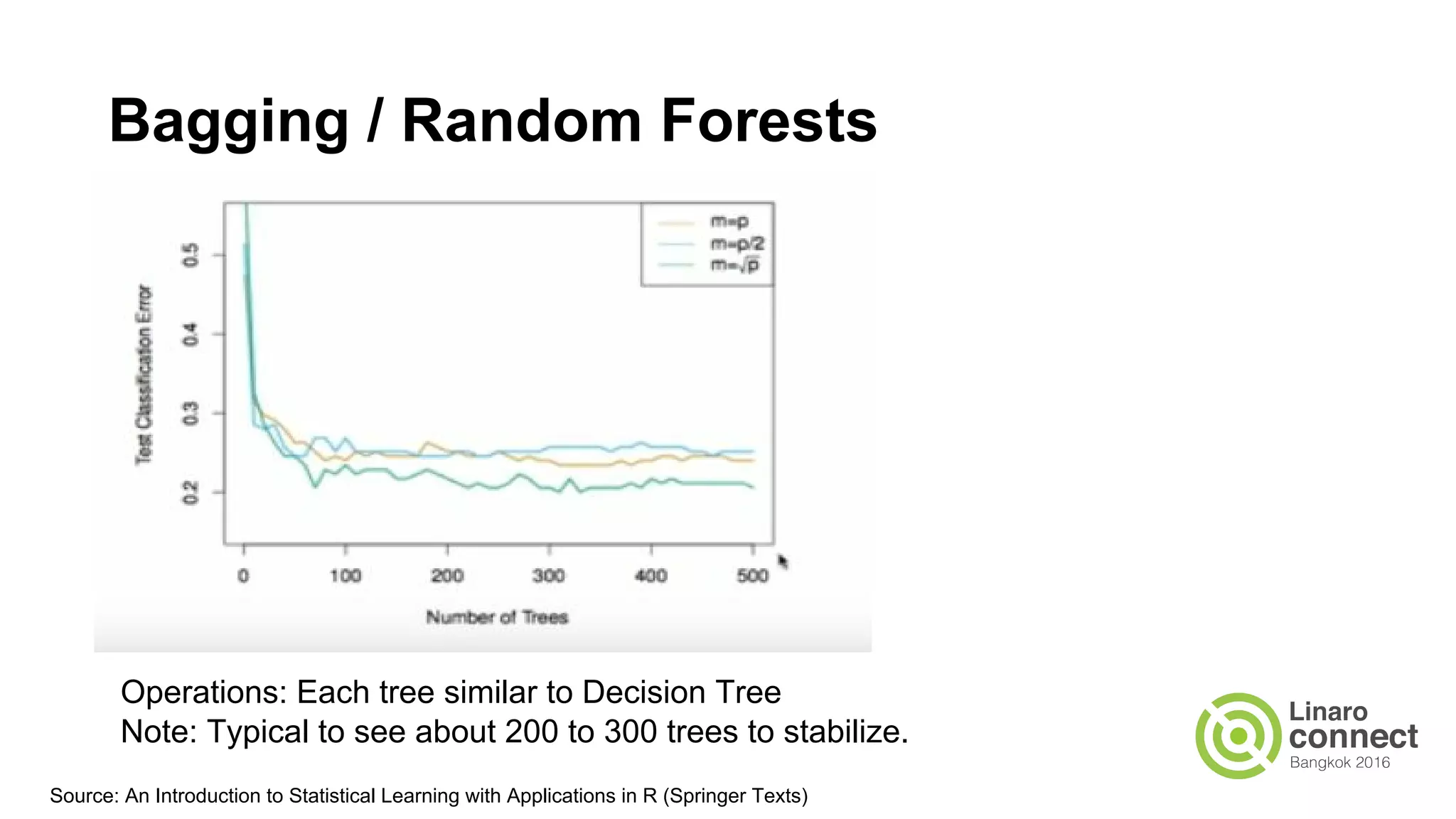
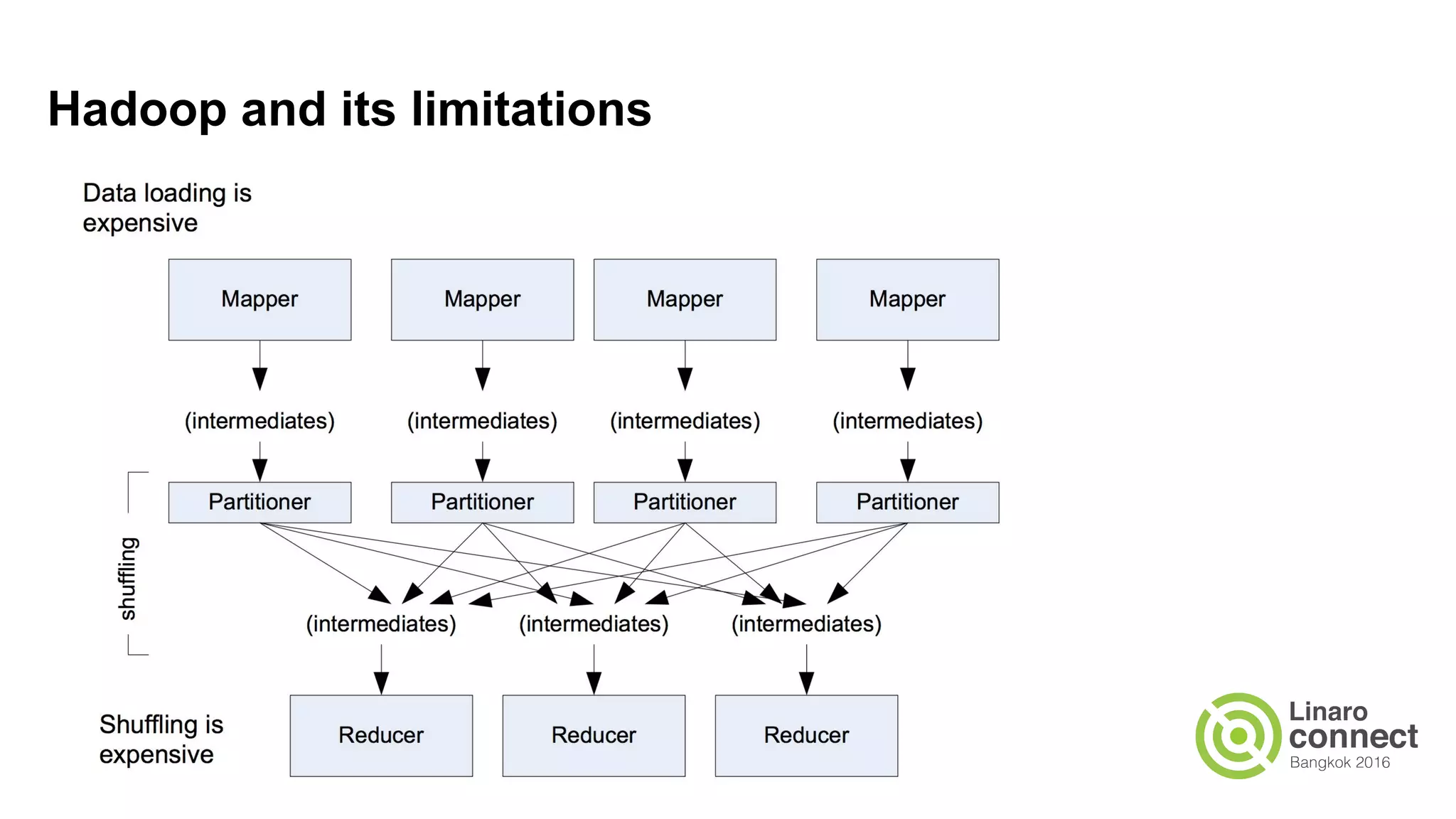
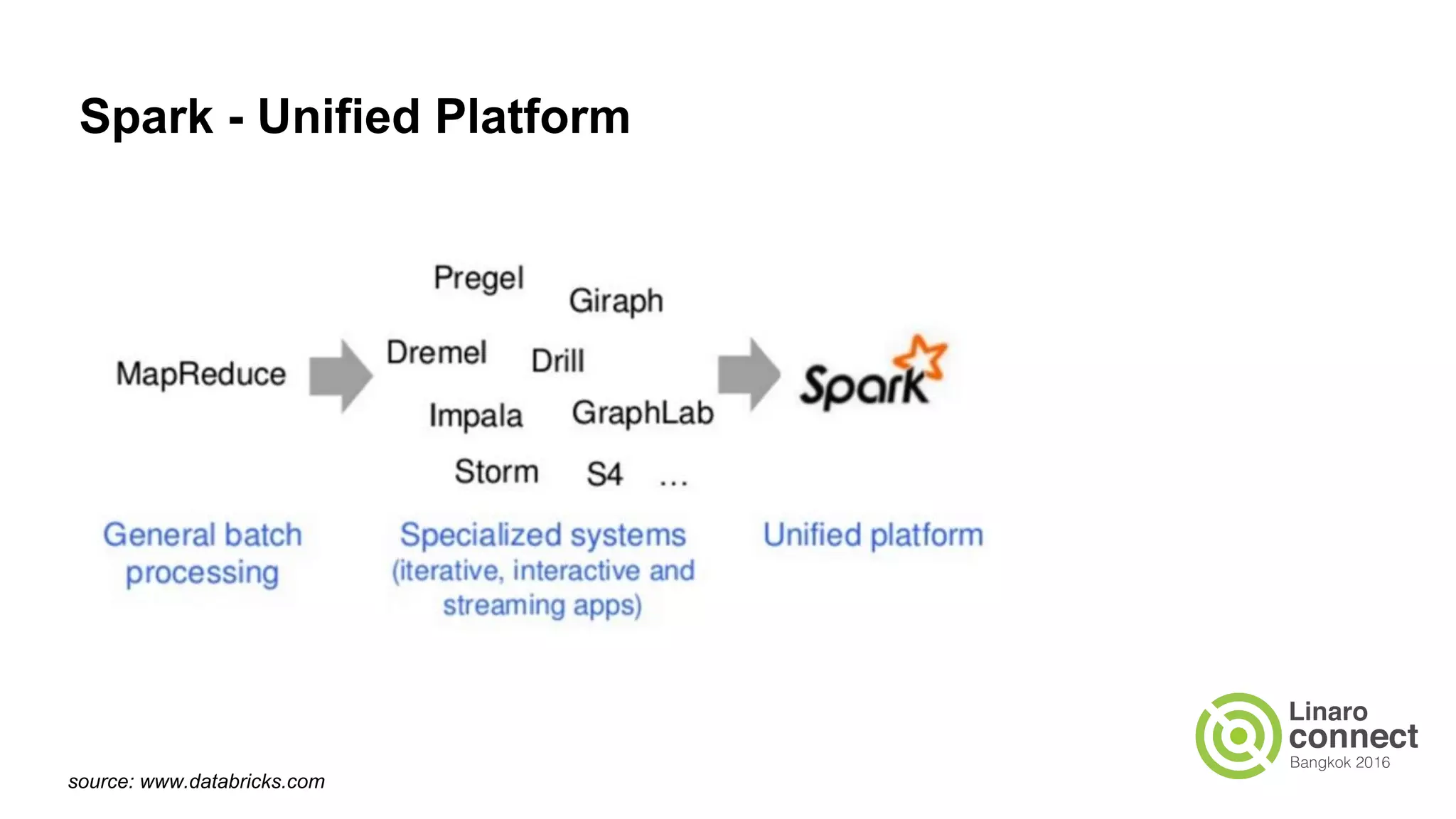
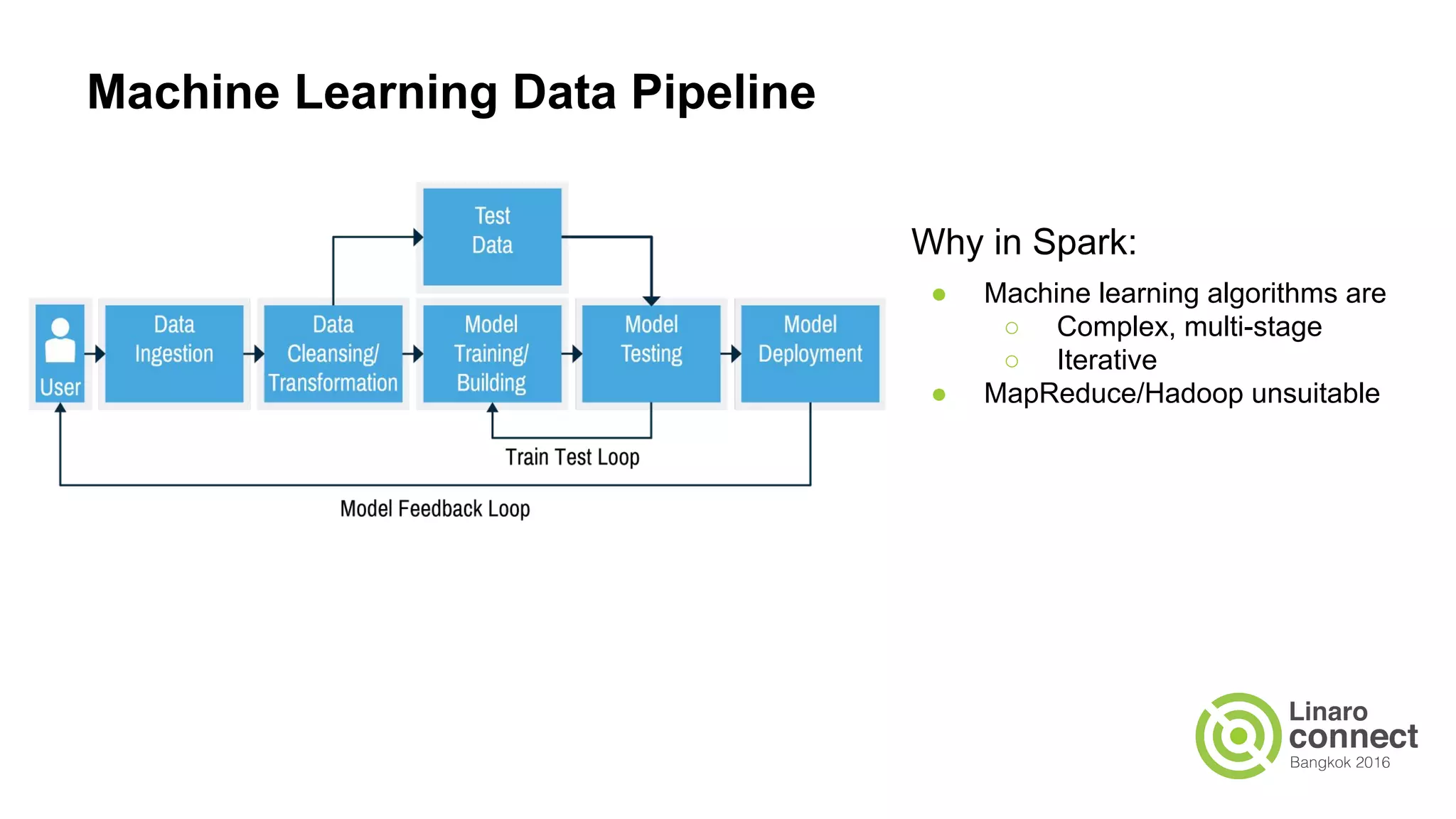
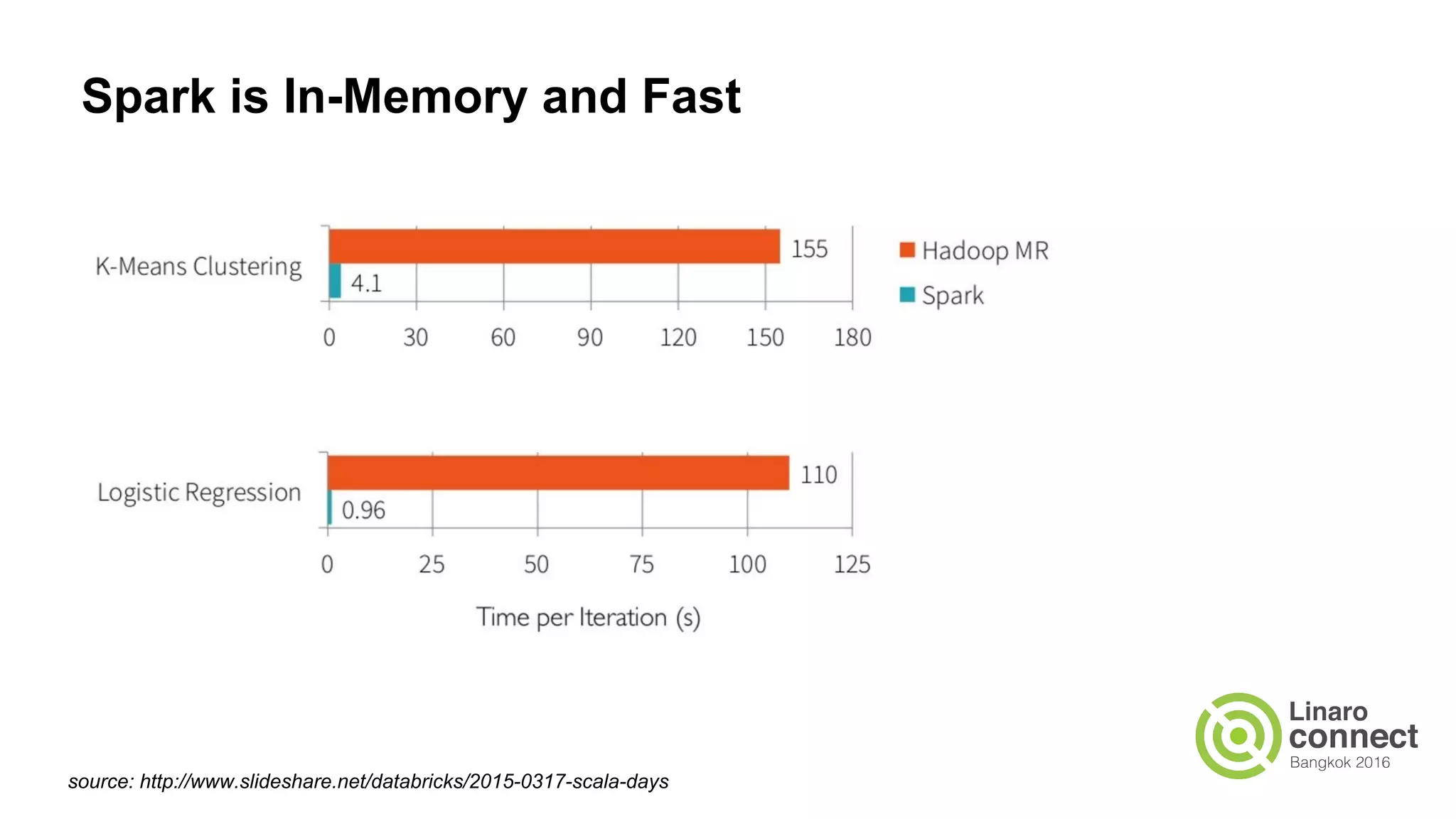
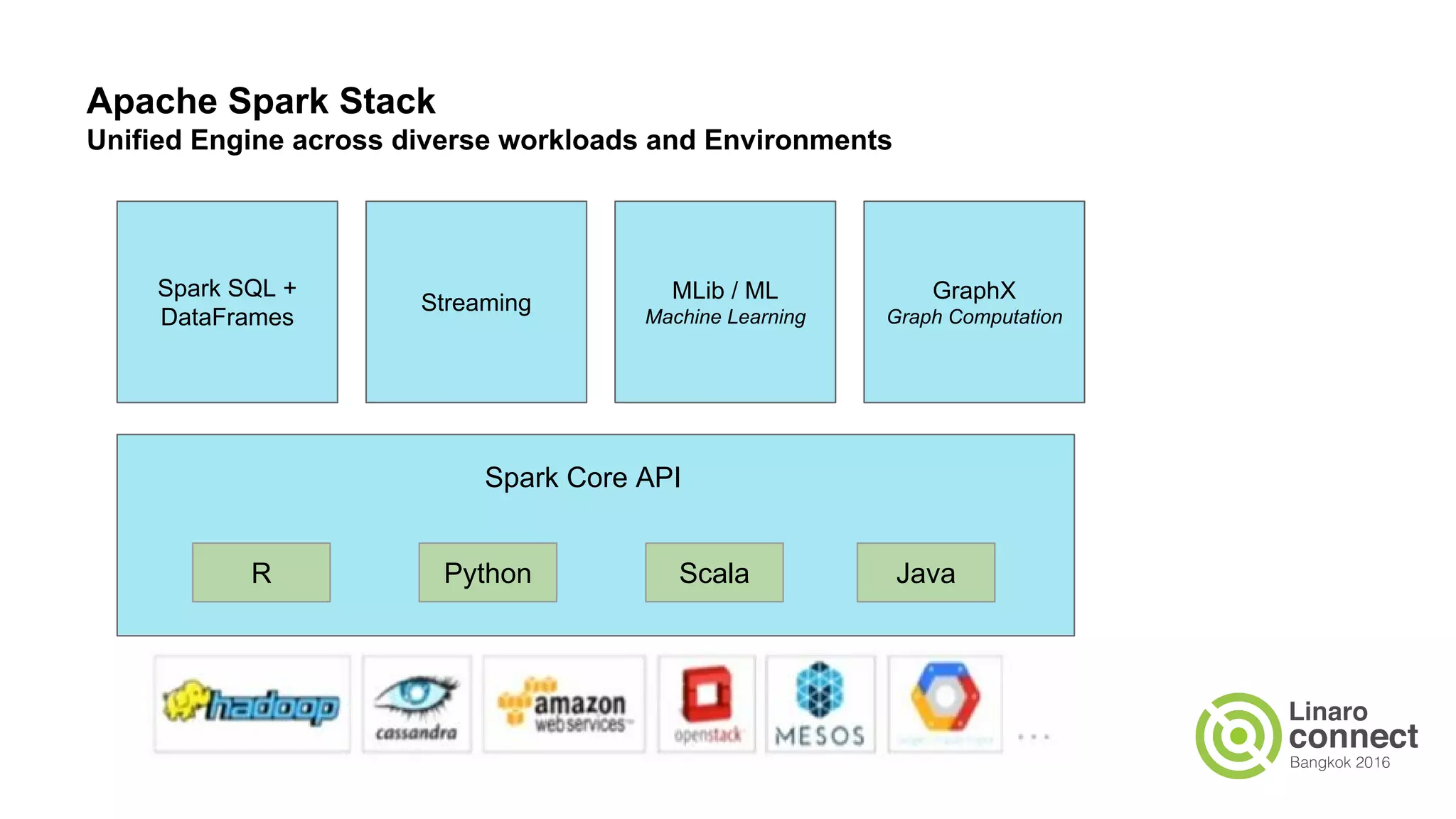
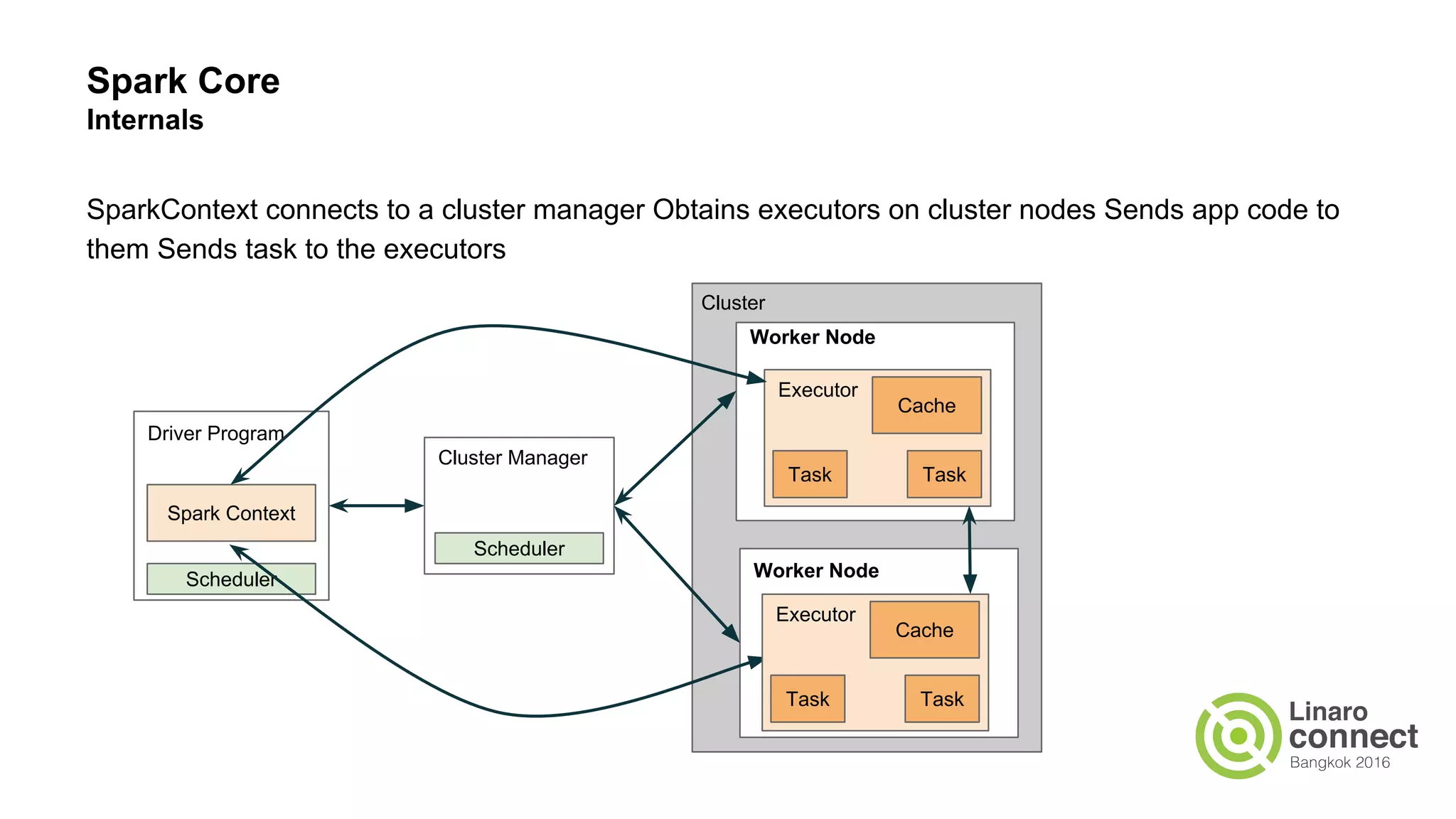
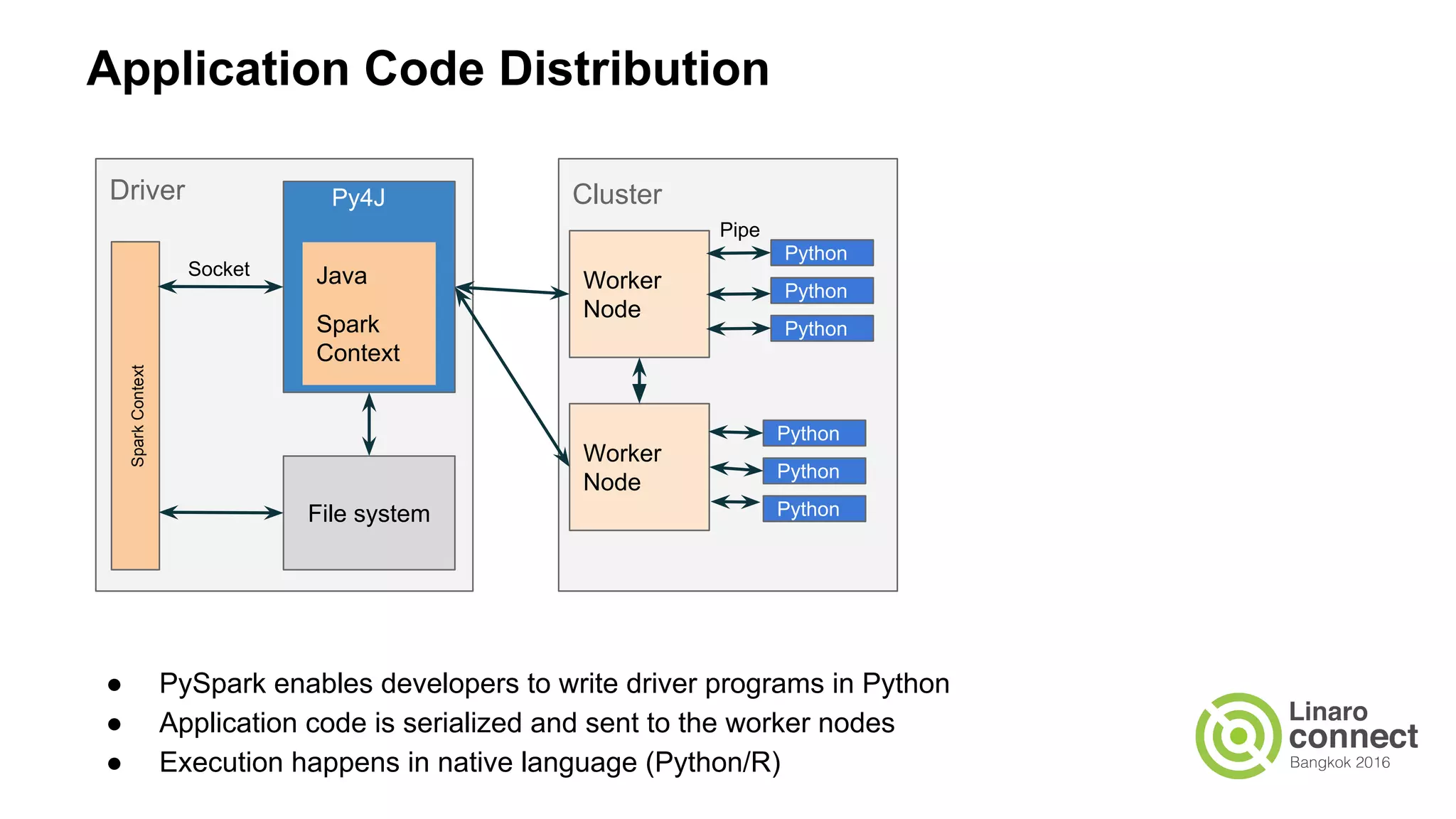
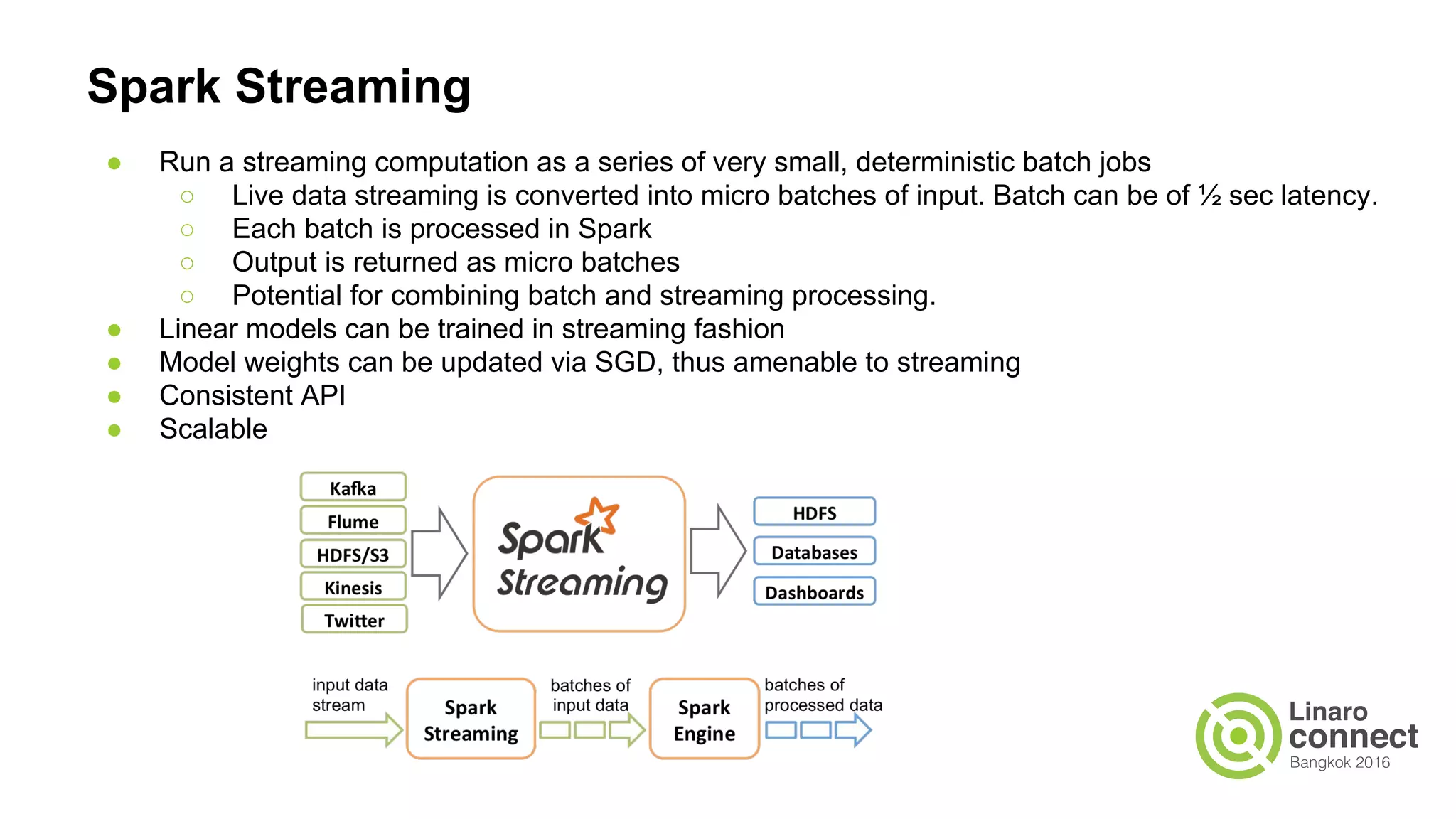
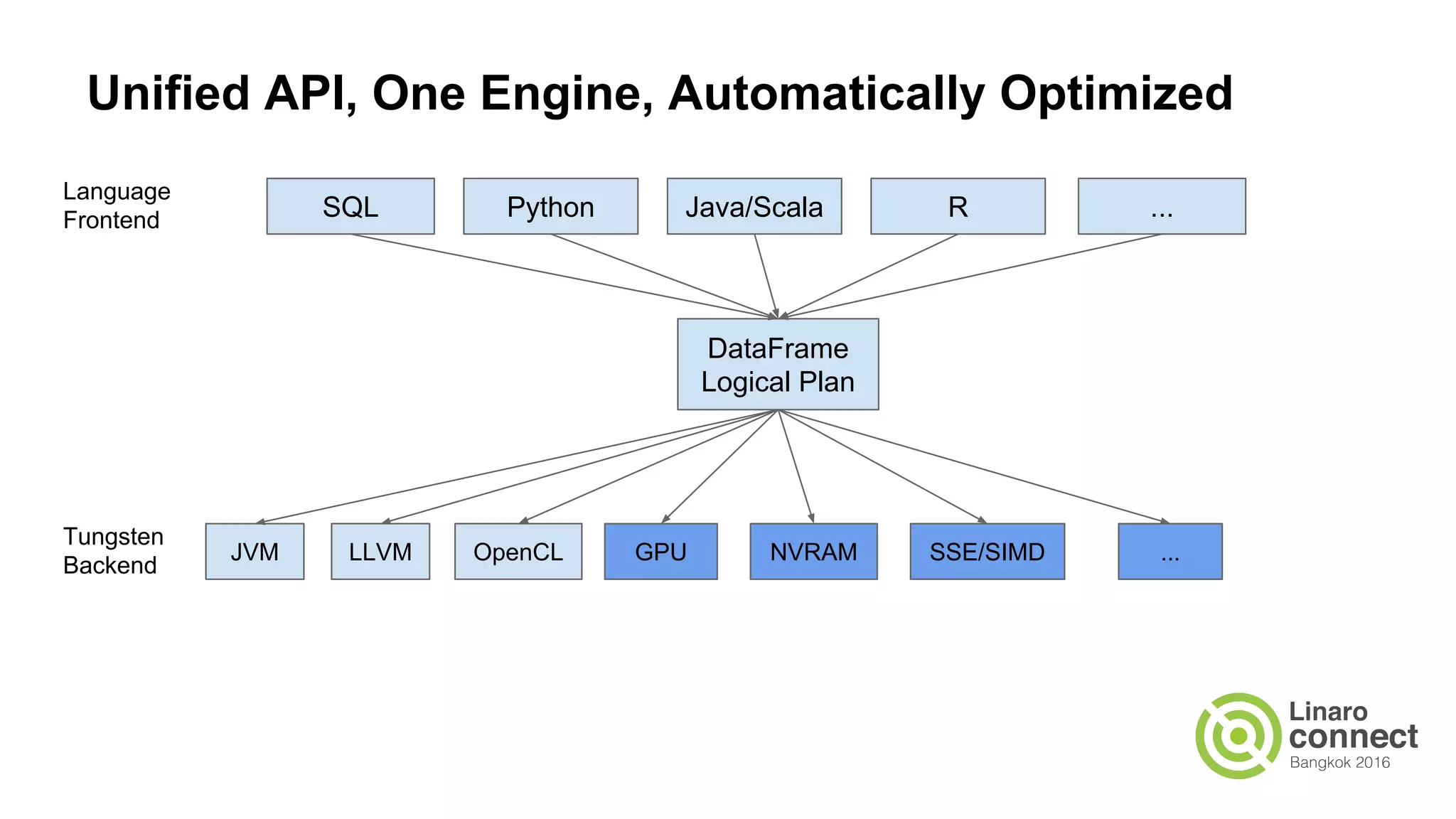
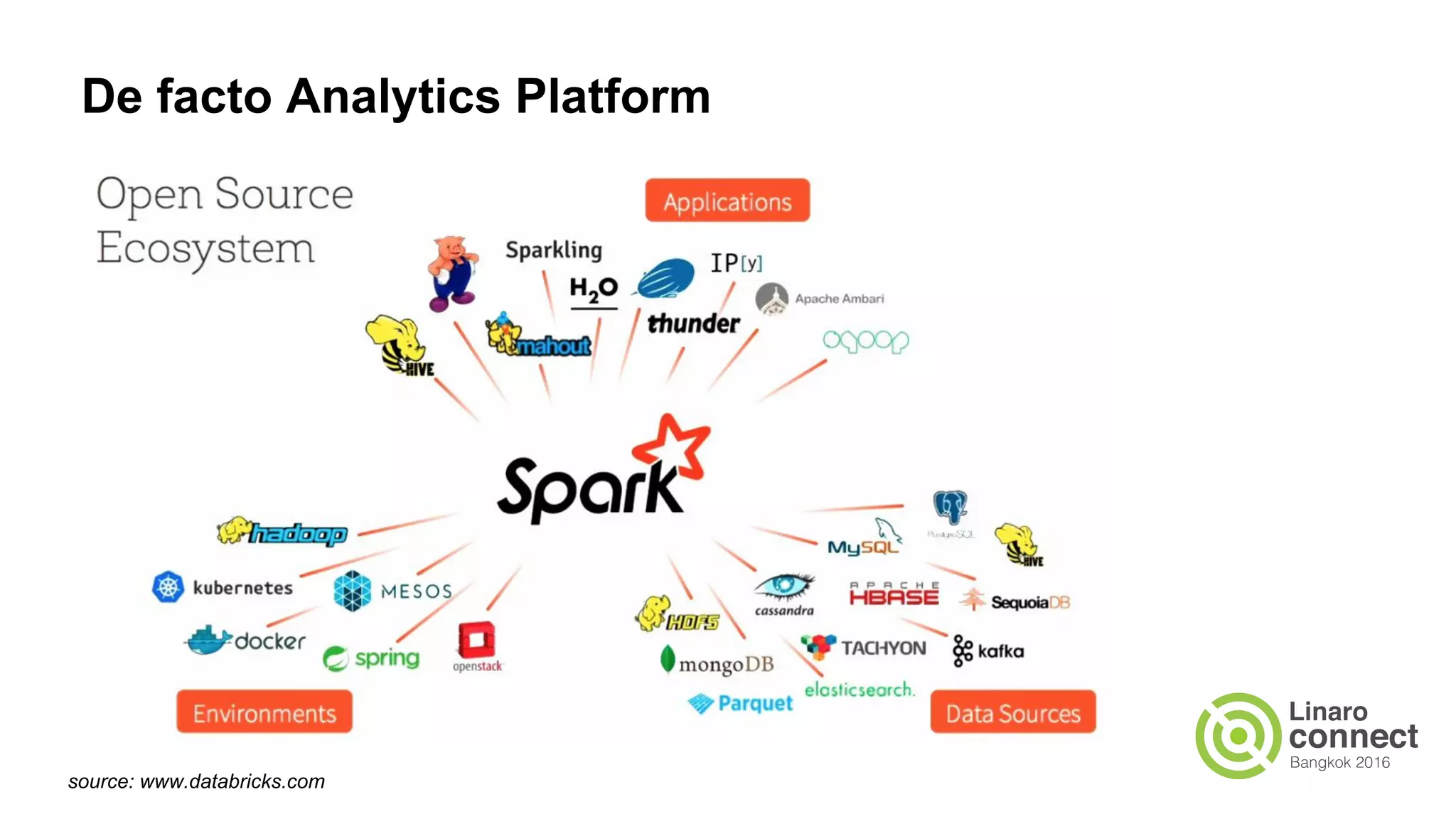
The document discusses the integration of data analytics and machine learning within the ARM ecosystem, emphasizing the need for optimized tools like Python libraries (e.g., pandas, scikit-learn) and tools for handling big data solutions. It outlines the operational capabilities of Apache Spark, comparing it with Hadoop, while presenting the necessity for a unified platform that supports various machine learning algorithms and efficient data pipelines. The document further explores strategies for scaling data science applications across clusters and highlights significant advancements in Spark's architecture and capabilities, particularly focusing on in-memory processing and resource optimization.