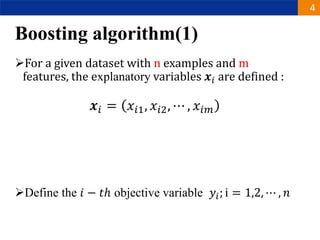
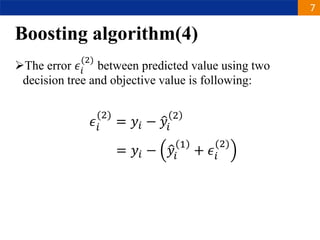
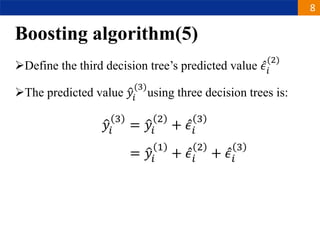
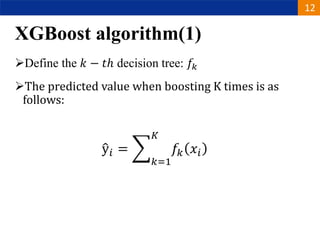
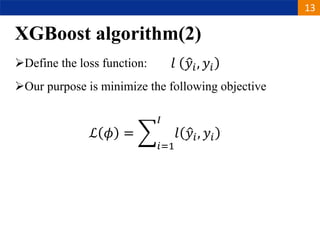
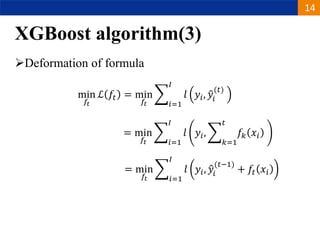
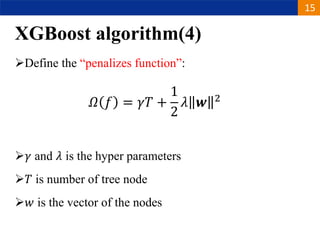
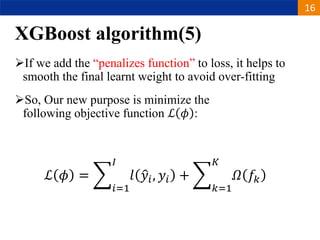
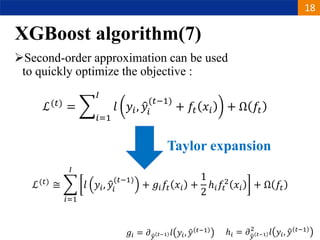
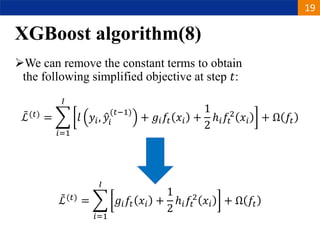
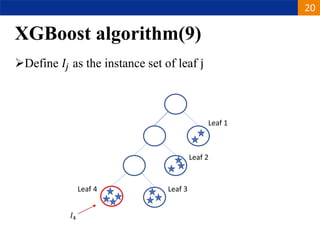
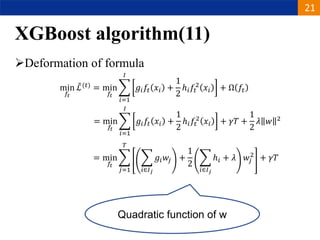
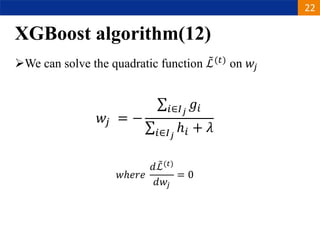
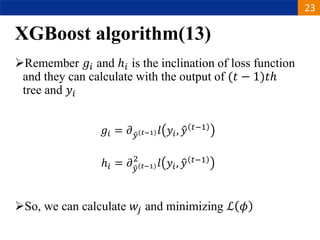
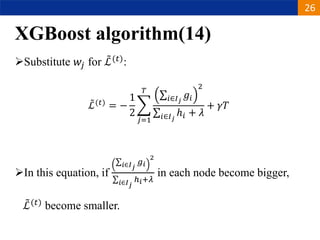
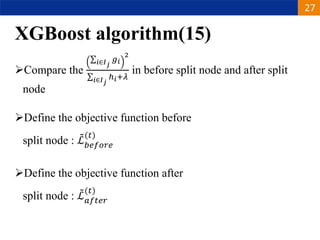
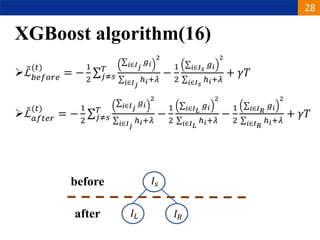
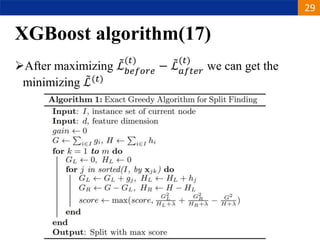
XGBoost is a machine learning algorithm based on boosting decision trees. It builds decision trees sequentially to optimize a specified loss function. At each step, it fits a decision tree to the residuals of the previous tree to minimize the loss. It uses regularization to control overfitting by penalizing complex trees with many leaves and high weights. To determine the best split at each node, it calculates the loss reduction from splitting the node versus keeping it whole. The split that maximizes loss reduction is selected.